Wistanian: Difference between revisions
m (→Relativizer Particles: Omitted incorrect detail) |
m (→Relativizer Particles: fixed typo) |
||
| Line 708: | Line 708: | ||
! style="text-align: center; font-weight:bold;" | Active | ! style="text-align: center; font-weight:bold;" | Active | ||
| style="text-align: center;" | <code>ACT</code> | | style="text-align: center;" | <code>ACT</code> | ||
| style="text-align: center; font-style:italic;" | | | style="text-align: center; font-style:italic;" | gaun | ||
| Indicates that the head does something. | | Indicates that the head does something. | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 26 August 2018
Wistanian (IPA: /wɪsˈteɪni.ən/), natively known as anigalilaun (IPA: /əˈniɡəˌlilɑn/), is the first constructed language (conlang) by world-builder, writer, and professional amateur Paul A. Daly, written in 2017 and 2018. The language was created for a novel series. The first novel is near completion, but will likely remain unpublished until the author finishes his education.
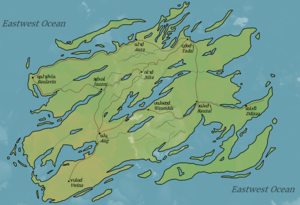
The language is spoken on the fictional planet Vale, on a large yet isolated island called Wistania. The language belongs to the Talivian sub-family, which evolved steadily throughout the Taliv's existence. After having been settled on by the Taliv for several hundred years, the island became the new home for the Bwolotil people, who had fled to the island to hide a large collection of magical and extremely dangerous ajmastones. The Bwolitil were originally apathetic toward the Taliv until they discovered that the Taliv held one such ajmastone as a central symbol of their culture. The Bwolotil, therefore, engaged in war with the Taliv to apprehend their ajmastone. Three separate people groups also inhabited the island during this war, one of which was the Nati people who allied with the Taliv to win the war. This alliance led to the formation of the Taliv-Nati pidgin, which was later named anigalilaun, which means "the language of peace". During the events of the novel series (about 300 years after the end of the war) Wistanian is the majority language of the island. The language also has a number of influences from the Katapu (sister peoples to the Nati and known for their religious traditionalism), the Uzin (a people distantly related to the Bwolotil who settled the island shortly after the beginning of the war), and the Bwolotil.
Wistanian is typologically an analytic language with elements of agglutination. Its grammar is initially simple to grasp, lacking noun gender and case, and possessing few verbal conjugations, although most of its difficulty is syntactic and lexical. Despite having a rather regular morphology due to pidginization, there are several groups of words within the same lexical category which operate differently from each other. Wistanian is primarily written using the Talivian Alphabet, but some alternate scripts do exist, namely the Diwa Alphabet and Nati Abugida.
Introduction
Setting
Wistanian is spoken on the fictional island nation of Wistania. The language stems from a pidgin created between the Nati and Taliv languages during The Wistanian War. After the peace treaty was signed, the Katapu, who were allied with Nati and Taliv but inactive in the war, documented and refined the Nati-Taliv Pidgin for use in the newly established government. Wistanian features mostly Taliv grammar, Nati vocabulary, Katapu influences, many Bwolotil loan words, and scientific terms, mathematics, and the lunar calendar derived from the work of the Uzin. Wistanian's native name, anigalilaun, is a compound of ani (language) and galilaun (peace). It is translated literally as "Peace Language."
The five different people groups of Wistania remained isolated from each other for part of the post-war era. However, trade and intermarriage became more commonplace, requiring a competent lingua franca. This is followed by religious evangelism by the Katapu, engineering from the Uzin, and entertainment from the Nati, all of which Wistanian was the primary language for distribution and promotion. Eventually, the language became taught as a mandatory subject in school. After only a couple centuries, Wistanian advanced from a government-only auxiliary language into the national language of the island, natively and fluently spoken by most of its citizens.
As a result, Wistanian is mostly regular, with a moderately small phonological inventory and vast dialectal variation. It is the most spoken and embraced by the Taliv and Nati people groups, and the least spoken by the Bwolotil people group, who often protest the language's difficulty. The other five languages are still spoken, especially the Bwolotil language which still has a number of monolingual non-Wistanian speakers. Both the Uzin and Katapu have important texts written in their languages, while Taliv and Nati have shifted into archaism, although they are still taught in school.
