Valtamic: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
|ancestor3 = Proto-Valtamic | |ancestor3 = Proto-Valtamic | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Valtamic''' (endonym: '''''äljämhor | '''Valtamic''' (endonym: '''''äljämhor lïcür''''' [ˈæˑʎɛm̥ˌχɔ̞ɾ̥ ˈʎiˑ(t)s̪ʏɾ̥]), also known as '''Livonian''', is an [[w:Italic languages|Italic language]] belonging to the [[w:Indo-European languages|Indo-European language family]]. It is spoken mostly in the Republic of Valtamia, wherein it is recognized as the official language, located within the [[w:Baltic region|Baltic]]. It is also the only continuously surviving member of the Italic language family, as well as being one of the two only non-extinct Italic languages, along with [[w:Latin|Latin]]. | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
| Line 360: | Line 360: | ||
===Latin alphabet=== | ===Latin alphabet=== | ||
Modern Valtamic employs the Latin alphabet, with the added vowel letters ''[[w:Ä|ä]]'', ''[[w:Ë|ë]]'', ''[[w:Ï|ï]]'', ''[[w:Ö|ö]]'', and ''[[w:Ü|ü]]'' and the extra consonant letters ''[[w:Ċ|ċ]]'', ''[[w:Ġ|ġ]]'', ''[[w:Ľ|ľ]]'', ''[[w:Ṅ|ṅ]]'', ''[[w:Ṡ|ṡ]]'', and ''[[w:Ż|ż]]''. Prior to the post-Soviet spelling reform, various polish-adjacent digraphs, such as ''cz'', ''ch'', ''sz'', etc. were used instead. The current orthography employs only three native digraphs, those being ''ou'', ''lj'', and ''nj''. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | |||
|+ '''Vowels''' | |||
|- style="font-weight:bold;" | |||
! rowspan="2" | Grapheme | |||
! colspan="2" | Sound (IPA) | |||
! rowspan="2" | Pre-Soviet spellings | |||
|- style="font-weight:bold;" | |||
! <small>Stressed</small> | |||
! <small>Unstressed</small> | |||
|- | |||
| a | |||
| [ɑ̝(ˑ)] | |||
| [ʌ] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ä | |||
| [æ(ˑ)] | |||
| rowspan="2" | [ɛ] | |||
| a, æ, e, ě | |||
|- | |||
| e | |||
| [e̞(ˑ)] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ë | |||
| [ɤ̞(ˑ)] | |||
| [ɜ] | |||
| ö, ø, œ | |||
|- | |||
| i | |||
| [i(ˑ)] | |||
| [ɪ] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ï | |||
| [ji(ˑ)] | |||
| [jɪ] | |||
| ji | |||
|- | |||
| o | |||
| [o̞(ˑ)] | |||
| [ɔ] ''or'' [ɔ̞] <sup>[a]</sup> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ö | |||
| [y(ˑ)] ~ [e̞(ˑ)] ~ [ɤ̞(ˑ)] <sup>[b]</sup> | |||
| [ʏ] ~ [ɛ] ~ [ɜ] <sup>[b]</sup> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ou | |||
| [u(ˑ)] | |||
| [ʊ] | |||
| u | |||
|- | |||
| u | |||
| [ɯ(ˑ)] | |||
| [ω] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ü | |||
| [y(ˑ)] | |||
| [ʏ] | |||
| ᵫ, y, u | |||
|- | |||
| y | |||
| [ɨ(ˑ)] | |||
| [ᵻ] | |||
| i, u | |||
|} | |||
<sup>[a]</sup> depending on vowel harmony | |||
<sup>[b]</sup> non-native and restricted to loanwords | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | |||
|+ '''Consonants''' | |||
|- style="font-weight:bold;" | |||
! Grapheme | |||
! Sound (IPA) | |||
! Pre-Soviet spellings | |||
! Grapheme | |||
! Sound (IPA) | |||
! Pre-Soviet spellings | |||
|- | |||
| b | |||
| [b] | |||
| | |||
| m | |||
| [m] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| c | |||
| [t̪͡s̪] | |||
| ts, tz | |||
| n | |||
| [n] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ċ | |||
| [t͡ʂ] ~ [t͡ɕ] | |||
| cz, tsj, tzj | |||
| nj <sup>[d]</sup> | |||
| rowspan="2" | [ɲ] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| d | |||
