Lortho
| Lortho ['loɾ.tʰo] | |
| Spoken in: | Lortho |
| Conworld: | A circumbinary planet |
| Total Speakers: | Under Development |
| Genealogical classification: | Under Development |
| Basic word order: | Verb-Subject-Object |
| Morphological Type: | Agglutinating |
| Morphosyntactic Alignment: | Nominative-Accusative |
| Created by: | |
| Brian Bourque | March 2017 |
Introduction
Lortho (IPA:[ˈloɾ·tʰo]) is an a priori constructed language created by Brian Bourque in the beginning of 2003. It originally started as a prop for a strategy board game where only the script was created for aesthetics. Fast forward about 13 years and it has now evolved into a agglutinating language with some minor fusional aspects. The verbs are conjugated with suffixes and nouns are modified to denote case.
Inspiration
A friend was creating a board game similar to Risk; however, instead of taking place on Earth, this new game was to take place on an inter-planetary scale. The game creator wanted to develop an extraterrestrial theme and requested a fictional script. The name of the race on this game is "Lortho" and thus the seed was planted. Brian was unable to work on this piece for quite sometime until he joined the CONLANG mailing list and observed both seasoned and novice conlangers discussing all aspects of linguistics. Since then he decided to move forward and bring Lortho into fruition.
Another inspirational source is Brian's daughter. Through her development of learning how to make speech sounds leading to coherent speech, Brian found certain "words" to use in Lortho which he used to develop its phonology.
Setting
| Under Development |
|---|
The people who speak Lortho live on a planetary system which orbits a binary star.
Phonology
Orthography
Writing System
The Lortho alphabet contains 21 letters, one of which is a vowel. The writing system behaves in a similar manner to an abugida; however, there are no conjunct consonants. Ligatures are only formed by the combination of consonants and vowels (other than the vowel [i]). Lortho's script was inspired by the Devanagari, Uchen, and Tengwar writing systems.

|
| Lortho Alphabet |
Vowels
The vowels are written similarly to the vowels seen in Devanagari.

|
| Lortho Vowels |
Sample Text
Below is a sample text with the conscript described above.
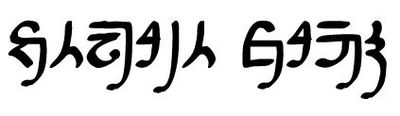
|
| konpharin lorthome I speak Lortho |
Consonant Inventory
There are 20 consonants in Lortho and all are strictly pronounced the same regardless of placement.
| Bilabial | Labiodental | Alveolar | Postalveolar | Velar | Glottal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | p pʰ | b | t tʰ | d dʰ | k kʰ | |||||||
| Nasal | m mː | n nː | ||||||||||
| Tap or Flap | ɾ | |||||||||||
| Fricative | f | s | ʃ | h | ||||||||
| Lateral Approximant | l lʰ | |||||||||||
Vowels and Diphthongs
Vowel Inventory
There are five vowels in Lortho and are strictly pronounced regardless of placement:
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Close-mid | o | ||
| Open-mid | ɛ | ||
| Mid | ɑ |
Diphthongs
The following diphthongs exist in Lortho:
- [aɪ], [aʊ], [eɪ], [ɔɪ]
Syllable Structure
The syllable structure is (C)V(V)(C).
Prosody
Stress
There are a few rules that govern stress (with exceptions):
- Stress is always on the second to the last syllable of the root or infinitive except:
- -n verbs will always receive stress on the last syllable of the infinitive or root.
- If the word is only two syllables long, then the stress is on the first syllable.
- Stress is never given to prefixes or suffixes, except
- Pluralized nouns will move the stress to the second to the last syllable
Intonation
| Under Development |
Phonotactics
Consonant Clusters
Consonant cluster onsets and codas are not allowed; however, clusters are allowed in certain adjacent syllables (e.g. CVC.CVC).
