Zemljask: Difference between revisions
Aleisi Galan (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Aleisi Galan (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|fam4 = [[w:Old-Zemljask|Old-Zemljask]] | |fam4 = [[w:Old-Zemljask|Old-Zemljask]] | ||
|ancestor = Old Zemljask | |ancestor = Old Zemljask | ||
|dia1 = Maribor (''Marborgask'') | |dia1 = Maribor (''Marborgask'') | ||
|dia2 = Sereian/Northern (''Serejask'') | |dia2 = Sereian/Northern (''Serejask'') | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
|mapsize = 280px | |mapsize = 280px | ||
|mapcaption = Borders of the Zemljask language (''Mladźe Zemljska Reći) | |mapcaption = Borders of the Zemljask language (''Mladźe Zemljska Reći) | ||
|creator = Aleisi Galan | |||
|notice = IPA | |notice = IPA | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
| style="border-right: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless alveolar sibilant|s]] || style="border-left: 0;" | [[w:Voiced alveolar fricative|z]] | | style="border-right: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless alveolar sibilant|s]] || style="border-left: 0;" | [[w:Voiced alveolar fricative|z]] | ||
| style="border-right: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless palato-alveolar fricative|ʃ]] || style="border-left: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless palato-alveolar fricative|ʒ]] | | style="border-right: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless palato-alveolar fricative|ʃ]] || style="border-left: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless palato-alveolar fricative|ʒ]] | ||
| style="border-right: 0;" | || style="border-left: 0;" | | | style="border-right: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless palato-alveolar fricative|ɕ]] || style="border-left: 0;" | [[w:Voiceless palato-alveolar fricative|ʑ]] | ||
| style="border-right: 0;" | [[w:Velar_fricative|x]] || style="border-left: 0;" | | | style="border-right: 0;" | [[w:Velar_fricative|x]] || style="border-left: 0;" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
# [ŋ] is an allophone of [n] when it occurs next to a Velar consonant (one of [k], [g], [x]) | # [ŋ] is an allophone of [n] when it occurs next to a Velar consonant (one of [k], [g], [x]). | ||
# The consonants /p/, /t/, /k/ are usually aspirated [p<sup>h</sup>], [t<sup>h</sup>], [k<sup>h</sup>]. | # The consonants /p/, /t/, /k/ are usually aspirated [p<sup>h</sup>], [t<sup>h</sup>], [k<sup>h</sup>]. | ||
# The pronunciation of the palatal consonants /t͡ɕ/ and /d͡ʑ/ varies by region. The Northern pronunciation is [t͡ɕ], [d͡ʑ], matching the Standard language as set out by the '' | # The pronunciation of the palatal consonants /t͡ɕ/ and /d͡ʑ/ varies by region. The Northern pronunciation is [t͡ɕ], [d͡ʑ], matching the Standard language as set out by the ''Rozjana Zemljska Reći'' while in the Central to Intermediate Southern regions, the typical pronunciation is [t͡ʃ], [d͡ʒ], and in the ''Dalmacask'' and ''Tragešćask'' dialects it typically is [t͡s], [d͡s]. The Southern feature is shared with some dialects of Polish. | ||
# [f] is a very rare sound in Zemljask and appears primarily in words loaned from other languages. Some speakers in informal settings may merge this sound with [v]. | # [f] is a very rare sound in Zemljask and appears primarily in words loaned from other languages. Some speakers in informal settings may merge this sound with [v]. | ||
# The sounds [v] and [l], in coda position, lenite to the approximant [ʋ]. | # The sounds [v] and [l], in coda position, lenite to the approximant [ʋ]. | ||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
! Back | ! Back | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! [[w:Mid vowel|Closed]] | ||
| [[w:IPA link|i]] | |||
| [[w:IPA link|ɪ]] | |||
| [[w:IPA link|u]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
! [[w:Mid vowel|Mid]] | ! [[w:Mid vowel|Mid]] | ||
| [[w:IPA link|e]] | | [[w:IPA link|e]] | ||
| [[w:Mid_central_vowel| | | [[w:Mid_central_vowel|ər]]<sup>1</sup> | ||
| [[w:IPA link|o]] | | [[w:IPA link|o]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 137: | Line 140: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
