Néekh: Difference between revisions
Jukethatbox (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Jukethatbox (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| name = Néekh | | name = Néekh | ||
| nativename = nêekhr | | nativename = nêekhr | ||
| pronunciation = | | pronunciation = ˈnɛjexr̩ | ||
| familycolor = Sino-Tibetan | | familycolor = Sino-Tibetan | ||
| creator = User:Jukethatbox | | creator = User:Jukethatbox | ||
| created = 2023 | | created = 2023 | ||
| setting = Radael | |||
| fam1 = [[Taskaric languages|Taskaric]] | | fam1 = [[Taskaric languages|Taskaric]] | ||
| fam2 = Iskvic | | fam2 = Iskvic | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
| notice = ipa | | notice = ipa | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Néekh''' (''nêekhr''; <small>Néekh pronunciation:</small> [[Help:IPA|[ | '''Néekh''' (''nêekhr''; <small>Néekh pronunciation:</small> [[Help:IPA|[ˈnɛjexr̩]]]) is a [[Taskaric languages|Taskaric]] language spoken by the Néekhs on [[:File:Etzean.jpeg|Etzeán Island]]. With 4,235,000 native speakers, it is the most spoken language on the island by a narrow margin above [[Etzeá]]; most speakers live in the highly urbanised and economically developed Tûznam Basin(Néekh: ''Tîkhgnul''), where the capital Arkhûz(<small>Néekh pronunciation:</small> [[Help:IPA|[ˈærxʊz̥]]]) is located. It is an official language of the West Birnu Economic Union, and is the second most spoken Taskaric language after [[Izhkut]]. | ||
Néekh is of the Iskvic branch of the Taskaric languages, making it a sister language of [[Iskvish]]; it is the only member of the Iskvic branch that is not endangered. | Néekh is of the Iskvic branch of the Taskaric languages, making it a sister language of [[Iskvish]]; it is the only member of the Iskvic branch that is not endangered. | ||
==Phonology== | ==Phonology== | ||
===Consonants=== | |||
{| class=wikitable style="text-align: center;" | |||
! colspan=2 | !! Labial !! Alveolar !! Retroflex !! Velar !! Palatal | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan=2 | Stop | |||
! voiceless | |||
| '''p''' /p/ || rowspan=2 | '''t, d''' /d̥/ || || '''k''' /k/ || | |||
|- | |||
! voiced | |||
| '''b''' /b/ || || '''g''' /g/ || | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan=2 | Fricative | |||
! voiceless | |||
| '''f''' /f/ || rowspan=2 | '''s, z''' /z̥/ || '''sh''' /ʂ/ || '''kh''' /x/ || | |||
|- | |||
! voiced | |||
| '''v''' /v/ || '''zh''' /ʐ/ || '''gh''' /ɣ/ || | |||
|- | |||
! colspan=2 | Nasal | |||
| '''m''' /m/ || '''n''' /n/ || || '''ng''' /ŋ/ || '''ny''' /ɲ/ | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan=2 | Approximant | |||
! lateral | |||
| || '''l''' /l/ || (ɭ) || '''ll''' /ɫ/ || | |||
|- | |||
! semivowel | |||
| (w) || || || (ɰ) || '''y, gy''' /j/ | |||
|- | |||
! colspan=2 | Trill | |||
| || '''r''' /r/ || || || | |||
|} | |||
/r l m n/ can all be syllabic, usually replacing unstressed /ɐ/, such as ''palabâ'''m''''' [[Help:IPA|[pæˈlæbm̩]]] "[[w:Muscat (grape)|Muscat grape]]", or ''zhollâ'''r''''' [[Help:IPA|[ˈʐoɫr̩]]] "north" | |||
Alveolar obstruents are not affected by voiceness; though often transcribed as devoiced /d̥ z̥/, they may be variably pronounced as /t~d/ and /s~z/ respectively and are ultimately dependent on speaker. | |||
/ɰ/ is an intervocalic allophone of /ɣ/, and has also been described as a vocalised allophone /ɨ/; however, the general consensus is that it is an approximant. | |||
⟨gy⟩ only appears in [[Etzeá]] loanwords, such as '''''gy'''êt'' [[Help:IPA|[ˈjɛd̥]]] "hill" (from Etzeá ''gyed'' "mountain"); between vowels, it is pronounced as a doubled /jj/, such as ''pî'''gy'''ero'' [[Help:IPA|[pɪjˈjero]]] "country hick" (from Etzeá ''pellêro'' "thee") | |||
===Vowels=== | ===Vowels=== | ||
{| class=wikitable style="text-align: center;" | {| class=wikitable style="text-align: center;" | ||
| Line 35: | Line 75: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Close | ! Close | ||
| i || ɪ || u || rowspan=2 | ʊ | | '''i''' /i/ || '''î''' /ɪ/ || '''u''' /u/ || rowspan=2 | '''ô, û''' /ʊ/ | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Mid | ! Mid | ||