Morphophonology
| Under Development |
|---|
Romanized Text
Since Lortho has its own script, a Romanized version has been set up to make it easy to read and pronounce as shown in the tables below.
| Alphabet | |||||||||||||||||||||
| IPA | dʰ | d | kʰ | k | lʰ | l | tʰ | t | pʰ | p | ʃ | s | n | nː | m | mː | h | b | f | i | ɾ |
| Romanization | dh | d | kh | k | lh | l | th | t | ph | p | sh | s | n | nn | m | mm | h | b | f | i | r |
| Vowels | ||||
| IPA | ɑ | ɛ | u | o |
| Romanization | a | e | u | o |
| Diphthongs | ||||
| IPA | aɪ | aʊ | ɔɪ | eɪ |
| Romanization | ai | au | oi | ei |
Morphology
Nouns
Introduction
Nouns in Lortho have three distinct features:
- They are one of three genders: masculine, feminine, or neuter
- All nouns are modified to denote case
- All nouns end in a vowel
| Masculine | Feminine | Neuter |
|---|---|---|
| -i | -u | -ɑ |
Grammatical Case
Lortho has ten cases. The vowels in parentheses are added if the word ends in a consonant.
| Case | Affix | Example | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | - | kansaptha | woods, forest |
| Accusative | -(i)me | kansapthame | forest (direct obj.) |
| Dative | -(i)mela | kansapthamela | forest (indirect obj.) |
| Genitive | -(i)nalo | kansapthanalo | of the forest |
| Sublative | -ina/-ena | kansaptaina | in/into the forest |
| Ablative | -(e)nat | kansapthanat | out of/from the forest |
| Allative | -(e)dan | kansapthadan | to/towards the forest |
| Prolative | -(e)danar | kansapthadanar | through/via/by way of the forest |
| Instructive | -(i)len | kansapthalen | using the forest |
| Vocative | fa- | Under Development | |
Personal Possessive Prefix
The personal possessive is formed using a prefix which is gender and number specific.
| Person | Singular | Plural | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person | ni- | nu- | - | nima- | numa- | - |
| 2nd person | lin- | lun- | - | nani- | nanu- | - |
| 3rd person | li- | lu- | la- | limi- | limu- | lima- |
Pluralization
Each noun is pluralized by adding a suffix:
- Feminine nouns (-u): simply add the plural ending -ne.
- Example: kansaphu (n. fem) tree; pl kansaphune
- Masculine nouns (-i): subtract the -i and add the plural ending -eni except :
- Masculine noun roots that end in -n, the plural ending will be changed to -emi.
- Examples:
- olakhi (n. masc) boat; pl olakheni
- phorenni (n. masc) peak, summit; pl phoɾennemi
- Neuter nouns (-a): simply add the plural ending -ne (many neuter nouns are collective nouns such as hammuna weather)
- Example: hadikha (n. neut) land, country; pl hadikhane
Verbs
Introduction
Verbs are conjugated in gender and in number which are governed by the subject (written or implied). For the most part the conjugations are simple and are formed through agglutination; however, there are slight fusional changes that occur when denoting aspect.
Conjugation
Regular Verbs
There are three main verbs in Lortho: -o verbs, -t verbs, and -n verbs. The conjugation tables below show a preview of how the regular verbs conjugate in each category. Conjugation in other tenses includes more fusional aspects.
