Brytho-Hellenic: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Infobox language | {{Infobox language | ||
|name = Brytho-Hellenic | |name = Brytho-Hellenic | ||
|nativename = Elynik (to | |nativename = Elynik (to kæn) | ||
|pronunciation = [ɛ'le:nik 'tɔ 'kai̯n] | |pronunciation = [ɛ'le:nik 'tɔ 'kai̯n] | ||
|region = Europe | |region = Europe | ||
|states = Elas to | |states = Elas to Kæn | ||
|nation = Elas to | |nation = Elas to Kæn | ||
|speakers = 52 millions | |speakers = 52 millions | ||
|date = 2012 | |date = 2012 | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|fam3 = Celto-Hellenic | |fam3 = Celto-Hellenic | ||
|map = Elas_mini.gif | |map = Elas_mini.gif | ||
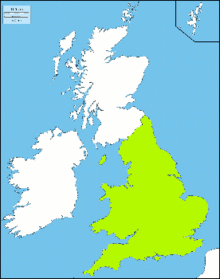
|mapcaption = New Greece or "Elas to | |mapcaption = New Greece or "Elas to Kæn" | ||
|iso1 = el | |iso1 = el | ||
|iso2 = ely | |iso2 = ely | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
In that timeline the Persians have won the wars against Greece and the Greeks have been forced to emigrate and to flee. Firstly the Greeks find protection in Magna Graecia, but, as the Persians conquer those territories, they shift to Northern Italy, where the Romans withstand the Persian troops. In 389 b.C. Rome is destroyed and both Romans and Greeks flee to Carthage, enemy of the Persian empire. Together they try to attack the Persian fleet, but they are defeated again. | In that timeline the Persians have won the wars against Greece and the Greeks have been forced to emigrate and to flee. Firstly the Greeks find protection in Magna Graecia, but, as the Persians conquer those territories, they shift to Northern Italy, where the Romans withstand the Persian troops. In 389 b.C. Rome is destroyed and both Romans and Greeks flee to Carthage, enemy of the Persian empire. Together they try to attack the Persian fleet, but they are defeated again. | ||
In the last days of 382 b.C. an imposing expedition sails away from a harbour on the coast of New Carthage - our Cartagena in Spain. Its mission is to find new territories where they can live in peace and prosperity, far from the Persian threat. | In the last days of 382 b.C. an imposing expedition sails away from a harbour on the coast of New Carthage - our Cartagena in Spain. Its mission is to find new territories where they can live in peace and prosperity, far from the Persian threat. | ||
In 381 b.C. ''Conon the Athenian'' and his Greeks reach our '''Scilly Islands''': they have chosen to sail northward, because they had heard about legends that spoke about a fertile and grassy island in the North. It is the beginning of the ''New Greece'' or '''Elas to | In 381 b.C. ''Conon the Athenian'' and his Greeks reach our '''Scilly Islands''': they have chosen to sail northward, because they had heard about legends that spoke about a fertile and grassy island in the North. It is the beginning of the ''New Greece'' or '''Elas to Kæn''' (IPA ['ɛlas 'tɔ 'kai̯n]). | ||
==Phonology== | ==Phonology== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
After the defeat against the Persians almost the entire Greek people fled towards Roman territory: Rome triplicated its population and was greekized. During their living together Greeks and Romans used mainly the '''Greek language''' to communicate, whereas the ''Latin language'' became a secondary and socially lower language, spoken mainly by common people. Nevertheless - almost incomprehensibly - the Greeks adopted the '''Latin alphabet''', maybe trying to be understood even by the lower social classes. | After the defeat against the Persians almost the entire Greek people fled towards Roman territory: Rome triplicated its population and was greekized. During their living together Greeks and Romans used mainly the '''Greek language''' to communicate, whereas the ''Latin language'' became a secondary and socially lower language, spoken mainly by common people. Nevertheless - almost incomprehensibly - the Greeks adopted the '''Latin alphabet''', maybe trying to be understood even by the lower social classes. | ||
As we are talking about the modern language, we don't consider the first versions of the alphabet that were used in ancient times. The alphabet of Brythohellenic contains | As we are talking about the modern language, we don't consider the first versions of the alphabet that were used in ancient times. The alphabet of Brythohellenic contains 25 letters: | ||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} style="text-align:center; vertical-align:middle" | {| {{Table/bluetable}} style="text-align:center; vertical-align:middle" | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