Goals
Wistanian was created with three goals in mind:
- To be naturalistic, yet unique. It should have its own unique phonology, grammar, and lexicon, not identical to any natural language on earth, but still naturalistic and sensible.
- To represent the Wistanian culture. This language was designed for songs and speeches, bedtime stories and battle cries, gentle wisdom and fierce ambition, hope and struggle. This language is designed for the Wistanians: their personality, their history, and their heart.
- To be novel-friendly. Crazy letters and long words will confuse and alienate most readers, which is why Wistanian was designed to have short, easily readable words that readers can enjoy, one small sentence at a time.
Inspiration
Like most first conlangs, Wistanian started as an English relex (but without tense and articles). However, after nearly four mass revisions over a year, Wistanian has become its own unique language. It's influenced by several languages, especially Spanish and Tamil, but their influence is mostly found in the lexicon while contributing only minimally to the grammar.
Phonology
Inventory
Consonants
The consonants are as follows (allophones are in [brackets]):
| Labial | Alveolar1 | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | [ŋ]2 | |||
| Stop | voiced | b | d | ɡ | ||
| unvoiced | p | t | k | |||
| Fricative | v | z | ʒ | [ɣ]3 | ɦ | |
| Liquid | w ~ βʷ4 | ɾ ~ r5 | j | |||
| Lateral | l | |||||
- Alveolars (except /ɾ ~ r/) are pronounced laminally.
- n > ŋ / _[velar]
- ɦ > ɣ / #_, [stress]_
- /w/ is spoken in emphasized or slow speech, while /βʷ/ is spoken in quick speech. Whenever immediately following a consonant, this is always pronounced as /w/. In the Western Dialect, it is always pronounced as /w/.
- /r/ is spoken in emphasized or slow speech, while /ɾ/ is spoken in quick speech. In some words, the trilled is preferred even in quick speech; for example, ggarauni (large) is almost always pronounced [kəˈrɑni].
Vowels
The vowels are as follows (allophones in [brackets]):
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | i [ɪ]1 | ɯ [u]2 | |
| Mid | e | [ə]1 | |
| Low | a | ɑ [ɒ]2 | |
| Diphthong: ai̯ | |||
- All vowels lengthen when stressed.
- All vowels become breathy after /ɦ/.
- /i/ and /a/ shift to [ɪ] and [ə] whenever unstressed. The only exception is when /i/ follows /j/, /w/, or /l/ or is at the end of a word.
- /ɯ/ and /ɑ/ shift to [u] and [ɒ] after /w~βʷ/.
Phonotactics
Syllable Structure
Wistanian has a (C/Fj/Fw)V(N) syllable structure where C represents any consonant, F represents any fricative, V represents any vowel, and N represents any consonant that is not /j/, /w/, or /ɦ/.
Syllable onsets may be any consonant or any fricative followed by /j/ or /w/:
- m, n, p, b, t, d, k, ɡ, v, vj, vw, z, zj, zw, ʒ, ʒj, ʒw, ɦ, ɦj, ɦw, w, r, j, l.
Syllable nuclei may be any vowel:
- i, e, a, ɑ, ɯ, ai̯
Syllable coda may be any consonant that is not /j/, /w/, or /ɦ/.
- m, n, p, t, k, b, d, ɡ, v, z, ʒ, ɾ, l
Stress
Stress usually falls on the first non-lax vowel (/ai̯/, /i/, /e/, /a/, /ɯ/, or /ɑ/). But there are many exceptions, especially where the vowels /i/ and /a/ come into place since you must know whether or not those sounds are the stressed /i/ or /a/ or the lax [ɪ] or [ə]. A prime example is between the words viman and viman, which are spelled identically. When stress is on the /i/ as in [ˈvimən], the word means “sugar”, but when stress is on the /a/ as in [vɪˈman], the word means “sky.” Stress is realized through vowel lengthening and sometimes a higher intonation.
