Flewtish
This article is private. The author requests that you do not make changes to this project without approval. By all means, please help fix spelling, grammar and organisation problems, thank you. |
This article is a construction site. This project is currently undergoing significant construction and/or revamp. By all means, take a look around, thank you. |
| Flewtish | |
|---|---|
| Flũťa / Флӯтьа | |
 Flag of the Flewtish people. It is a simplified version of an ancient flag. The green represents nature, the white represents peace and the orange represents the joy to be alive. | |
| Pronunciation | [ɸlûːtwa] |
| Created by | Aggelos Tselios |
| Date | 2023 |
| Native to | Russia, Finland |
| Native speakers | approx. 1 million (2023) |
Language Isolate
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Flewtish Autonomous Republic, Russia |
| Regulated by | Instituto Standarzabüro Flutadene Glung (Institute of Standardization of the Flewtish Language) |
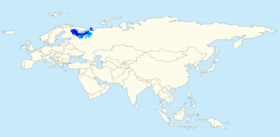 Map of where Flewtish is spoken today. Dark blue areas indicate a majority Flewtish-speaking population, whereas light blue indicate areas where Flewtish is an important language. | |
Flewtish (endonym: Флӯтьа [ɸlûːtʷa] or Флӯтьа глӯн [ɸlûːtʷa ɡluːŋ] ) is a languauge spoken in much of Northwest Russia and the Karelia region, as well as a large pocket in Eastern Finland since 500BC, following the Flewtish migrations westwards. Flewtish is a language isolate, meaning it does not genetically relate to any other known language on the planet, similar to Basque in Europe.
Flewtish is a polysynthetic language, something uncommon for the Siberian or the European languages, hinting a distant Urheimat far away from today's Russia (Usually placed near the Mongolian border, see Proto-Flewtish). The language is split into 4 periods: Proto-Flewtish, Old Flewtish, Ḟlǔṫas Eṽétt (Modern Latin Orthography: Fluṫas Ewet), and Modern Flewtish, each one signified by the historical events accompanying them. It is a biscriptal language, using both the Latin and Cyrillic scripts to be written (In Finland and elsewhere respectively), although during the early medieval period there were Turkic writings too. An important aspect of the language is differentiating between labialized and non-labialized consonants (Referred in Flewtish as "rounded" and "unrounded") see eg. [kʷáɣ.op] "Warmth" and [káɣ.op] "Deer".
While standardized, the language spans over a massive geographical area and as a result, forms a dialect continuum with the most extreme corners (from east Finland to the Ukhta city being completely unintelligible to each other. One example could be the simple sentence "My favorite pets are cats". Following are the two examples in the dialects spoken in Ukhta (Chukwa in Flewtish) and Kvuppeg (Kuumu, a city in Finland), both written using the Latin script for convenience:
- Wo tepō päzćocha enokka mäua [wo ˈtʲepoːa ˈpɘʐʷot͡ʃa ˈenʲoka ˈmɘua] "Me pet favourite is cat"
- Pezoḱōgwo nētepoga nemäja [ˈpezokʷoːɡwo ˈneːtepoga ˈnemɘja] "Favourite-me pets cat"
For this reason, some classify Flewtish as a language family, the common ancestor of which is Proto-Flewtish.
Etymology and history
Flũta is an evolution of Proto-Flewtish *flȳdʰa, meaning "Blooming" or "Saturated". The reason for this name is that the regions that Flewtish speakers settled were far more greener and developed than their previous homeland. Flewtish is possibly a Paleo-siberian language that through migration reached it's current territory. This can be further supported by similarities with the Yeniseian languages, like having a pitch accent, vowel harmony and vowel length distinction.
Following harsh winters in the area and raids from other local tribes, migrations westwards began in search of a better homeland. Eventually, after ~1000 years, Flewtish people decided to settle to modern day Arkhangelsk (Tengwrikutt in Old Flewtish, lit. God's city) and the areas around, where their language would remain. Small pockets of their language that settled in the way during that migration period survived for a few more centuries before being assimilated to neighboring nations.
Flewtish, from it's early years, was influenced by Mongolic, Turkic and later Indo-European and Uralic languages. The most obvious example would be the large amount of Turkic and Finnic loanwords into Flewtish (eg. Кӣлъиту "to converse") but even titles from the states with Flewtish rule such as "Gǎngÿán [ʔgâŋɢán]" (Leader, possibly related to Khagan), "Tãngṽrǐ [ʔtaːŋʷɾiː/" (Same origin as Tengri) and "Tãěrṽágn /ʔtɘɾ.wáŋ/" (Local ruler, related to Tarkhan). On the Indo-European side, the word "оѡыг /ˈówyg/" (Sheep) is probably borrowed from the Proto-Indo-European word *h₂ówis (Or perhaps from Proto-Balto-Slavic) and the word "ғамегь" (milking, from PIE *h₂melǵ-).