| ɛ || e || o | | '''ê''' /ɛ/ || '''e''' /e/ || '''o''' /o/ | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Near-open | ! Near-open | ||
| æ || ɐ || || | | '''a''' /æ/ || '''â''' /ɐ/ || || | ||
|} | |} | ||
Néekh vowels are contrastive by [[w:Tenseness#Vowels|tenseness]], with 5 tense and 4 lax vowels. Lax vowels are usually written with a circumflex, as in ⟨â î | Néekh vowels are contrastive by [[w:Tenseness#Vowels|tenseness]], with 5 tense and 4 lax vowels. Lax vowels are usually written with a circumflex, as in ⟨â î ô û⟩ for /ɐ ɪ ʊ/; ⟨ê⟩ contradictingly represents tense /ɛ/. They also appear non-syllabically at the end of diphthongs, as in ''ghr'''ou'''l'' [[Help:IPA|[ɣroʊ̯l]]]. | ||
[[Category:Néekh]] [[Category:Taskaric languages]] [[Category:Radael]] [[Category:Languages]] [[Category:Conlangs]] | [[Category:Néekh]] [[Category:Taskaric languages]] [[Category:Radael]] [[Category:Languages]] [[Category:Conlangs]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:32, 16 September 2025
This article is a construction site. This project is currently undergoing significant construction and/or revamp. By all means, take a look around, thank you. |
| Néekh | |
|---|---|
| nêekhr | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈnɛjexr̩] |
| Created by | Jukethatbox |
| Date | 2023 |
| Setting | Radael |
| Native to | Etzeán Island |
| Ethnicity | Néekhs |
| Native speakers | 4,235,000 (400 BH) |
Taskaric
| |
Early forms | Proto-Taskaric
|
Dialects |
|
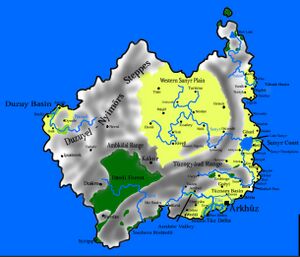 Etzeán Island. Most Néekh speakers live on the eastern side of the island, primarily in the Tûznam Basin. | |
Néekh (nêekhr; Néekh pronunciation: [ˈnɛjexr̩]) is a Taskaric language spoken by the Néekhs on Etzeán Island. With 4,235,000 native speakers, it is the most spoken language on the island by a narrow margin above Etzeá; most speakers live in the highly urbanised and economically developed Tûznam Basin(Néekh: Tîkhgnul), where the capital Arkhûz(Néekh pronunciation: [ˈærxʊz̥]) is located. It is an official language of the West Birnu Economic Union, and is the second most spoken Taskaric language after Izhkut.
Néekh is of the Iskvic branch of the Taskaric languages, making it a sister language of Iskvish; it is the only member of the Iskvic branch that is not endangered.
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Retroflex | Velar | Palatal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | voiceless | p /p/ | t, d /d̥/ | k /k/ | ||
| voiced | b /b/ | g /g/ | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f /f/ | s, z /z̥/ | sh /ʂ/ | kh /x/ | |
| voiced | v /v/ | zh /ʐ/ | gh /ɣ/ | |||
| Nasal | m /m/ | n /n/ | ng /ŋ/ | ny /ɲ/ | ||
| Approximant | lateral | l /l/ | (ɭ) | ll /ɫ/ | ||
| semivowel | (w) | (ɰ) | y, gy /j/ | |||
| Trill | r /r/ | |||||
/r l m n/ can all be syllabic, usually replacing unstressed /ɐ/, such as palabâm [pæˈlæbm̩] "Muscat grape", or zhollâr [ˈʐoɫr̩] "north"
Alveolar obstruents are not affected by voiceness; though often transcribed as devoiced /d̥ z̥/, they may be variably pronounced as /t~d/ and /s~z/ respectively and are ultimately dependent on speaker.
/ɰ/ is an intervocalic allophone of /ɣ/, and has also been described as a vocalised allophone /ɨ/; however, the general consensus is that it is an approximant.
⟨gy⟩ only appears in Etzeá loanwords, such as gyêt [ˈjɛd̥] "hill" (from Etzeá gyed "mountain"); between vowels, it is pronounced as a doubled /jj/, such as pîgyero [pɪjˈjero] "country hick" (from Etzeá pellêro "thee")
Vowels
| Front | Back | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tense | lax | tense | lax | |
| Close | i /i/ | î /ɪ/ | u /u/ | ô, û /ʊ/ |
| Mid | ê /ɛ/ | e /e/ | o /o/ | |
| Near-open | a /æ/ | â /ɐ/ | ||
Néekh vowels are contrastive by tenseness, with 5 tense and 4 lax vowels. Lax vowels are usually written with a circumflex, as in ⟨â î ô û⟩ for /ɐ ɪ ʊ/; ⟨ê⟩ contradictingly represents tense /ɛ/. They also appear non-syllabically at the end of diphthongs, as in ghroul [ɣroʊ̯l].