Prosody
In Wistanian culture, speaking loudly is considered rude. Therefore, Wistanian language is typically spoken softly and clearly. It is arguably a stress-timed language that realizes stressed syllables and stressed words by lengthening vowel duration.
Orthography
Romanization
Wistanian employs its own script, but it is romanized with a system that reflects the script and its spellings. The romanization rules are as follows:
- /m/, /n/, /b/, /d/, /ɡ/, /v/, /z/, and /l/ are represented with the corresponding IPA symbol.
- /p/, /t/, and /k/ are represented by ⟨bb⟩, ⟨dd⟩, and ⟨gg⟩, respectively.
- /ʒ/, /ɦ/, /ɾ~r/, /w~βʷ/ and /j/ are represented by ⟨j⟩, ⟨h⟩, ⟨r⟩, ⟨w⟩, and ⟨y⟩, respectively.
- /ɯ/ and [u] are represented by ⟨u⟩.
- /a/ and [ə] are represented by ⟨a⟩.
- /i/ and [ɪ] are represented by ⟨i⟩.
- /ai̯/ is represented by ⟨ai⟩.
- /e/ is represented by ⟨aa⟩.
- /ɑ/ and [ɒ] is represetned by ⟨au⟩.
Script
Wistanian has an alphabet which represents the different sounds in Wistanian. The alphabet was inspired by Latin, IPA, and Greek, but is often described as Armenian-looking. The font, based on Cambria, was created using Autodesk Sketchbook for the iPad and converted into a font using Calligraphr and TypeLight.
The script, often referred to as araman taliv auzanigza (lit. "dishes of the Taliv") began its evolution during the Diwa oppression when the Taliv people were secretly plotting escape by setting their dishes outside their homes in certain orders to convey messages. After their escape and resettlement on the Wistanian island, the dishes gave form to the written language.
Another interesting feature of the script is "compound glyphs." They are /k/, /t/, /p/, /e/, and /ɑ/, and they are made by doubling or combining two different glyphs together. This is why the romanization of Wistanian uses ⟨gg⟩ for /k/, ⟨au⟩ for /ɑ/, as well as the other digraphs.
Like the lexicon and grammar, Daly redesigned the Wistanian script multiple times - three, to be exact. The original script was an alphabet, but it did not capture the "spirit" of Wistanian, so it was scrapped for an abugida. The abugida, which was beautiful, was also difficult to learn and write, prompting yet another redesign. The original design is now considered as the old Diwa alphabet, while the abugida is an alternative script used by the Nati.
Syntax
Wistanian follows a rigid syntax and tight grammar due to its analytical tendencies. However, these strict standards, along with the simple phonology, help Wistanian people groups to remain understandable and intelligible among each other.
Word Order
Wistanian has predominant Verb-Subject-Object word order, modifiers that follow their head (except for possessive pronouns, numbers, and colors), post-positional suffixes, and particles that come before their head. Modifier phrases will usually come at the beginning or end of the sentence.
azavyi ravu miramwi daz ilam aa din naulam ggarauni ggaun zi maumu. azavi-i ravu miram-wi daz ilam aa din naulam ggarauni ggaun zi maumu. carry-TEL fast store-LAT man young ACC three melon large BEN 3Sa.POSS mother. "The young man quickly carried three large melons to the store for his mother." *carried fast store to man young three melons large for his mother.
Questions
Questions will typically follow the same syntactic pattern as declarative sentences, except with rising intonation. All questions should end with the question particle a (Q). This is especially important in writing since the Talivian Alphabet does not have an equivalent to the question mark. However, some dialects and informal registers do not include it in speech.
Polar
Typically, Yes/No questions will consist of a statement followed by zau/baun (Yes/No).
magin va raul, zau a? magin va raul, zau a? table COP red, yes Q? "Is the table red?” (Lit. "The table is red, yes?")