-o verbs
| Present Tense | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| konpharo [kon.'pʰɑ.ɾo] to speak verbal root: konphar- | ||||||
| Singular | Plural | |||||
| masc | fem | neut | masc | fem | neut | |
| 1st pers | konpharin | un | - | -inan | -unan | - |
| 2nd pers | konpharanni | -annu | - | -amin | -amun | - |
| 3rd pers | konphari | -u | -a | -imi | -imu | -ima |
-t verbs
| Present Tense | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phramit ['pʰɾɑ.mit] to push verbal root: phramid- | ||||||
| Singular | Plural | |||||
| masc | fem | neut | masc | fem | neut | |
| 1st pers | pramidin | -un | - | -inan | -unan | - |
| 2nd pers | phramidanni | -annu | - | -amin | -amun | - |
| 3rd pers | phramidi | -u | -a | -imi | -imu | -ima |
-n verbs
| Present Tense | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shailan [ʃaɪ.'lɑn] to sit verbal root: shailan- | ||||||
| Singular | Plural | |||||
| masc | fem | neut | masc | fem | neut | |
| 1st pers | shailanin | -un | - | -inan | -unan | - |
| 2nd pers | shailananni | -annu | - | -amin | -amun | - |
| 3rd pers | shailani | -u | -a | -imi | -imu | -ima |
Irregular Verbs
Although labelled irregular, the verbs still have a regular feel in that they still use the same personal endings; however, the root is derived slightly differently. One example is the verb harlan.
| Present Tense | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| harlan [hɑɾ.'lɑn] to be verbal root: harl- | ||||||
| Singular | Plural | |||||
| masc | fem | neut | masc | fem | neut | |
| 1st pers | harlin | un | - | -inan | -unan | - |
| 2nd pers | harlanni | -annu | - | -amin | -amun | - |
| 3rd pers | harli | -u | -a | -imi | -imu | -ima |
Adjectives
Adjectives behave a little differently from other words in that they:
- must be placed in front of the noun which they modify
- must agree in gender, but not in number or grammatical case
Syntax
Morphosyntactic Alignment
The morphosyntactic alignment of Lortho is Nominative - Accusative.
Word Order
Verb-Subject-Object (VSO). Lortho contains a lot of information in the verb and the noun or noun phrase. The verb is conjugated by person and gender and thus pronouns are largely unnecessary except for emphasis or clarification. The nouns are altered to denote case, removing almost entirely the need for prepositions.
Example texts

| |
| Text | Translation |
| kalanune denimanimu kalanune khonaminalo hana tomidikhimu ma kansapthaina |
The people are known as people of the lanterns and they lived in that forest. |

| |
| Text | Translation |
| lharidikhin kansapthanat hana tharnidikhin dharakhime. konpharinin toshanimela hana semanikhin, "hankhanin malhiro danadanar." remedikhi toshani, "dhamalhirianni danadanar." |
I ran out of the forest and climbed the mountain. I was speaking to the dragon and said, "I want to walk through here." The dragon replied, "You will not walk through here." |
| Source: Brian's Instagram post | |
Additional Information
Word Agreement
The three following rules govern agreement between words:
- Verbs must agree in gender and number with the subject (explicit or implied)
- Nouns are not pluralized when counted (e.g. there are trees vs there are two tree)
- Adjectives must agree with the noun which they modify in gender, but not in grammatical case or number
Resources
Linguistics
Endangered Alphabets - YouTube channel about 14 of the world's writing systems threatened with extinction
International Phonetic Alphabet
Glossika Phonics - YouTube channel for IPA pronunciation
NativLang - YouTube channel about the history of written and spoken language
Omniglot
Online Etymology Dictionary (English)
Reddit: Linguistics
Wikitongues - A not for profit YouTube project to help preserve the world's living languages
World Atlas of Language Structures (WALS)
Constructed Languages
Conlang Atlas of Language Structures (CALS)
Conlang Bulletin Board (CBB)
Conlang Critic - A YouTube vlogger who offers insight on conlangs
Conlang Mailing List
Conlang Relay Museum on CALS
ConWorkShop - an online one-stop-shop for cataloging your conlang
Language Creation Society (LCS)
LCS on YouTube
Reddit: Conlangs
Reddit: Neography (Constructed Scripts)
Speculative Grammarian - A satirical periodical on linguistics and conlangery
Zompist Bulletin Board (ZBB)
Lortho
Lortho on CALS
Lortho on ConWorkShop
Lortho on FrathWiki
Miscellaneous
Sajem Tan (Common Honey) Collaborative Conlang Discord Server