Weddish: Difference between revisions
m (→Abstract Nouns: .) |
m (tweaks) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|posteriori = Yiddish | |posteriori = Yiddish | ||
|script = [[w:Hebrew script|Hebrew]] | |script = [[w:Hebrew script|Hebrew]] | ||
|image = Weddish tree.jpg | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Weddish''' (''Weddish'': '''װעדיש''', ''X"Q'': '''וֶדִש''', ''Romanization'': '''Vediš''') is a constructed, ''a posteriori'', naturalistic [[auxlang]], made from Yiddish with heavy influences from Hebrew, English, German, and | '''Weddish''' (''Weddish'': '''װעדיש''', ''X"Q'': '''וֶדִש''', ''Romanization'': '''Vediš''') is a constructed, ''a posteriori'', naturalistic [[auxlang]], made from Yiddish with heavy influences from Hebrew, English, German, and Basque ideas. It has ergative-absolutive [[Linguistics:Morphosyntactic alignment|morphosyntactic alignment]] and a pervasive yet symbolic use of the dual. It is meant to promote the institution of marriage, foster better communication between persons, and improve the constructs of Systematic Theological discussions. It is well-suited as an auxlang for Jewish intermarriage. | ||
The language was created in 2013 by [[User:aquatiki|Robert Murphy]] as part of an assignment at [[w:Covenant Theological Seminary|Covenant Theological Seminary]] for Professor Jerram Barrs. | The language was created in 2013 by [[User:aquatiki|Robert Murphy]] as part of an assignment at [[w:Covenant Theological Seminary|Covenant Theological Seminary]] for Professor Jerram Barrs. | ||
== Philosophy == | == Philosophy == | ||
First and foremost, there is the [[w:Monism#Creator-creature_distinction|Creator-Creature distinction]]. That means, God is wholly other than the Universe. Second, human beings are made in the [[w:Image of God|image of God]]. This means that we are persons -- like God is -- and our ''agency'' is our single-most important feature. Third, we reflect the image of God as females ''''' | First and foremost, there is the [[w:Monism#Creator-creature_distinction|Creator-Creature distinction]]. That means, God is wholly other than the Universe. Second, human beings are made in the [[w:Image of God|image of God]]. This means that we are persons -- like God is -- and our ''agency'' is our single-most important feature. Third, we reflect the image of God as females '''''or''''' males. The marriage bond is God-created and a fundamental part of our identity in this life. Hence it is, that we may divide the world into: actors, non-actors, and actions. Stated grammatically, this list becomes: ergative nouns, absolutive nouns, and verbs. Furthermore, ergative nouns may be divided up into married and non-married actors, which we will mark with the ''dual'' or not. | ||
We have said that ontologically speaking, there are ultimately only | We have said that ontologically speaking, there are ultimately only Two (God and not-God). However, the 800lb. gorilla in the room -- philosophically speaking -- is [[w:Abstraction|abstraction]]. Since before [[w:Pythagoras|Pythagoras]], abstract nouns (such as numbers, "goodness", etc.) had been held by the Greeks to be [[w:Ontology|ontic]]. Westerners betray their affinity to Greek ideals, classifying humanity as ''homo sapiens'' - "thinking man". We seek to disenthrall ourselves from this metaphysic and therefore ''banish'' abstract nouns from our language. Numerals are adjectives. Infinity is that which we cannot see the end of. Universals are the same as aggregates ("all" is the same as "sum" ... but not "some"!). | ||
The [[w:Language Creation Society|Language Creation Society]] ( | The [[w:Language Creation Society|Language Creation Society]] (an excellent institution) waves the flag of the [[w:Tower of Babel|Tower of Babel]]. Unlike the hubristic men of the initial chapters ''In the Land of Invented Languages'' ([[w:Arika Okrent|Arika Okrent]]'s chronicle), we do not believe we can undo what God has done to human speech by intellectual rigor. Our aim is for Jews and Christians to discuss the truth in ''better'' terms. The status of English as a ''lingua franca'', German as a language of science, and Hebrew as a holy language suggests that an Indo-European language is still the best option for an ''a posteriori'' auxlang, but with Semitic components. Rather than compete with those vital languages, however, it seems most prudent to build upon a base of all at once, utilizing a language that is already as eclectic as English, similar to German, and informed by Hebrew. That language is Yiddish. Basque serves as an inspiration for new categories and "outside the box" thinking. | ||