Non-Polar
Non-polar or content questions are formed using a "dangling particle" and rising intonation, inviting the listener to respond by completing the thought.
lu va a? lu va a? 2S.NOM COP Q? “Who are you?” (Lit. "You are...?")
yigai auzi aa a? yiga -i auzi aa a? speak-TEL 3Sa.NOM ACC Q. "What did he say?" (Lit. "He said...?")
ddaij yaun auv a? dda-i -j yaun auv a? go -TEL-IRR 1P.NOM when Q? "When will we go?" (Lit. "We will go when/during...?)
yi luj ddal a? yi luj ddal a? 1S.POSS boat LOC Q? "Where is my boat?" (Lit. "My boat is located in...?)
magin va raul, diri a? magin va raul, diri a? table COP red, why Q? “Why is the table red?” (Lit. "The table is red because...?")
Imperatives
In imperatives, word order changes to VOS. In polite requests, a speaker uses the irrealis mood conjugation on the main verb and includes a subject noun (usually an honorific). In rude demands, the speaker does not use the irrealis mood conjugation nor includes a subject noun.
vigaj aa garauda baul. viga-a -j aa garauda baul. eat -ATEL -IRR ACC food HON. "Please, eat the food, sir."
viga aa garauda. viga-a -∅ aa garauda ∅ eat -ATEL ACC food "Eat the food (as a rude demand)."
Morphology
Wistanian has a low morpheme-to-root ratio, most words being inflectionless and rather interacting with nearby words and word order to express grammatical (and sometimes lexical) distinctions.
Nouns
Wistanian nouns come in three classes: proper, improper, and pronouns. Proper nouns refer to names of people or places ("Wistania", "Alija"), while improper nouns refer to generic terms (e.g., "country", "man"), and pronouns refer to substitute words for other nouns and noun phrases. Proper nouns are never inflected, however, improper nouns can be inflected for number and position, be compounded, or undergo derivational morphology to become a verb or modifier. Pronouns can take on more inflections than improper nouns.
Number
Wistanian has three grammatical numbers: singular, paucal, and plural. Proper nouns do not inflect for number at all, improper nouns only distinguish between paucal and plural, while pronouns only distinguish singular and plural. This unique distinction arose as a result of Middle Taliv, which had a singular/paucal/plural distinction, then merged the paucal and singular before it transitioned to New Taliv. The pronouns, however, maintained the singular/paucal/plural distinction, then later lost the paucal, resulting in a singular/plural distinction in pronouns.
All count nouns can be declined into the plural number with the suffix -(a)n. For improper nouns, they are not conjugated as plural if a) there is only one or a few of a thing, or b) it is modified with a number.
Location
Nouns distinguish ten locative cases, all of which come from the Nati language and were adopted into the Taliv language during the pidgin era:
| Inessive | INE
|
-ddal | ujadiddal | "in the house" |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elative | ELA
|
-al | ujadyal | "outside the house" |
| Lative1 | LAT
|
-wi | ujadiwi | "to/toward the house" |
| Ablative2 | ABL
|
-igza | ujadyigza | "(away) from the house" |
| Adessive | ADE
|
-nuz | ujadinuz | "near the house" |
| Distantive | DSTV
|
-bin | ujadibin | "far from the house" |
| Superessive | SUPE
|
-jazid | ujadijazid | "above/over the house" |
| Subessive | SUBE
|
-bbaggu | ujadibbaggu | "below/under the house" |
| Antessive | ANTE
|
-ana | ujadyana | "before/left of the house" |
| Postessive | POST
|
-azi | ujadyazi | "after/right of the house" |
- The Lative is also used as the Dative case for indirect objects.
- The Ablative is also used as the Genitive case to indicate possession.
Once a noun takes on a locative case, it is treated as a modifier, coming immediately after its head. However, it can still be given modifiers of its own that may intervene between the locative and its head. In this case, locative nouns take on their own group, alongside subject nouns and object nouns.
budai yau yi ujadiwi ggarauni. buda-ai yau yi ujadi-wi ggarauni. walk-TEL 1S.NOM 1S.POSS house-LAT large. "I walk to my large house."
Pronouns
Pronouns come in five persons: first, second, third animate, third inanimate, and third person spiritual. These four persons are split into four grammatical categories:
- Nominative (
NOM) Used as the subject of the sentence. - Accusative (
ACC) Used as the object of the sentence. - Possessive (
POSS) Used for possession, as an alternative to using the ablative. - Adpositional (
ADP) Used for pronouns conjugated for location.