| [d] | |||
| | |||
| ṅ <sup>[d]</sup> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| dz <sup>[c]</sup> | |||
| [d͡z] | |||
| | |||
| p | |||
| [p] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| dż <sup>[c]</sup> | |||
| [d͡ʐ] ~ [d͡ʑ] | |||
| dzs, dj | |||
| q <sup>[c]</sup> | |||
| [k] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| f | |||
| [ʋ̊] | |||
| | |||
| r | |||
| [ɾ] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| g | |||
| [ɡ] | |||
| | |||
| s | |||
| [s̺] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ġ | |||
| [ɦ] | |||
| h, gh, vh | |||
| ṡ | |||
| [ʂ] | |||
| sz, sj | |||
|- | |||
| h | |||
| [x] | |||
| ch | |||
| t | |||
| [t̪] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| j | |||
| [j] | |||
| | |||
| v | |||
| [ʋ] | |||
| w | |||
|- | |||
| k | |||
| [k] | |||
| | |||
| w | |||
| [w] | |||
| u | |||
|- | |||
| l | |||
| [l̪] | |||
| | |||
| x <sup>[c]</sup> | |||
| [ks̺] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| lj <sup>[d]</sup> | |||
| rowspan="2" | [ʎ] | |||
| | |||
| z | |||
| [ɕ] ''or'' [z] <sup>[e]</sup> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ľ <sup>[d]</sup> | |||
| | |||
| ż | |||
| [ʐ] ~ [ʑ] | |||
| zs, zj | |||
|} | |||
===Cyrillic orthographies=== | ===Cyrillic orthographies=== | ||
Revision as of 15:00, 17 August 2024
This article is private. The author requests that you do not make changes to this project without approval. By all means, please help fix spelling, grammar and organisation problems, thank you. |
| Valtamic | |
|---|---|
| Äljämhar, Аьляьмхар | |
 Flag of the Republic of Valtamia | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈæˑʎɛm̥ˌχʌɾ̥] |
| Created by | Vrianne |
| Date | 2024 |
| Setting | Alt-History Baltic |
| Native to | Valtamia |
| Ethnicity | Valtamian, Livonian |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | Proto-Indo-European
|
Standard form | Standard Valtamic (--)
|
Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Official language in | Valtamia |
Recognised minority language in | |
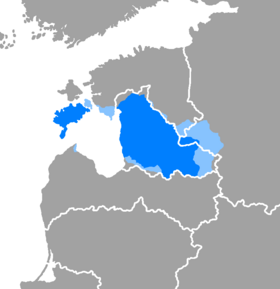
Map of areas where Vlatamic is spoken
...as a majority language
...as a minority language | |
Valtamic (endonym: äljämhor lïcür [ˈæˑʎɛm̥ˌχɔ̞ɾ̥ ˈʎiˑ(t)s̪ʏɾ̥]), also known as Livonian, is an Italic language belonging to the Indo-European language family. It is spoken mostly in the Republic of Valtamia, wherein it is recognized as the official language, located within the Baltic. It is also the only continuously surviving member of the Italic language family, as well as being one of the two only non-extinct Italic languages, along with Latin.
Classification
Valtamic belongs to the Italic branch of the Indo-European language family, along with Latin and other extinct languages such as Faliscan, Oscan, and Umbrian. It is not to be mis-classified as a Romance language, due to its relation with Latin.
Comparison with Romance languages
Due to Valtamic being the only continuously surviving Italic language, it may be erroneously grouped with the Romance languages, which are directly descended from Vulgar Latin, as opposed to Valtamic being directly descended from Proto-Italic. Even though, evolutionarily, Valtamic much older and more conservative than modern Romance languages, its evolutionary path made quite different from even Classical Latin.