# The syllabic consonant [r̩] is typically (and officially permitted to be) pronounced as [ər]. | # The syllabic consonant [r̩] is typically (and officially permitted to be) pronounced as [ər]. | ||
# the vowels [ɛ] and [ɔ] are both phonetic and phonemic, being vowels in their own right (written as <è> and < | # the vowels [ɛ] and [ɔ] are both phonetic and phonemic, being vowels in their own right (written variously as <è>, <ai>, <ò>, and <au>) as well as allophones of [e] and [o] when preceeded by a Soft-Consonant. | ||
===Prosody=== | ===Prosody=== | ||
Stress in Zemljask, in theory, is unpredictable, however it most often is placed moderately heavily on the initial syllable. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 50em; text-align: left; border-collapse:collapse;" | |||
! colspan="30" | Zemljask Prosody | |||
|- | |||
| Alovac || [ˈalovat͡s] || Here, the stress is placed on the initial syllable. | |||
|- | |||
| Alovca || [alˈoʋt͡sa] || However, stress often moves in certain inflections. In this case, the loss of a vowel pushes it forwards, like in most roots with mobile vowels. | |||
|- | |||
| Fanèla || [fa.ˈnɛ.la] || In most Illyrian loans, and a few native Zemljask words, the stress falls on the penultimate syllable. | |||
|- | |||
| Gavati || [ga.ˈva.ti] || For verbs, the stress on the infinitive is penultimate. | |||
|- | |||
| Gavaš || [ˈga.vaʃ] || While the primary stress when conjugated falls upon the root-final syllable. | |||
|- | |||
| Kytiti || [ˈkɪ.ti.ti] || However, -iti verbs have permanent root-final stress. | |||
|- | |||
| Gavljenje || [gaʋ.ˈʎɛ.ɲɛ] || When an ending is composed of multiple syllables, the verb once again gains penultimate stress. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Morphophonology== | |||
There exists in Zemljask a rich morphophonology of numerous variations in stems that take place under a variety of conditions: | |||
===Consonant Alternation=== | |||
# Consonants are split into hard and soft, based on their phonetic value and may alternate between these forms under certain conditions (typically Hard to Soft): | # Consonants are split into hard and soft, based on their phonetic value and may alternate between these forms under certain conditions (typically Hard to Soft): | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 50em; text-align: center; border-collapse:collapse;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 50em; text-align: center; border-collapse:collapse;" | ||
! colspan=" | ! colspan="25" | Hard and Soft Consonants | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Hard || m || n || p || b || t || d || k || g || f || v || s || z || - || - || - || - || - || - || - || h || l || - | | Hard || m || n || p || b || t || d || k || g || - || - ||f || v || s || z || - || - || - || - || - || - || - || h || l || - | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Soft || mlj || nj || plj || blj || ć || dź || č || dž || flj || vlj || š || ž || š || ž || č || dž || ć || dź || š || rj/š || lj || j | | Soft || mlj || nj || plj || blj || ć || dź || č || dž || c || dz || flj || vlj || š || ž || š || ž || č || dž || ć || dź || š || rj/š || lj || j | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Mobile Vowels=== | |||
The other primary mode of alternation is the ''mobile "A"'', which may appear or disappear in certain cases or inflections. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
Latest revision as of 08:02, 13 May 2022
| Zemljask | |
|---|---|
| Reć Zemljska | |
| Pronunciation | [ret͡ɕ zémʎska] |
| Created by | Aleisi Galan |
| Setting | Slovenia, Northern Croatia |
| Native to | The State of Zemlia, Illyria-Zemlia (RI&Z) |
| Native speakers | 4 575 376[1] (2012 census) |
Early form | Old Zemljask
|
Standard form | Standard Zemljask
|
Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Official language in | Illyria-Zemlia (RI&Z) |
| Regulated by | The Council of the Zemljask Language (Rozjana Zemljska Reći) |
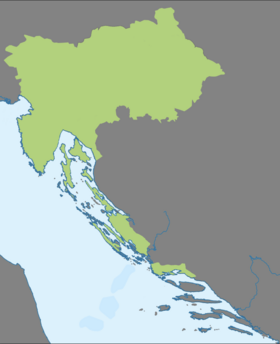 Borders of the Zemljask language (Mladźe Zemljska Reći) | |
Zemljask (autoglossonym: reć zemljska; Zemljask: [ret͡ɕ zémʎska]) is an isolate Slavic language with strong influence from Vulgar Latin, Italian, and most of all Illyrian, the Latin-derived language to the south which historically controlled Zemlia until the Illyrian Civil War of 1978-1982. After this war, Zemlia became an independent country, with Zemljask as its sole official language, while Illyrian was relegated to regional minority status soon after the conclusion of the conflict.