1st Person
First person singular (1S) pronouns are used to refer to the speaker. First person plural (1P) is used to refer to the speaker and an indeterminate number of others.
| Nominative | Accusative | Possessive | Adpositional | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | yau | dau | yi | ya |
| Plural | yaun | daun | yin | yan |
2nd Person
2nd person singular (2S) pronouns are used to refer to the listener/reader. 2nd person plural (2P) is used to refer to two or more listeners/readers.
| Nominative | Accusative | Possessive | Adpositional | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | lu | liv | luhi | luha |
| Plural | lun | livan | luhin | luhan |
3rd Person Animate
3rd person animate pronouns are used to refer to people and some animals, especially pets and birds. They come as both singular (3Sa) and plural (3Pa).
| Nominative | Accusative | Possessive | Adpositional | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | auzi | auzi | zi | auza |
| Plural | auzin | auzin | zin | auzan |
3rd Person Inanimate
3rd person inanimate pronouns are used to refer to wild animals, objects, events, and noun clauses. They come as both singular (3Si) and plural (3Pi).
| Nominative | Accusative | Possessive | Adpositional | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | vi | vai | vi | va |
| Plural | vin | vain | vin | van |
3rd Person Spiritual
3rd person animate pronouns are used to refer to spirits, sacred objects and places, and the dead. They come as both singular (3Ss) and plural (3Ps).
| Nominative | Accusative | Possessive | Adpositional | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | ja | ja | ji | ja |
| Plural | jan | jan | jin | jan |
Verbs
Verbs only conjugate four lexical aspects. There is no tense, but it is rather expressed through context and other modifier phrases. Only the irrealis mood is conjugated to the verb, while other moods are expressed through modifiers and context. Verbs do not compound with any other part of speech.
Aspect
The Wistanian understanding of aspect is different than what one will find in most natural languages. Rather than conjugating for grammatical aspect, Wistanian conjugates for lexical aspect. In other words, the very definition of a verb may change based on its conjugation.
The four lexical aspects are: stative, durative, telic, and atelic.
- Stative verbs (
STA) describe a situation or action that is unchanging over a long period of time. Stative verbs do not describe temporary actions, but rather the result of a temporary action or a series of temporary actions that identify the subject. - Durative verbs (
DUR) are dynamic and indicate that an action is in progress from one state to another. - Telic verbs (
TEL) are dynamic and punctual, describing an action with an endpoint. More specifically, it refers to any action that has been completed as intended. In most situations, it strongly implies the past or future tense and the perfective grammatical aspect. - Atelic verbs (
ATEL) are dynamic and punctual, describing an action that does not have an intended endpoint. Like the telic, this aspect strongly implies the past or future tense, but is often grammatically imperfective.
ASPECT
/ \
STATIVE DYNAMIC
/ \
DURATIVE PUNCTUAL
/ \
TELIC ATELIC
For example, the verb bima means to "fall" in the telic, "precipitate" in the atelic, "descend" in the durative, and "to be fallen (i.e., lying on the ground after a fall)" in the stative. bima still expresses the same basic meaning — "the subject goes downward" — but its implications change based on its conjugations. This is also true of the verb ja, which means "like" in the stative, "fall in love" in the durative, "achieve or accomplish" in the telic, and "want" in the atelic. Again, the basic meaning remains — "the subject has a desire" — but the differing conjugations further explain what kind of desire is being had: an unchanging desire (stative), a growing desire (durative), a satisfied desire (telic), or an unsatisfied desire (atelic).
These aspects also imply certain grammatical features. Indeed, these aspects originally did refer to grammatical aspects a thousand years within Wistanian's history. The stative was once the gnomic aspect, the durative was once the continuous aspect, and the telic and atelic were once the perfective and imperfective aspects, respectively. This shift was slow, however, but it picked up mightily during the pidginization with the Nati, since lexical aspect could allow them to communicate using fewer verb roots, so words such to "to put on" were replaced with the durative conjugation for the stative "to wear".