|[a] | |[a] | ||
| - | | - | ||
|- | |||
|æ | |||
|[ai̯] | |||
|it is actually a diphthong, this letter (together with '''ø''') seems to be a Nordic loan, since in medieval manuscripts only ''ae'', ''ai'' and ''au'' are found | |||
|- | |- | ||
|b | |b | ||
| Line 96: | Line 100: | ||
|[ɔ] / [o] | |[ɔ] / [o] | ||
|it can be either open or closed, but it doesn't affect the meaning | |it can be either open or closed, but it doesn't affect the meaning | ||
|- | |||
|ø | |||
|[ɔi̯] | |||
|it is actually a diphthong, the letter (together with '''æ''') seems to be a Nordic loan, since in medieval manuscripts only ''oe'', ''oi'' and ''ou'' are found | |||
|- | |- | ||
|p | |p | ||
| Line 131: | Line 139: | ||
|y | |y | ||
|[i] / [e] | |[i] / [e] | ||
|in monosyllabic words it is read as [i], in polysyllabic words it is read [i] if in the last syllable, otherwise [e]; in the diphthong '''wy''' it can be either the vocalic (it is written ''' | |in monosyllabic words it is read as [i], in polysyllabic words it is read [i] if in the last syllable, otherwise [e]; in the diphthong '''wy''' it can be either the vocalic (it is written '''ŷw''') or consonantical element (it is written yŵ) | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 247: | Line 255: | ||
!'''Pronunciation''' | !'''Pronunciation''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'' | |''æ'', ''ai'', ''ay'' | ||
|[ai̯] | |[ai̯] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 271: | Line 279: | ||
|[ju] | |[ju] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |''oi'', ''oy'' | ||
|[ɔi̯] / [oi̯] | |[ɔi̯] / [oi̯] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 289: | Line 297: | ||
|[wɔ] / [wo] | |[wɔ] / [wo] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'' | |''ŵy'' / ''wŷ'' | ||
|[wi] / [ | |[wi] - [we] / [ui̯] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'' | |''ŷw'' / ''yŵ'' | ||
|[iu̯] / [ | |[iu̯] - [eu̯] / [ju] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 319: | Line 327: | ||
* '''as''', less spread and used with both masculine and feminine nouns. | * '''as''', less spread and used with both masculine and feminine nouns. | ||
Unfortunately there are also some irregularities which have to be learned by heart, ex.: the plural of '''ith''', "fish", is '''ith''w''as'''; the plural of '''gys''', "earth", is '''gae'''; the plural of '''ŵr''', "water", is ''' | Unfortunately there are also some irregularities which have to be learned by heart, ex.: the plural of '''ith''', "fish", is '''ith''w''as'''; the plural of '''gys''', "earth", is '''gae'''; the plural of '''ŵr''', "water", is '''wdhas''', and so on. Irregular nouns, however, are few. | ||
Here is a list of nouns with plural form: | Here is a list of nouns with plural form: | ||
Revision as of 13:23, 30 March 2013
This article is private. The author requests that you do not make changes to this project without approval. By all means, please help fix spelling, grammar and organisation problems, thank you. |
| Brytho-Hellenic | |
|---|---|
| Elynik (to kæn) | |
| Pronunciation | [[Help:IPA|ɛ'le:nik 'tɔ 'kai̯n]] |
| Created by | – |
| Native to | Elas to Kæn |
| Native speakers | 52 millions (2012) |
Indo-European
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Elas to Kæn |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | el |
| ISO 639-2 | ely |
| ISO 639-3 | ely |
New Greece or "Elas to Kæn" | |
General information
Brytho-Hellenic, Brythohellenic or simply Neohellenic (the native name is Elynik) is a language that is spoken nowadays in a different timeline in a country that corresponds almost exactly to our England and to our Wales. In that timeline the Persians have won the wars against Greece and the Greeks have been forced to emigrate and to flee. Firstly the Greeks find protection in Magna Graecia, but, as the Persians conquer those territories, they shift to Northern Italy, where the Romans withstand the Persian troops. In 389 b.C. Rome is destroyed and both Romans and Greeks flee to Carthage, enemy of the Persian empire. Together they try to attack the Persian fleet, but they are defeated again. In the last days of 382 b.C. an imposing expedition sails away from a harbour on the coast of New Carthage - our Cartagena in Spain. Its mission is to find new territories where they can live in peace and prosperity, far from the Persian threat. In 381 b.C. Conon the Athenian and his Greeks reach our Scilly Islands: they have chosen to sail northward, because they had heard about legends that spoke about a fertile and grassy island in the North. It is the beginning of the New Greece or Elas to Kæn (IPA ['ɛlas 'tɔ 'kai̯n]).