Orthography
Flewtish is officially written with the Cyrillic script as law enforces it in Russia. However, up until the Soviet Union's dissolution in 1991, the language was actually written with the Latin script, which was brought over by Viking sailors around the 9th-10th century. The Latin script is used mostly in Finland with the local dialects and by older people elsewhere, but any new speakers are taught to write with the Cyrillic alphabet.
| Cyrillic Script for Flewtish | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Аа /a/ | Бб /b/ | Вв /v/ | Гг /g/ | Ғғ /ɣ/ | Дд /d/ | Ðð /ð/ | Ее /e/ | Зз /z/ | Ии /i/ | Ыы /y/ | Кк /k/ | Лл /l/ | Мм /m/ | Нн /n/ | Оо /o/ | Пп /p/ | Рр /ʁ/ | Тт /t/ | Сс /s/ | Уу /u/ | Фф /ɸ/ | Ьь (ʷ) | Хх /x/ | Цц /t͡s/ | Чч /t͡ʃ/ | Шш /ʃ/ | Ѡѡ /w/ | Ъъ /ʔ/ |
| Latin Script for Flewtish | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aa /a/ | Bb /b/ | Cc /t͡s/ | Dd /d/ | Đð /ð/ | Ää /ɘ/ | Ee /e/ | Ff /f/ | Gg /g/ | Hh /x/ | Ii /i/ | Yy /ɣ/ | Jj /j/ | Kk /k/ | Ll /l/ | Mm /m/ | Nn /n/ | Oo /o/ | Pp /p/ | Rr /ʁ/ | Ss /s/ | Tt /t/ | Uu /u/ | Üü /y/ | Vv /v/ | Ww /w/ | Xx /ʒ/ | Zz /z/ |
Grammar
Pronouns
Flewtish contains the usual three pronouns, with a distinction on the third person pronouns for animate and inanimate objects. Flewtish does not use standalone pronouns often, resorting instead to suffixes on the root verb.
| English | Flewtish |
|---|---|
| I | Гѡо |
| You | Ðи |
| (He or she)/it | У/Шов |
| We | Негѡо |
| You (pl.) | Неши |
| They | Увок(ы) |
Cases
Flewtish has 10 cases, most of which correspond to English prepositions. Depending on the dialect, the number or the actual inflection of the cases may vary significantly (The easternmost dialects spoken in Finland for example preserved the ancient attributive case whereas all other dialects eventually lost it).
| Case | Affix | Example | English Approximation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | (None) | House | - | |
| Genitive | -den | Dõmmaden | Of the house | - |
| Accusative | -n | Dõmman | The house | The accusative is formed when an action is done upon the object. |
| Vocative | -e | (Ē) Dõmmae | (Hey) house! | Dialectal only, conflicts with suffix -e (Similar to English 'the') |
| Adessive | -je | Dõmmaje | At the house | Dialectal only, usually fused with the inessive |
| Inessive | -seg | Dõmmaseg | In the house | Also exists as e-root-sek |
| Ablative | -sce | Dõmmasce | From the house | - |
| Essive | -l | Ēne Dõmmal | As a house | Rare, now usually the Russian borrowing 'как' is used. |
| Translative | -se | Dõmmase | (Transformed) into a house | |
| Instrumental | -om | Dõmmaom | With a house | If it conflicts with the accusative, then it becomes -on |
| Causal-Final | -d | Dommad | For the house | - |
| Comitative | k-, -to | Kodommato | With (the company of) the house | It is often fused with the instrumental. |
Basic Vocabulary
Numbers
| Number | English | Flewtish |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Zero | Нўл |
| 1 | One | Sál/Сал |
| 2 | Two | Āwy/А̄ѡы |
| 3 | Three | Děgn/Денг |
| 4 | Four | Sãx/Саж |
| 5 | Five | Ðōgn/Ðōнг |
| 6 | Six | Káwo/Каѡо |
| 7 | Seven | Evé/Еве |
| 8 | Eight | Xü/Жў |
| 9 | Nine | Nãkk/На̄кк |
| 10 | Ten | Cárposct/Къарпошт |
Sample text
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
English: All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
Flewtish (Latin): Ikeyü emūpkeü uvokü kitewük nesvabodū vem ānnu edostonsvansek vem nejuse. Uvokü bülek snatćenom vem eḿo, vem uvokü velka kiwukütta esalseksald sal sakkŕam ḱongopden.
Flewtish (Cyrillic): Икеғы емӯпкеы увокы китеѡык несвабодӯ вем а̄нну едостонсвансек вем нейусе. Увокы былек сначьеном вем емьо, вем увокы велка киѡукытта есалсексалд сал сакрьам кьонгопден.
IPA: [íkeɣy èmuːpkey úvoky kitewyk nèsvaboduː vém ânu edóstonsvansek vém néjuse || úvoky býlek snat͡ʃenom vém emʷo | vém úvoky vélka kìwukyta esálseksald sál ˈsakrʷam kʷongopden]