While its vocabulary derives for the most part from Proto-Slavic, Latin influence is most notable in its grammar, as well as the colloquial speech of the southern regions.
Etymology
In English, the name of the language, Zemlian (officially Zemljask) derives directly from the name of the country - Zemlia. This name, in turn, derives from Zemljask "Zemlja", meaning land. This is a shortening of the traditional, now patriotic, Naša Zemlja (lit. our land) which, over time, became simply Zemlia. The name for the language is a derivative of this, being composed of the roots zemľa+-ьskъ[2], forming Zemľьskъ, which evolved into the modern Zemljask.
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ȵ | (ŋ)1 | ||||||
| Stop | p2 | b | t2 | d | k2 | ɡ | ||||
| Affricate | t͡s | d͡z | t͡ʃ | d͡ʒ | t͡ɕ3 | d͡ʑ3 | ||||
| Fricative | f4 | v5 | s | z | ʃ | ʒ | ɕ | ʑ | x | |
| Approximant | j | |||||||||
| Lateral | l5 | ȴ | ||||||||
| Trill | r | |||||||||
Notes:
- [ŋ] is an allophone of [n] when it occurs next to a Velar consonant (one of [k], [g], [x]).
- The consonants /p/, /t/, /k/ are usually aspirated [ph], [th], [kh].
- The pronunciation of the palatal consonants /t͡ɕ/ and /d͡ʑ/ varies by region. The Northern pronunciation is [t͡ɕ], [d͡ʑ], matching the Standard language as set out by the Rozjana Zemljska Reći while in the Central to Intermediate Southern regions, the typical pronunciation is [t͡ʃ], [d͡ʒ], and in the Dalmacask and Tragešćask dialects it typically is [t͡s], [d͡s]. The Southern feature is shared with some dialects of Polish.
- [f] is a very rare sound in Zemljask and appears primarily in words loaned from other languages. Some speakers in informal settings may merge this sound with [v].
- The sounds [v] and [l], in coda position, lenite to the approximant [ʋ].
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed | i | ɪ | u |
| Mid | e | ər1 | o |
| Mid-Open | ɛ2 | - | ɔ2 |
| Open | a |
Notes:
- The syllabic consonant [r̩] is typically (and officially permitted to be) pronounced as [ər].
- the vowels [ɛ] and [ɔ] are both phonetic and phonemic, being vowels in their own right (written variously as <è>, <ai>, <ò>, and <au>) as well as allophones of [e] and [o] when preceeded by a Soft-Consonant.
Prosody
Stress in Zemljask, in theory, is unpredictable, however it most often is placed moderately heavily on the initial syllable.
| Zemljask Prosody | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alovac | [ˈalovat͡s] | Here, the stress is placed on the initial syllable. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alovca | [alˈoʋt͡sa] | However, stress often moves in certain inflections. In this case, the loss of a vowel pushes it forwards, like in most roots with mobile vowels. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fanèla | [fa.ˈnɛ.la] | In most Illyrian loans, and a few native Zemljask words, the stress falls on the penultimate syllable. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gavati | [ga.ˈva.ti] | For verbs, the stress on the infinitive is penultimate. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gavaš | [ˈga.vaʃ] | While the primary stress when conjugated falls upon the root-final syllable. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kytiti | [ˈkɪ.ti.ti] | However, -iti verbs have permanent root-final stress. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gavljenje | [gaʋ.ˈʎɛ.ɲɛ] | When an ending is composed of multiple syllables, the verb once again gains penultimate stress. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Morphophonology
There exists in Zemljask a rich morphophonology of numerous variations in stems that take place under a variety of conditions:
Consonant Alternation
- Consonants are split into hard and soft, based on their phonetic value and may alternate between these forms under certain conditions (typically Hard to Soft):
| Hard and Soft Consonants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard | m | n | p | b | t | d | k | g | - | - | f | v | s | z | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | h | l | - |
| Soft | mlj | nj | plj | blj | ć | dź | č | dž | c | dz | flj | vlj | š | ž | š | ž | č | dž | ć | dź | š | rj/š | lj | j |
Mobile Vowels
The other primary mode of alternation is the mobile "A", which may appear or disappear in certain cases or inflections.