Phonology
Alphabet
After the defeat against the Persians almost the entire Greek people fled towards Roman territory: Rome triplicated its population and was greekized. During their living together Greeks and Romans used mainly the Greek language to communicate, whereas the Latin language became a secondary and socially lower language, spoken mainly by common people. Nevertheless - almost incomprehensibly - the Greeks adopted the Latin alphabet, maybe trying to be understood even by the lower social classes. As we are talking about the modern language, we don't consider the first versions of the alphabet that were used in ancient times. The alphabet of Brythohellenic contains 25 letters:
| Letters | Pronunciation | Further informations |
|---|---|---|
| a | [a] | - |
| æ | [ai̯] | it is actually a diphthong, this letter (together with ø) seems to be a Nordic loan, since in medieval manuscripts only ae, ai and au are found |
| b | [b] | - |
| d | [d] | - |
| dh | [ð] / [j] / [v] / [ ] | generally it is pronounced as th in the word this; when it occurs between vowels its pronunciation can vary between [j] and [v]: generally it is [j] when the vowel that follows is a, e, i or y, while it is [v] when the vowel that follows is o or u. Some speakers don't pronounce it at all when it comes in patterns o-o, u-u, o-u and u-o |
| e | [ɛ] | it is always pronounced open |
| f | [f] | - |
| g | [g] / [x] / [h] | when it comes beforse or after other consonants it is pronounced [g], between vowels it is pronounced [x], even if some speakers tend to pronounce it as [h] in this position |
| h | [h] | - |
| i | [i] / [j] | often it forms a diphthong when precedes or follows another vowel |
| k | [k] | it is always pronunced as in the English word kite |
| l | [l] | - |
| m | [m] | - |
| n | [n] | - |
| o | [ɔ] / [o] | it can be either open or closed, but it doesn't affect the meaning |
| ø | [ɔi̯] | it is actually a diphthong, the letter (together with æ) seems to be a Nordic loan, since in medieval manuscripts only oe, oi and ou are found |
| p | [p] | - |
| r | [r] | trilled just as in Italian |
| s | [s] | always voiceless |
| t | [t] | - |
| th | [θ] | as th in the English thin |
| u | [i] | - |
| v | [v] | - |
| w | [u] / [w] | it is pronounced as [u] when it is followed by a consonant; it is pronounced [w] when it is preceded or followed by a vowel; when it is followed by l or r it can have either a consonantal or vocalic value, to distinguish it, it is written ŵ when it has a vocalic value; in the diphthong wy it can be either the vocalic (it is written ŵy) or consonantical element (it is written wŷ) |
| y | [i] / [e] | in monosyllabic words it is read as [i], in polysyllabic words it is read [i] if in the last syllable, otherwise [e]; in the diphthong wy it can be either the vocalic (it is written ŷw) or consonantical element (it is written yŵ) |
Consonantal phonemes
Brythohellenic has the following consonantic phonemes:
| Phonemes | Bilabial | Labiodental | Dental | Alveolar | Postalveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | p b | t d | k g | |||||
| Affricate | ||||||||
| Nasal | m | (ɱ) | n | (ŋ) | ||||
| Fricative | f v | θ ð | s | x | h | |||
| Approximant | r̥ r | j | w | |||||
| Lateral approximant | l |
Vocalic phonemes
Brythohellenic has the following vowel system:
| Phonemes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Opening | Front | Back |
| Closed | i | u |
| Mid-closed | e | o |
| Mid-open | ɛ | ɔ |
| Open | a | |
Diphthongs and digraphs
In Brythohellenic there are 22 diphthongs, that is clusters of two vowels pronounced with a single emission of air. These diphthongs are:
| Diphthongs | Pronunciation |
|---|---|
| æ, ai, ay | [ai̯] |
| aw | [au̯] |
| ei, eu, ey | [ɛi̯] |
| ew | [ɛu̯] |
| ia | [ja] |
| ie | [jɛ] |
| io | [jɔ] / [jo] |
| iw | [ju] |
| oi, oy | [ɔi̯] / [oi̯] |
| uw | [iu̯] |
| wa | [wa] |
| we | [wɛ] |
| wi | [wi] |
| wo | [wɔ] / [wo] |
| ŵy / wŷ | [wi] - [we] / [ui̯] |
| ŷw / yŵ | [iu̯] - [eu̯] / [ju] |
Brythohellenic has got only one digraph: rh [r̥], which is rare enough. The other combinations as dh and th are considered true letters.
Stress
Ancient Greek has undergone deep changes during its coexistence with Latin and above all with the Brythonic languages. Two main changes have been:
- often the hiatus with 'i' has become a diphthong, ex.: σοφία > *σόφια > hef, "knowledge";
- almost always the last syllable has fallen, ex.: καινός > kaen, "new"; θάνατος > thanadh, "death".
These two phoenomena have influenced heavily the stress system of Brythohellenic. Nowadays the stress steadily falls on the last but one syllable: this means that in the plural forms of nouns it shifts, ex.: thalas ['θalas], "sea" > thalasas [θa'lasas], "seas"; aelŵr ['ai̯lur], "cat" > aelŵroe [ai̯'luroi̯], "cats".
Grammar
Nouns, gender and number
Even if Ancient Greek had three genders and three numbers, the system simplified a lot and Modern Elynik has got two genders - masculine and feminine - and two numbers - singular and plural. It is hard to distinguish the gender of a noun, because there are not specific gender-linked endings: mostly nouns end with consonant regardless for the gender. Forming plural is not so complicated, as there are only three plural endings:
- oe, that is typical of masculine nouns;
- ae, that is used with feminine nouns;
- as, less spread and used with both masculine and feminine nouns.