Mood
Verbs are conjugated for the irrealis mood, which is used in polite requests, questions, and in conjunction with epistemic or deontic particles. This is done with the suffix ⟨-j⟩. Indicative negative verbs are not conjugated as irrealis.
| NOMINAL | VERBAL | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STATIVE | DYNAMIC | |||||||
| DURATIVE | PUNCTUAL | |||||||
| TELIC | ATELIC | |||||||
| realis | irrealis | realis | irrealis | realis | irrealis | realis | irrealis | |
| viga | vigiya | vigiyaj | viga | vigaj | vigai | vigaij | viga | vigaj |
| zani | zaniya | zaniyaj | zana | zanaj | zanyi | zanyij | zanya | zanyaj |
| hadu | hadiya | hadiyaj | hada | hadaj | hadwi | hadwij | hadwa | hadwaj |
Modifiers
Modifiers immediately follow their head, except for colors, numbers, and possessives. Morphologically, there is no difference between an adjective and an adverb, since they rely on word order. Modifier phrases can be expressed either at the beginning or end of a sentence or after the verb, if it modifies it. Locative nouns, which are syntactically treated as modifiers, usually prefer after the verb. Temporal phrases prefer the beginning of the sentence.
Negation
Nouns, verbs, and modifiers can be negated using the prefix bau(n)-.
Particles
Particles in Wistanian are words which have a grammatical meaning rather than a semantic meaning. They also do not inflect. Particles always come before their head.
Object Particles
All non-subject, non-locative nouns are considered as objects in Wistanian grammar and are therefore featured at the end of the sentence, and are required an object particle. Object order depends on the following hierarchy.
ACC > INST > BEN/CAU
The noun particles are:
| Accusative | ACC
|
aa | Marks the object of the sentence. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Instrumental | INS
|
il | Marks the means by which an action is done. |
| Benefactive | BEN
|
ggaun | Marks the reason for which something is done volitionally. |
| Causative | CAU
|
diri | Marks the reason for which something is done involitionally. |
ila yau aa ujadi il divu ggaun yi jyaman. ila -a yau aa ujadi il divu ggaun yi jyam -an. build-DUR 1S.NOM ACC house INS wood BEN 1S.POSS child-PL. "I am building a house with wood for my children."
Modal Particles
These particles are featured before the verb and indicate verbal modality.
| Conditional | COND
|
a | Denotes "if" the verb will occur. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capable | CAP
|
yaj | Denotes that the subject "can" do something. |
| Hypothetical | HYP
|
zaggu | Denotes something that might happen, but does not. |
| Deontic | DEO
|
daaya | Denotes something that ought to happen. |
| Epistemic | EPIS
|
ibiz | Denotes something that might have happened. |
The conditional mood (COND) is used to form "if" clauses, such as "if she sings" and "if we go", etc. This is homonymous with the question particle, and they are often considered the same word. The verb head of the conditional particle is always conjugated for the irrealis mood.
a murwij ya, junaij dimddal lu dau. a muru-i -j yau, juna-i -j dim -ddal lu dau. COND die -TEL-IRR 1S.NOM, bury-TEL-IRR hill-INE 2S.NOM 1S.ACC "If I die, you will bury me on the hill."
The capable mood (CAP) is used to form "can" verbs, such as "she can sing" and "we can go". It is often used as not only an indicator of ability, but also permissiveness. To denote incapability, the speaker will attach the negation prefix to the verb.
yaj iliya yau aa maliya. yaj ilu-iya yau aa maliya. CAP see-STA 1S.NOM ACC mountain. "I can see the mountains."
The hypothetical mood (HYP) denotes an action that could occur but doesn't, such as "I could go" or even "I could have gone". The verb head of a hypothetical particle is always conjugated for the irrealis mood.
zaggu umaadaij yi luj, a hiyaj yaad vaddal. zaggu umaada-i -j yi luj, a hi -iya-j yaadd va -ddal HYP sink -TEL-IRR 1S.POSS boat, COND exist-STA-IRR hole 3Si.ADP-INE "My boat could sink if there is a hole in it."
