Template:Front/featured: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox language | |||
|image = Lutho-Ravennese Flag.png | |||
|imagesize = 185px | |||
|imagecaption = Flag of the Luthic-speaking Ravenna | |||
|name = Luthic | |||
|nativename = Lûthica | |||
|pronunciation = ˈlu.ti.xɐ | |||
|pronunciation_key = IPA for Luthic | |||
|states = [[w:Ravenna|Ravenna]]; [[w:Ferrara|Ferrara]] and [[w:Bologna|Bologna]] | |||
|setting = Alternative history [[w:Italy|Italy]] | |||
|region = [[w: Southern Europe|Southern Europe]] | |||
|speakers = 149,500 | |||
|date = 2020 | |||
|created = 2023 | |||
|familycolor = Indo-European | |||
|fam2 = [[w:Italic languages|Italic]] | |||
|fam3 = [[w:Latino-Faliscan languages|Latino-Faliscan]] | |||
|fam4 = [[w:Italo-Western languages|Italo-Western]] | |||
|fam5 = Gotho-Romance | |||
|fam6 = Italo-Luthian Romance | |||
|creator = User:Lëtzelúcia | |||
|dia1 = Upper Luthic (''Altalûthica''), Ferraresi Luthic (''Lûthica Estense'') | |||
|dia2 = Standard Bolognese Luthic (''Lûthica Bolognesa'') | |||
|dia3 = Paulistan Luthic (''Lûthica Paülista'') | |||
|stand1 = Standard Ravennese Luthic (''Lûthica'') | |||
|script1 = Latn | |||
|script2 = Brai | |||
|minority = [[w:Italy|Italy]] (recognised by the Luthic Community of Ravenna) <br >[[w:Brazil|Brazil]] (recognised in [[w:São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]]) | |||
|agency = Council for the Luthic Language | |||
|map = Spoken_Luthic_status.png | |||
|mapsize = 280px | |||
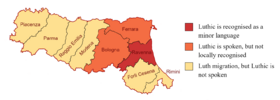
|mapcaption = The areas where Luthic (red and orange) is spoken. | |||
|notice = IPA | |||
|ethnicity = Luths | |||
|ancestor = Proto-Luthic | |||
|ancestor2 = Gothic Luthic | |||
|ancestor3 = Mediaeval Luthic | |||
|ancestor4 = Late Mediaeval Luthic | |||
| clcr = qlu | |||
| brcl = luth | |||
}} | |||
[[Luthic]] ([[w:Help:IPA|/ˈluːθ.ɪk/]] [[w:Help:Pronunciation respelling key|''LOOTH-ik'']]; [[w:Endonym|endonym]]: ''Lûthica'' [[IPA for Luthic#Standard_Ravennese_Luthic|[ˈlu.ti.xɐ]]]) is an [[w:Italic languages|Italic language]] that is spoken by the Luths, with strong [[w:East Germanic languages|East Germanic]] influence. Unlike other [[w:Romance languages|Romance languages]], such as [[w:Portuguese language|Portuguese]], [[w:Spanish language|Spanish]], [[w:Catalan language|Catalan]], [[w:Occitan language|Occitan]] and [[w:French language|French]], Luthic has a large inherited vocabulary from [[w:East Germanic languages|East Germanic]], instead of only proper names that survived in historical accounts, and [[w:Loanword|loanwords]]. About 250,000 people speak Luthic worldwide. | |||
Luthic is the result of a prolonged contact among members of both regions after the [[w:Goths|Gothic raids]] towards the [[w:Roman Empire|Roman Empire]] began, together with the later [[w:Germanic peoples|West Germanic]] merchants’ travels to and from the [[w:Western Roman Empire|Western Roman Empire]]. These connections, the interactions between the [[w:Papal States|Papal States]] and the conquest by the Germanic dynasties of the Roman Empire slowly formed a [[w:Creole language|creole]] as a [[w:Lingua franca|''lingua franca'']] for mutual communication. | |||
As a standard form of the Gotho-Romance language, Luthic has similarities with other [[w:Italo-Dalmatian languages|Italo-Dalmatian languages]], [[w:Western Romance languages|Western Romance languages]] and [[w:Sardinian language|Sardinian]]. The status of Luthic as the regional language of Ravenna and the existence there of a regulatory body have removed Luthic, at least in part, from the domain of [[w:Italian language|Standard Italian]], its traditional [[w:Abstand_and_ausbau_languages#Roofing|''Dachsprache'']]. It is also related to the [[w:Florentine dialect|Florentine dialect]] spoken by the [[w:Italians|Italians]] in the Italian city of [[w:Florence|Florence]] and its immediate surroundings. | |||
Luthic is an [[w:Inflection|inflected]] [[w:Fusional language|fusional language]], with four [[w:Grammatical case|cases]] for nouns, pronouns, and adjectives (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative); three [[w:Grammatical genders|genders]] (masculine, feminine, neuter); and two [[w:Grammatical number|numbers]] (singular, plural). | |||
<noinclude>[[Category:Templates]][[Category:Main page]][[Category:Meta]]</noinclude> | <noinclude>[[Category:Templates]][[Category:Main page]][[Category:Meta]]</noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 22:31, 12 January 2025
| Luthic | |
|---|---|
| Lûthica | |
 Flag of the Luthic-speaking Ravenna | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈlu.ti.xɐ] |
| Created by | Lëtzelúcia |
| Date | 2023 |
| Setting | Alternative history Italy |
| Native to | Ravenna; Ferrara and Bologna |
| Ethnicity | Luths |
| Native speakers | 149,500 (2020) |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | Proto-Luthic
|
Standard form | Standard Ravennese Luthic (Lûthica)
|
Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Council for the Luthic Language |
| Language codes | |
| CLCR | qlu |
| BRCL | luth |
The areas where Luthic (red and orange) is spoken. | |
Luthic (/ˈluːθ.ɪk/ LOOTH-ik; endonym: Lûthica [ˈlu.ti.xɐ]) is an Italic language that is spoken by the Luths, with strong East Germanic influence. Unlike other Romance languages, such as Portuguese, Spanish, Catalan, Occitan and French, Luthic has a large inherited vocabulary from East Germanic, instead of only proper names that survived in historical accounts, and loanwords. About 250,000 people speak Luthic worldwide.
Luthic is the result of a prolonged contact among members of both regions after the Gothic raids towards the Roman Empire began, together with the later West Germanic merchants’ travels to and from the Western Roman Empire. These connections, the interactions between the Papal States and the conquest by the Germanic dynasties of the Roman Empire slowly formed a creole as a lingua franca for mutual communication.
As a standard form of the Gotho-Romance language, Luthic has similarities with other Italo-Dalmatian languages, Western Romance languages and Sardinian. The status of Luthic as the regional language of Ravenna and the existence there of a regulatory body have removed Luthic, at least in part, from the domain of Standard Italian, its traditional Dachsprache. It is also related to the Florentine dialect spoken by the Italians in the Italian city of Florence and its immediate surroundings.
Luthic is an inflected fusional language, with four cases for nouns, pronouns, and adjectives (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative); three genders (masculine, feminine, neuter); and two numbers (singular, plural).