Unfortunately there are also some irregularities which have to be learned by heart, ex.: the plural of ith, "fish", is ithwas; the plural of gys, "earth", is gae; the plural of ŵr, "water", is wdhas, and so on. Irregular nouns, however, are few. Here is a list of nouns with plural form:
| Singular | Plural | Gender | Meaning | Singular | Plural | Gender | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lidd | liddoe | masculine | stone | pwd | pwdas | masculine | foot |
| kŵr | kŵrae | feminine | land | ŵran | wranoe | masculine | sky, heaven |
| kryfid | kryfidas | feminine | shoe | ffws | ffwddas | masculine | light |
| biodd | bioddoe | masculine | life | lws | lwsae | feminine | language |
| thyr | thyras | masculine | animal | bifyl | bifloe | masculine | book |
| ef | afae | feminine | love | alwfik | alwfikae | masculine | fox |
| koeran | koeranoe | masculine | lord | koeren | koeranae | feminine | lady |
| enyr | annyr | masculine | man | gunys | gunae | feminine | woman |
| pur | puroe | masculine | fire | keffel | keffalae | feminine | head |
| tof | tofoe | masculine | place | kron | kronoe | masculine | time |
| oddyr | oddroe | masculine | morning | yfer | yferae | feminine | day |
| dyl | dylae | feminine | afternoon | effer | efferae | feminine | evening |
| nuth | nuthas | feminine | night | hilyn | hilynae | feminine | moon |
| seldd | selddoe | masculine | priest | sildd | selddae | feminine | priestess |
| dennyr | dennyras | masculine | tree | kadd | kaddas | masculine | hand |
| etyr | eteras | masculine | star | omadd | omaddas | masculine | eye |
| keddydd | keddyddas | masculine | teacher | ffil | ffiloe | masculine | friend |
| ethyr | ethroe | masculine | enemy | eddaer | eddaeroe | masculine | lover |
| kuwn | kunoe | masculine | dog | kom | komoe | masculine | world |
Loan words
As the Greeks reached Great Britain found a completely new world, full of animals and plants they had never seen. Celtic people had highly different customs and beliefs and spoke an unintelligible language. Even if the Greeks considered them to be barbarian, they were the "owners" of the new land, so Greeks had to learn to live together with Brythons and to forget about prejudices like "superiority" or "inferiority". During the coexistence and the mixing with Brythons, the Greeks have adopted some Celtic words:
| Original word | Singular | Plural | Gender | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| derwen | darwen | darwenae | feminine | oak |
| derwydd | darwydd | darwyddas | masculine | priest, magician, druid |
| bryn | bryn | brynae | feminine | hill |
| nifwl | nifyl | nifloe | masculine | mist, fog |
| llyn | lyn | lynoe | masculine | lake |
| gwellt | gweldd | gwelddas | feminine | grass |
| ofydd | ofydd | ofyddas | masculine | ovate |
| bardos | bard | bardas | masculine | poet |
| awen | awen | awenae | feminine | inspiration |
| bleydh | bleudh | bleuddas | masculine | wolf |
| lowarth | lowarth | lowarthas | feminine | paradise |
| calon | kalen | kalenae | feminine | heart |
Some words have a counterpart whose meaning has shifted: from the Greek ουάτις, a word mentioned by Strabo and of Proto-Celtic origin (*vatis), comes gwedd, "astute person" < "one who can predict the moves of enemies" < "soothsayer". From the same root comes of course the Brythonic word ofydd, that has been taken as loan once the Greeks reached Great Britain. Another example is the word bard, that has substituted the Ancient Greek ἀοιδός, whose descendant, awid, has got the meaning of "artist". Even the word awen has substituted another Greek word, daefon < *δαιμόνος < δαιμόνιον, that now has the meaning of "puck, spirit"; the plural Awenae is also used to mean Mwsae, plural of Mws < Mοῦσα, "Muse".
Formation of feminine
It isn't easy to distinguish between a masculine and a feminine noun, because there is no gender-linked ending. However, when we speak about entities that have got a physical gender, such as people and animals, it can be useful to be able to distinguish between masculine and feminine gender. Mostly the feminine form of such nouns come from the masculine one by adding some suffixes:
- -yr (pl. -(y)rae), mostly added to masculine nouns ending with -ydd and denoting agent, ex.: melbydd (= "singer") > melbyddyr (plural: melbyddrae);
- -en (pl. -anae), added to many nouns, ex.: ethyr > ethren (plural: ethranae); ffil > ffilen (plural: ffilanae);
- -e- (pl. -a-ae), that replaces the ending a + consonant of many masculine nouns, ex.: elaff (= "deer") > eleff (plural: elaffae); maw (= "sorcerer") > mew (= "witch") (plural: mawae).