The deontic mood (DEO) denotes an action that should happen, whether by obligation or logical progression. It's like a stronger hypothetical particle. The verb head of a deontic particle is always conjugated for the irrealis mood.
auv zij, daaya bimaj daridd. diri va luvi va au. auv zij, daaya bima-a -j daridd. diri va luvi va au. TEMP near.future, DEO fall-ATEL-IRR rain. CAU COP cloud(PL) COP gray. "Soon, the rain should fall because the clouds are gray."
The epistemic mood (EPIS) denotes an action or state that might have happened, however, the speaker is unsure due to lack of evidence. It can also be used as a weaker hypothetical marker. Verb heads of the epistemic particle must be in the irrealis mood. This mood marker also accompanies "I think" sentences which are typically constructed as "I think this. I may have a hammer with me."
garya yau vai. ibiz auwiniyaj yanuz guddi. gari -a yau vai. ibiz auwina -iya-j ya -nuz guddi. think-ATEL 1S.NOM 3Si.ACC. EPIS possess-STA-IRR 1S.ADP-ADE hammer. "I think I have a hammer with me."
Relativizer Particles
There are four relativizer particles that are normally expressed initially in a relative clause and after the noun that relative clause modifies. These can also be used as copula.
| Copulative | COP
|
va | Indicated that the head is equal to something. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Possessive | POSS
|
na | Indicates that the head possesses something. |
| Active | ACT
|
gaun | Indicates that the head does something. |
| Locative | LOC
|
ddal | Indicates where the head is located. |
As relativizers, they can be translated as such: COP = which is, POSS = which has, ACT = which does, and LOC = which is located.
As copula, COP equates a subject noun with another noun, possessive pronoun, color, or number; POSS equates a subject noun with an adjective that's not a possessive pronoun, color, or number; ACT doubles as a gnomic aspect particle; and LOC indicates the location of the subject. Since these are particles, the word order for these particular types of sentences appears to change to SVO and the accusative particle is omitted (this does not apply to objects of a gnomic verb).
wizddaaniya va ggarimalun. wizddaaniya va ggarimalun. Wistania COP large.island "Wistania is a large island." "Wistania, which is a large island,..."
wizddaaniya na lazai. wisddaaniya na lazai. Wistania POSS great. "Wistania is great." (Lit. "Wistania has great.") "Wistania, which is great,..."
wizddaniya gaun liya. wizddaniya gaun liya. Wistania ACT fly. "Wistania fares well" (Lit. "Wistania flies.") "Wistania, which fares well,..."
wizddaniya ddal vimanbbaggu wizddaniya ddal viman-bbaggu. Wistania LOC sky -SUBE. "Wistania is under the sky." "Wistania, which is located under the sky,..."
Technically, these are incomplete sentences, indicating only a noun and a relative clause without a compliment. However, they are considered perfectly viable sentences.
Coordinating Particles
Wistanian coordinating particles come in four types: normal coordination, weak coordination, contrastive coordination, and alternative coordination.
Normal coordination (CO) is similar to the English "and". However, each item in the list is proceeded by the word ya.
dajyi ya dari ya lari. daji-i ya dari ya lari. hide-TEL CO boy CO girl. "The boy and the girl hid."
Weak coordination (WCO) refers to a co-actor in the sentence while keeping the focus on a specific item of the list, which is usually featured at the beginning of the list and without a particle. It is denoted with the word nuz.
dajyi dari nuz lari. daji-i dari nuz lari. hide-TEL boy WCO girl. "The boy hid with the girl."
Contrastive coordination (CCO) is equivalent to the English "but" and is expressed through the particle bbal.
auvin vaun liyiya, bbal gaunun vaun bauliyiya. auvi-n vaun liya-iya, bbal gaunu-n vaun bau-liya-iya. bird-PL GNO fly-STA, CCO fish-PL GNO NEG-fly -STA "Birds fly, but fish do not fly."
Alternative coordination (ALTCO) denotes a choice or alternative among a group of items in a list, equivalent to the English "or", and denoted with the word i. Like the normal coordinating particle ya, this particle is featured before each item in a list.
ja lu aa i garauvi i diyan a. ja -a lu aa i garauvi i diyan a. want-ATEL 2S.NOM ACC ALTCO water ALTCO juice Q. "Do you want water or juice?"