| English translation | Latin | Romance | Valtamic | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| French | Italian | Spanish | Romanian | |||
| one | ūnus | un | uno | unu | ljar | |
| to eat | edō, mandūcō | manger | mangiare | comer | mânca | ṡëmëco |
| to know | sciō, sapiō | savoir | sapere | saber | ști | hnejo |
| to be familiar with | cognōscō | connaître | conoscere | conocer | cunoaște | |
| to hear | audiō | entendre | udire | oír | auzi | ozjo |
| language | lingua | langue | lingua | lengua, idioma | limbă | ljicür, tämva |
| cow | vacca | vache | vacca, mucca | vaca | vacă | aha |
| sheep | ovis | mouton | pecora | carnero, oveja | oaie | banar, ġüny |
| happy | laetus, fēlīx | heureux | felice | feliz | fericit | ilür |
| small | parvus, paulus | petit | piccolo | pequeño | mic | folër |
| all | omnēs | tous | tutto | todos | tot | mür |
History
Etymology
The English exonym Valtamic is a loan from Latin Vāltamicus ("Valtamic; Livonian"), with the most likely source being from Proto-Valtamic *βältämu, from *βältä ("strange") + *ämu ("man, human"), a theorized calque of a Finnic exonym. Nearly all European languages follow with loaning the Latin exonym, such as German Waltamisch, French Valtamien, and Russian Валтамский (Valtamskij).
The native endonym Äljämhar is unrelated to the Latin exonym, instead coming from Proto-Valtamic *βärjämu, from *βäre ("foreign") + *ämu ("man, human"), + Modern Valtamic -har (adjective-nominalizing suffix) , with unexplained loss of the initial *β. It's also a theorized calque of another Finnic exonym.
Proto-Valtamic
Modern Valtamic
Phonology
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | |||
| Close | i | y | ɨ | ɯ | u | |
| Mid | e | ɤ | o (ɔ)1 | |||
| Open | æ | ɑ | ||||
- /ɔ/ only exists due to vowel harmony and isn't recognized as phonemic in it's own right. Its pronunciation can range from [ɒ] to [ɔ].
Phonemically, there exist 10–11 contrasting phones. In practice though, vowels are slightly lengthened [◌ˑ] when stressed and experience slight reduction when unstressed, either lowering or centralizing.
| Front | Central | Back | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | ||||||||
| Stressed | Unstressed | Stressed | Unstressed | Stressed | Unstressed | Stressed | Unstressed | Stressed | Unstressed | ||
| Close | [i(ˑ)] | [ɪ] | [y(ˑ)] | [ʏ] | [ɨ(ˑ)] | [ᵻ] | [ɯ(ˑ)] | [ω] | [u(ˑ)] | [ʊ] | |
| Mid | [e̞(ˑ)] | [ɛ] | [ɤ̞(ˑ)] | [ɜ] | [o̞(ˑ)] | [ɔ] | |||||
| Open | [æ(ˑ)] | [ɑ̝(ˑ)] | [ʌ] | [ɔ̞] | |||||||
- [ᵻ ω] are unused IPA symbols representing near-close [ɪ̈ ɯ̽].
- Back [ɑ̝(ˑ) ɤ̞(ˑ) o̞(ˑ) ɯ(ˑ) u(ˑ)] [ʌ ɜ ɔ ω ʊ ɔ̞] become central [ä̝(ˑ) ɘ̞(ˑ) ɵ̞(ˑ) ɨ(ˑ) ʉ(ˑ)] [ɐ ɜ ɞ ᵻ ᵿ ɐ] in the presence of a palatal consonant.
- Unstressed [ᵻ] may alternatively be pronounced as central [ə].
- Stressed [ɤ̞(ˑ)] may alternatively be pronounced as front [ø̞ˑ], even though it messes with the harmony of inflectional endings.
- Unstressed [ɜ] may alternatively be pronounced as central [ə], merged with [ʌ], or (in the case of stressed [ø̞ˑ]) front [œ].
- Stress-pairs [æ(ˑ) ɛ] [ɑ̝(ˑ) ʌ] may alternatively be pronounced as true open [æ̞(ˑ) ɛ̞] [ɑ(ˑ) ʌ̞].