Sometimes the feminine form is obtained by changing the last vowel, ex.: seldd > sildd (plural: selddae).
Articles
Brythohellenic hasn't got indefinite article, to translate phrases like "a cat" or "some women" we have just to omit the article: aelŵr means both "a cat" and "cat", and gunaes means both "some women" and "women". There is only one kind of article, the definite one: this article is used to talk about well known things that are familiar to the speakers, because they have already been talked about, or because they belong to the experiences baggage of the speakers, that is we use the definite article to talk about known informations, to talk about determined informations. The definite article has got one invariable form, to, that is used both for masculine and feminine nouns, for singular and plural nouns: to omyr, "the rain"; to hwfadd, "the body"; to lwsae, "the languages"; to nysoe, "the islands", and so on.
When a noun is determined, that is preceded by the article or other determiners (such as possessives or demonstratives) and is followed by an adjective - in standard Elynik the adjectives always follow the substantives - the article shifts bewtween noun and adjective, ex.:
- to omyr > omyr to surin (= "the cold rain", lit. "rain the cold (one)");
- to nysoe > nysoe to eueddoe (= "the fertile islands", lit. "islands the fertile (ones)").
Even when a noun doesn't need the article - for example proper nouns - it appears between this noun and the possible adjective, ex.:
- Elas (= "Greece") > Elas to Kaen (= "New Greece", lit. "Greece the New (one)");¹
- Elyn (= "Helena") > Elyn to plyd kalin (= "the most beautiful Helena", lit. "Helena the most beautiful (one)").
¹ Nowadays they tend to use the word Elas to mean Elas to Kaen, while the "Old Greece" is known as Elas to Paladd.
Adjectives
Elynik adjectives always follow the noun(s) they are referred to: when the noun is undetermined they simply follow it, but, when the noun is determined, then the definite article, to, is put between the noun and the adjective. Usually adjectives' singular form is identical for masculine and feminine, even if there can be exceptions, the plural forms are two, instead: one for masculine, usually ending in -oe, and one for feminine, ending in -ae. Some adjectives:
| Singular | Masculine plural | Feminine plural | Meaning | Singular | Masculine plural | Feminine plural | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iwydd | iwyddoe | iwyddae | good | penyr | penyroe | penyrae | bad |
| elyf | elfoe | elfae | happy | lur | luroe | lurae | sad |
| egrin | egrinoe | egrinae | tall / high | thafal | thafaloe | thafalae | short |
| kalin | kalinoe | kalinae | beautiful / goodlooking | aehyr | aehroe | aehrae | ugly |
| meal | mealoe | mealae | big / great | migrin | migrinoe | migrinae | little / small |
| paladd | paladdoe | paladdae | old | yfik | yfikoe | yfikae | young |
| thenar | thenaroe | thenarae | strong | athin | athinoe | athinae | weak |
| therfin | therfinoe | therfinae | hot | surin | surinoe | surinae | cold |
| ffofer | ffoferoe | ffoferae | terrible | plys | plysoe | plysae | near / close |
| tyleddin | tyleddinoe | tyleddinae | far / distant | semyk | semykoe | semykae | tired |
Some usage examples:
- migrin + aelŵr > aelŵr migrin (= "(a) little cat");
- meal + to enyr > enyr to meal (= "the big man");
- semyk + to koerenyf > koerenyf to semyk (= "my tired lady").
Comparative
The higher degree comparative is usually formed with the word wa that precedes the adjective to which is referred, the second term is introduced by y ex.:
- Andd wa kalin y dennyr > A flower more beautiful than a tree.
In the written language it is still used the old form with the suffix -wn, ex.:
- Andd kalddwn y dennyr > A flower more beautiful than a tree.
The same degree comparative is formed with the periphrasis wddys + adjective + yffer, ex.:
- Andd wddys kalin yffer dennyr > A flower as beautiful as a tree,
The lower degree comparative is formed with the periphrasis myon + adjective + y, ex.:
- Andd myon kalin y dennyr > A flower less beautiful than a tree.
Adjectives with an irregular higher degree comparative
Some adjectives have got an irregular form of higher degree comparative:
| Positive | Comparative | Positive | Comparative |
|---|---|---|---|
| iwydd | areddwn | penyr | yswn |
| kalin | kalddwn | red (= "easy") | rawn |
| migrin | meddwn | meal | myswn |
| polus (= "many/much") | pleddwn | alwyn (= "painful/agonizing") | alddwn |
Irregular higher degree comparatives are used as normal comparatives, ex.:
- Ys hi areddwn y ey - You are better than me.
The comparative form is the same for both masculine and feminine nouns, but in the plural the two forms are different: areddwnoe vs. areddwnae.
Superlative
The superlative degree is generally formed with the word plyd, that precedes the adjective to which is referred. The relative superlative is the same form of the absolute superlative, but it takes the definite article and is generally followed by a limitation, that is expressed with en (= "in") / efan (= "of"), ex.:
- Andd to plyd kalin en to kom - The most beautiful flower in the world.