Honorifics
Wistanian has a very exciting honorific system with several unique features. Honorifics are used for almost everyone: familial relationships and close friendships, authorities and superiors, and people who are younger than you. They are often said after a proper noun, take inflectional morphology, and can replace the 2nd person pronouns.
The formal honorifics one uses depends on the age and respective rank of the second person:
| Inferior | Peer | Superior | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | iz | - | baada |
| Child | yi / yin | yi / yin | auzi / auzin |
Familial honorifics are used among close family members. These honorifics will change depending on culture and sometimes family. Children, in particular, have unique honorifics given by their parents, like a nickname. For example, a boy named Maudu could be given the honorific ravu (fast), and only his parents, aunts/uncles by blood, and grandparents can call him "Maudu Ravu". While his sister Zamara could be Zamara Viyaz (kind) to her parents.
The most common Familial Honorifics are included under Kinship Terms below.
Semantics
The Wistanian Lexicon currently stands at 400 words as of August 2018, with a goal of accomplishing 2,500 words by the end of the year. A link to the lexicon can be found at the bottom of this article, under "Other Resources"
Kinship
Wistanian kinship is a modified version of the Hawaiian system common in most Malayo-Polynesian languages. In this system, siblings and first cousins share terms with only a gender and age distinction. Mothers are usually given a term of endearment by their children (usually mu), but a child's aunts will also be called "mother" and the father and uncles will share terms as well. Most of Wistanian culture is ambilineal and matrifocal, so that children live and associate closest to their mother and her side of the family. For this reason, a child's mother's brother will often be just as much of a father figure as the child's biological father, who may or may not be involved in the family.
| English | Kinship Term | Honorific |
|---|---|---|
| male older brother or cousin | daran | bai |
| male younger brother or cousin | yida | |
| female older sister or cousin | madya | |
| female younger sister or cousin | yima | |
| uncle/aunt by marriage | imaun | baada |
| mother/aunt by blood | maumu | iv |
| father/uncle by blood | vauhi | anda |
| grandmother | aumi | ivi |
| grandfather | audi | andi |
| husband | yi daz | - |
| wife | yi laz | |
| child, offspring, son/daughter | jyam | Variable |
| grandchild | aujyam |
The Bwolotil people are more nuclear, consisting of only a mother, father, and one or two children. They have their own kinship terms from their language. Some Katapu people share the typical family structure and kinship terms. However, most family structures are extended so that families live amongst the mother's extended family, and fathers are usually present in the home. Most of their kinship terms also come from the Katapu language, but some Wistanian terms are borrowed as well.
Colors
under construction
Numbers
under construction
Example Texts
auv lin zun, buda yau, ya injai yau aa vaggan ggarauni id. auv yum, bbirai ya aa vaggan, ya gguji min min ddal vabbaggu. ya yigai yau vai: addai vaggan idi aa jyam.
"One day, I was walking, and I found this big log. Then, I rolled the log over, and underneath was this tiny little stick. And I was like, “That log had a child!”
— from "Seagulls (Stop It Now)" by Bad Lip Reading
auv lin zun, buda yau, ya injai yau aa vaggan ggarauni id. auv lin zun, buda-a yau, ya inja-i yau aa vaggan ggarauni id during one day, walk-ATEL 1S.NOM, and find-TEL 1S.NOM ACC log big PROX. "One day, I was walking, and I found this big log."
auv yum, bbirai ya aa vaggan, auv yum, bbira-i yau aa vaggan, during next, roll -TEL 1S.NOM ACC log, "Then, I rolled the log over,"
ya gguji min min ddal vabbaggu. ya gguji min min ddal va -bbaggu and stick small~small LOC 3Sa.ADP-SUBE. "and underneath was this tiny little stick."
ya yigai yau vai: ya yiga -i yau vai: and speak-TEL 1S.NOM 3Si.ACC: "And I was like"
addai vaggan idi aa jyam. adda -i vaggan idi aa jyam. birth-TEL log MED ACC offspring. "That log had a child!"