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | (ɳ) | ɲ | (ŋ) | ||
| Polsive | Voiceless | p | t | k | |||
| Voiced | b | d | ɡ | ||||
| Fricative | Voiceless | f | θ s | ʂ | ɕ | x | ɦ |
| Voiced | v | (z) | ʐ ~ ʑ | ||||
| Affricate | Voiceless | t͡s | t͡ʂ ~ t͡ɕ | ||||
| Voiced | (d͡z) | (d͡ʐ ~ d͡ʑ) | |||||
| Trill/Tap | r | ||||||
| Lateral | l | ʎ | |||||
| Non-lateral approximant | j | w | |||||
- /m n ɲ r l ʎ/ become devoiced [m̥ n̥ ɲ̊ ɾ̥ l̥ ʎ̥] syllable-finally.
- [ŋ ɳ] are allophones of /n/ near velar and retroflex consonants respectively.
- /t l/ are pronounced as dental [t̪ l̪] while /n d/ as true alveolar [n d].
- /f v/ are pronounced as approximants [ʋ̊ ʋ].
- /θ/ only appears in the cluster ⟨tr⟩ /θr/.
- /s/ is pronounced as apical/retracted [s̺] while /t͡s/, like /t/, is pronounced as dental/laminal [t̪͡s̪]. /t͡s/ de-affricates when unstressed and non-initial, giving rise to an apical/laminal distinction [s̺] [s̻] in unstressed syllables, as seen in words like ⟨uhsoucux⟩ /ˈɯxsut͡sɯx/ [ˈɯˑχs̺ʊˌs̪ωχ].
- /z/ appears in modern loanwords but is, in practice, in free variation with /ɕ/.
- /x l w/ are pronounced as [χ ɫ w] near back vowels and [x̟ l ɥ] near front vowels.
- /r/ is pronounced as a tap [ɾ] in most dialects.
Orthographies
Latin alphabet
Modern Valtamic employs the Latin alphabet, with the added vowel letters ä, ë, ï, ö, and ü and the extra consonant letters ċ, ġ, ľ, ṅ, ṡ, and ż. Prior to the post-Soviet spelling reform, various polish-adjacent digraphs, such as cz, ch, sz, etc. were used instead. The current orthography employs only three native digraphs, those being ou, lj, and nj.
| Grapheme | Sound (IPA) | Pre-Soviet spellings | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stressed | Unstressed | ||
| a | [ɑ̝(ˑ)] | [ʌ] | |
| ä | [æ(ˑ)] | [ɛ] | a, æ, e, ě |
| e | [e̞(ˑ)] | ||
| ë | [ɤ̞(ˑ)] | [ɜ] | ö, ø, œ |
| i | [i(ˑ)] | [ɪ] | |
| ï | [ji(ˑ)] | [jɪ] | ji |
| o | [o̞(ˑ)] | [ɔ] or [ɔ̞] [a] | |
| ö | [y(ˑ)] ~ [e̞(ˑ)] ~ [ɤ̞(ˑ)] [b] | [ʏ] ~ [ɛ] ~ [ɜ] [b] | |
| ou | [u(ˑ)] | [ʊ] | u |
| u | [ɯ(ˑ)] | [ω] | |
| ü | [y(ˑ)] | [ʏ] | ᵫ, y, u |
| y | [ɨ(ˑ)] | [ᵻ] | i, u |
[a] depending on vowel harmony
[b] non-native and restricted to loanwords
| Grapheme | Sound (IPA) | Pre-Soviet spellings | Grapheme | Sound (IPA) | Pre-Soviet spellings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | [b] | m | [m] | ||
| c | [t̪͡s̪] | ts, tz | n | [n] | |
| ċ | [t͡ʂ] ~ [t͡ɕ] | cz, tsj, tzj | nj [d] | [ɲ] | |
| d | [d] | ṅ [d] | |||
| dz [c] | [d͡z] | p | [p] | ||
| dż [c] | [d͡ʐ] ~ [d͡ʑ] | dzs, dj | q [c] | [k] | |
| f | [ʋ̊] | r | [ɾ] | ||
| g | [ɡ] | s | [s̺] | ||
| ġ | [ɦ] | h, gh, vh | ṡ | [ʂ] | sz, sj |
| h | [x] | ch | t | [t̪] | |
| j | [j] | v | [ʋ] | w | |
| k | [k] | w | [w] | u | |
| l | [l̪] | x [c] | [ks̺] | ||
| lj [d] | [ʎ] | z | [ɕ] or [z] [e] | ||
| ľ [d] | ż | [ʐ] ~ [ʑ] | zs, zj |