In the written language it is also used the old superlative with the suffix -yd:
- Andd to kalyd efan to kom - The most beautiful flower of the world.
Adjectives with an irregular superlative
The same adjectives that have an irregular higher degree comparative have got also an irregular superlative form:
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative | Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iwydd | areddwn | aryd | penyr | yswn | ykyd |
| kalin | kalddwn | kalyd | red | rawn | rad |
| migrin | meddwn | elehyd | meal | myswn | meyd |
| polus | pleddwn | plyd | alwyn | alddwn | alwyd |
Other adjectives form the comparative and the superlative degree regularly, ex.:
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| paladd | wa paladd / paladdwn | plyd paladd / paladdyd |
| lur | wa lur / lurwn | plyd lur / luryd |
| egrin | wa egrin / egrinwn | plyd egrin / egrinyd |
| plys | wa plys / plyswn | plyd plys / plysyd |
The superlative has got only one singular form, in the plural masculine and feminine are different, ex.: aryd > arydoe, arydae.
Numerals
Numerals don't inflect. Here are the numerals from 0 to 100:
| Number | Cardinal | Ordinal | Number | Cardinal | Ordinal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | wden | - | 1 | eis | prwdd |
| 2 | dios | deudder | 3 | trys | tridd |
| 4 | tethar | tethardd | 5 | pen | pendd |
| 6 | es | eth | 7 | efft | eudodd |
| 8 | oth | owodh | 9 | enah | enadd |
| 10 | deg | degadd | 11 | enneg | ennegadd |
| 12 | dydeg | dydegadd | 13 | trydeg | trydegadd |
| 14 | tethardeg | tethardegadd | 15 | penneg | pennegadd |
| 16 | eddeg | eddegadd | 17 | effteg | efftegadd |
| 18 | othwdeg | othwdegadd | 19 | enadeg | enadegadd |
| 20 | iwaen | iwaed | 21 | iwaen sun eis | iwaed sun prwdd |
| 22 | iwaen sun dios | iwaed sun deudder | 30 | iwaen-deg | iwaendegadd |
| 31 | iwaen-deg sun eis | iwaendegadd sun prwdd | 40 | dioewaen | dioewaed |
| 50 | dioewaen-deg | dioewaendegadd | 60 | triwaen | triwaed |
| 70 | triwaen-deg | triwaen-degadd | 80 | tetharwaen | tetharwaed |
| 90 | tetharwaen-deg | tetharwaendegadd | 100 | egadd | egaddod |
From egadd on, the numbers can be masculine or feminine:
| Number | Cardinal | Ordinal | Number | Cardinal | Ordinal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | diagesioe/ae | diagesiod | 300 | trygesioe/ae | trygesiod |
| 400 | tethragesioe/ae | tethragesiod | 500 | pennagesioe/ae | pennagesiod |
| 600 | esagesioe/ae | esagesiod | 700 | efftagesioe/ae | efftagesiod |
| 800 | othagesioe/ae | othagesiod | 900 | enagesioe/ae | enagesiod |
| 1000 | hilioe/ae | hiliod | 2000 | diahilioe/ae | diahiliod |
| 3000 | tryhilioe/ae | tryhiliod | 4000 | tethrahilioe/ae | tethrahiliod |
| 5000 | pennahilioe/ae | pennahiliod | 6000 | esahilioe/ae | esahiliod |
| 7000 | efftahilioe/ae | efftahiliod | 8000 | othahilioe/ae | othahiliod |
| 10000 | mirioe/ae | miriod | 11000 | mirioe/ae sun hilioe/ae | miriod sun hiliod |
| 20000 | dimirioe/ae | dimiriod | 100000 | egadd-hilioe | egadd-hiliod |
| 500000 | pennagesioe-hilioe | pennagesioe-hiliod | 1000000 | kryn | krynod |
| 2000000 | dios krynoe | deudder krynod | 1000000 | riagryn | riagryd |
Pronouns and kinds of adjectives
Personal pronouns
Brythohellenic personal pronouns have three cases: nominative, accusative, and dative.
| Case | 1st person | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Plural | |||
| Nominative | ew | fys | ||
| Accusative | fe | fas | ||
| Dative | foe | fin | ||
| Case | 2nd person | |||
| Singular | Plural | |||
| Nominative | hi | ffy | ||
| Accusative | he | ffas | ||
| Dative | hoe | ffyn | ||
| Case | 3rd person | |||
| Masculine s. | Feminine s. | Masculine pl. | Feminine pl. | |
| Nominative | o | ỳ | oe | ae |
| Accusative | ton | tyn | tws | tas |
| Dative | tw | ty | toes | taes |
In a sentence the pronouns in dative case are positioned before of those in accusative case, so prepositions can be omitted, ex.:
- Dwn hi foe tyn - Give it to me.
The neuter pronoun it is translated in Brythohellenic with ỳ. The feminine pronoun ỳ is written with the accent to be distinguished from the preposition y (= "than"). When there are a pronoun and a noun, the pronoun always precedes the noun, ex.:
- Dwn hi tyn bros to koeren - Give it to the lady;
- Dwn hi ty to kuwn - Give her the dog.
Demonstratives
There are two demonstratives: wdd (= "this") and egyn (= "that"). The first demonstrative matches perfectly the first person, whereas the second one matches both the second and the third person:
| Person | Adverb | Demonstrative | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | nawdd | wdd | this |
| 2nd | kys | egyn | that |
| 3rd |
Demonstratives always follow the nouns they are referred to, and the nouns take also the article, ex.:
- To aelŵr ŵdd - This cat.
Demonstratives also got plural forms:
| Number | Wdd | Egyn |
|---|---|---|
| Singular | wdd (f. aedd) | egyn |
| Plural | ddoe (f. ddae) | egynoe (f. egynae) |
Some examples:
- Yf ew en to oek wdd - I'm in this house;
- Ew erhonn e tho oek egyn - I come from that house.
Possessives
Possessives are enclitical, so they need always that the substantive they are referred to is explicit. If they have to be used as pronouns, then they are used with the definite article:
| Person | Possessive |
|---|---|
| ew | -(y)f |
| hi | -(y)s |
| o | -(y)t |
| ỳ | -(y)t |
| fys | -(y)n |
| ffy | -(y)dd |
| oe / ae | -(y)t |
Here are some examples:
- To aelŵryf > Tof - My cat > Mine;
- To kuwns > Tos - Your dog > Yours;
- To gunyst > Tot - His wife > His;
- To enyrt > Tot - Her man > Hers;
- To thyrn > Ton - Our animal > Ours;
- To ffildd > Todd - Your friend > Yours;
- To kalent > Tot - Their heart > Theirs.
Plural:
- To aelŵroef > Tof - My cats > Mine;
- To kunoes > Tos - Your dogs > Yours;
- To gunaet > Tot - His wifes > His;
- To annyrt > Tot - Her men > Hers;
- To thyrasyn > Ton - Our animals > Ours;
- To ffiloedd > Todd - Your friends > Yours;
- To kalenaet > Tot - Their hearts > Theirs.
In the "possessive form" of a noun, the accent doesn't shift.
Relatives and 'interro-exclamatories'
Interrogative pronouns, which are used also to make exclamations, function also as relatives:
| Case | Tis (who) | Ti (what) |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | tis | ti |
| Accusative | ten | ti |
| Dative | ty | ty |
| Genitive | twn | twn |
Ex.:
- Tis ys o? - Who is he?
- Tis kalin kuwn! - What a beautiful dog!
- Twn ys to bifyl wdd? - Whose is this book?
- Ty elehas tyn? - Whom have you said it to?
- To egyn ys to gunys ten ew afonn - That is the woman whom I love.
Indefinites
Indefinites give us incomplete informations, because they don't define the precise quantity or the identity:
| Indefinite | Meaning |
|---|---|
| wddis | someone/anyone |
| eddi | something/anything |
| mydys | nobody |
| myden | nothing |
| olen | each |
| pan | all |
| edder | other |
| ofodd | same, self |
When pan is used as adjective, it has the singular form pas and the plural forms panas for masculine and pasae for feminine. Also edder has got plural: edderoe for masculine and edderae for feminine.
Indefinites can be formed also with the word alen:
- To alenoe/ae - The others;
- Ys hi krysonn eddi alen? - Do you need something else?
- Ys ỳ gnokonn wddis alen? - Does she know someone else?
Adverbs
Usually adverbs are formed by suffixation: many adverbs derive from adjectives, to that the suffix -ews is added. Some examples:
- elyf > elfews (happy - happily);
- lur > lurews (sad - sadly);
- meal > mealews (great - greatly);
- thenar > thenarews (strong - strongly);
- athin > athinews (weak - weakly).
Some adverbs have got suppletive forms, ex.: iwydd > eu; penyr > ffawl.
Adverbs have got a precis position within the sentence:
- 1) adverbs always follow subject when in the sentence there is only the verb ynyn (= to be), ex.: yf ew mal elyf (= "I am very happy");
- 2) adverbs always follow the semantic verb, when it appears, ex.: ys ỳ dagrwonn thenarews (= "She cries strongly");
- 3) adverbs always precede adjectives, ex.: ys o elion lur (= "He's a little sad").
Vocabulary
Colour terms
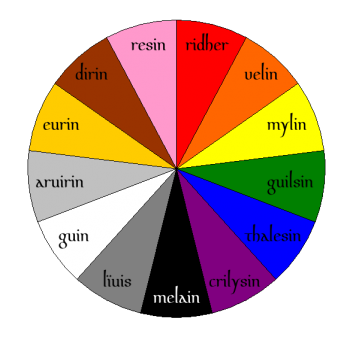
The colour system of Brythohellenic is particular, because, except white, black and red, colours' names derive from flowers or natural elements. Historians have supposed that as the Greeks of Conon reached Great Britain they used natural elements to estabilish a first contact between their languagage and the language of Celtic people. There are also other colour terms that come from Ancient Greek, such as klŵr (= "green"), porhur (= "purple-red"), arwirin (= "silver") or hegin (= "bronze-coloured"), but they are old-fashioned nowadays and they are used almost exclusively in literature.
| Colour terms | ||
|---|---|---|
| Source | Brythohellenic | English |
| μέλαινα (Ancient Greek) | melaen | black |
| κελαινός (Ancient Greek); furvus (Latin) | kelaen; ffwrg | dark, obscure |
| λαμπρός (Ancient Greek) | lemyr | light, pale, fair |
| lividus (Latin), llwyd (Welsh), disliw (Cornish) | liwys | grey |
| gwyn (Welsh), gwynn (Cornish) | gwyn | white |
| φαλακρός (Ancient Greek) x eglur (Welsh) | ffaeglur | bright, lucid |
| rudhvelyn (Cornish), "orange" | felin | orange |
| ἐρυθρός (Ancient Greek), rhudd (Welsh), rudh (Cornish) | ruddyr | red |
| πορφυροῦς (Ancient Greek) | porhur | purple-red |
| gwaed (Welsh), "blood" | gwaedin | burgundy |
| crinllys (Welsh), "violet (flower)" | krilysin | violet, purple |
| ινδικόν (Ancient Greek), "that comes from India" | ynnik | indigo |
| χλωρός (Ancient Greek); gwels (Cornish), "grass" | klŵr; gwylsin | green |
| ebron (Cornish), "sky" | brenin | light blue, cyan |
| θάλασσα (Ancient Greek), "sea" | thalesin | dark blue |
| mêl (Welsh), mel (Cornish), "honey" | mylin | yellow |
| dur (Cornish), "earth" | durin | brown |
| χρυσός (Ancient Greek), "gold"; owr (Cornish), "gold"; | krusin; ŵrin | golden |
| rosen (Cornish), "rose" | resin | pink |
| ἄργυρος (Ancient Greek), "star"; steren (Cornish), "star" | arwirin; ytrin | silver |
| χαλκός (Ancient Greek), "bronze"; efydd (Welsh), "bronze" | helgin; yfyddin | bronze-coloured |
Fruit and vegetables
| Fruit and vegetables | ||
|---|---|---|
| Source | Brythohellenic | English |
| μῆλον (Ancient Greek), "apple" | myl | red apple |
| afal (Welsh), aval (Cornish), "apple" | afal | yellow apple, generic apple |
| κυδωνία (Ancient Greek), "quince" | kudwn | green apple |
| στάλαγμα (Ancient Greek), "drop" | talamadd | grape |
| citreum (Latin), "lemon" | siddyr | lemon |
| χρυσοῦν μῆλον (Ancient Greek), "golden apple" | krumyl | orange |
| هلو (Persian), "peach" | heulf | peach |
| ἐλαία (Ancient Greek), "olive" | eladd | olive |
| لیموترش (Persian), "lemon" | lamewtyr | lime |
| κέρασος (Ancient Greek), "cherry" | seres | cherry |
| ruber (Latin), "bright red" | rywyr | watermelon |
| αγγούριον (Ancient Greek), "cucumber" | onwyr (pl. onwŷr-) | cucumber |
| انجیر (Persian), "fig" | neyar | fig |
| ananas (Tupian or Guaraní) > ananassum (Neolatin), "pineapple" | nanas | pineapple |
| sevien (Cornish), syfien (Welsh), "strawberry" | syfyn | strawberry |
| νύξ (Ancient Greek), "night" + mwyaren (Welsh), "berry" | nithwyrn | blueberry |
| du (Welsh), du (Cornish), "black" + mwyaren (Welsh), "berry" | duwyrn | blackberry |
| tomatl (Nauhatl) > tomatĭlum (Neolatin), "tomato" | tofydd | tomato |
| mahiz (Arawakan) > mahīsum (Neolatin), "maize" | mehys | maize |
| موز (Persian), "banana" | mews | banana |
| زردآلو (Persian), "apricot" | serdel | apricot |
| προυνον (Ancient Greek), "plum" | brwn | plum |
| قهوة (Arabic) > قهوه (Perisan), "coffee" | hewyff | coffee |
| 茶 (Chinese) > چای (Persian), "tea" | sea (pl. seae) | tea |
| xocolatl (Nahuatl) > chocolatĭlum (Neolatin), "chocolate" | segolydd | cacao (beans) |
| باذنجان (Arabic) > بادنجان (Persian), "eggplant" | badynyn | eggplant |
| cucurbĭta (Latin), "courgette" | kurfedd | courgette |