== Phonology == | == Phonology == | ||
Weddish has 25 consonantal sounds, which is typologically average <ref>http://wals.info/chapter/1</ref>, and common in Europe as well as the Middle East. English speakers will find it to be common, apart from the lack of <tt>/w/</tt> and the abundance of <tt>/x/</tt> (like the ''ch'' in ''Bach'' or ''loch''). Weddish has 6 vowels, which is also average<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/2</ref>, as is the resulting consonant-to-vowel ration<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/3</ref>. This is typologically equivalent to Yiddish and Hebrew, but far less than German or English. | Weddish has 25 consonantal sounds, which is typologically average <ref>http://wals.info/chapter/1</ref>, and common in Europe as well as the Middle East. English speakers will find it to be common, apart from the lack of <tt>/w/</tt> and the abundance of <tt>/x/</tt> (like the ''ch'' in ''Bach'' or ''loch''). Weddish has 6 vowels, which is also average<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/2</ref>, as is the resulting consonant-to-vowel ration<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/3</ref>. This is typologically equivalent to Yiddish and Hebrew, but far less than German or English. | ||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} style="float:left;" | {| {{Table/bluetable}} style="float:left; font-size:large;" | ||
|+ '''Consonants of Weddish''' | |+ '''Consonants of Weddish''' | ||
! colspan="9"|Consonant phonemes | ! colspan="9"|Consonant phonemes | ||
| Line 101: | Line 102: | ||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} style="margin-left:10px; float: right;" | {| {{Table/bluetable}} style="margin-left:10px; float: right; font-size:large;" | ||
|+ '''Vowel phonemes in Weddish''' | |+ '''Vowel phonemes in Weddish''' | ||
! | ! | ||
| Line 116: | Line 117: | ||
! Mid | ! Mid | ||
| '''ע''' <tt>/e/~/ɛ/</tt> | | '''ע''' <tt>/e/~/ɛ/</tt> | ||
| <tt>/ə/</tt> | | ''' ׳ ''' <tt>/ə/</tt> | ||
| ''' | | '''ﭏ''' <tt>/o/~/ɔ/</tt> | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Low | ! Low | ||
| | | | ||
| ''' | | '''א''' <tt>/ɐ/~/ä/</tt> | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 133: | Line 134: | ||
! a | ! a | ||
| '''ײַ''' = ay | | '''ײַ''' = ay | ||
| '''אַו''' = aw | | <small>'' '''אַו''' = aw'' *</small> | ||
|- | |- | ||
! e | ! e | ||
| Line 141: | Line 142: | ||
! o | ! o | ||
| '''ױ''' = oy | | '''ױ''' = oy | ||
| '''אָו''' = ow | | <small> '' '''אָו''' = ow'' * </small> | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br clear="both" /> | <br clear="both" /> | ||
Voicing is contrastive in both plosives and fricatives, like Yiddish and English<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/4</ref>. Vowel nasalization and rounding are not phonemic<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/11</ref>. | |||
There are several issues in the pronunciation of individual sounds. The rhotic of Weddish is either alveolar or uvular<ref>As in Hebrew, uvular may be seen as the most prestigious form: http://wals.info/chapter/6</ref> and may be anything from a fricative, to a flap, to a trill, to an approximant. No R-colors vowels are permitted. Words that begin with a vowel are separated from a prior open syllable by a glottal stop. The velar nasal only occurs when an "n" is assimilated in place of articular before or after an "x", "k", or "g", in a syllable coda<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/9</ref>. '''ng''' is pronounced <tt>/ŋg/</tt>, not just <tt>/ŋ/</tt>. '''L''' is typically dark (aka "velarized") except before '''i'''. '''Ayen''' is always romanized '''e''', but signifies the schwa in unaccented syllables. | There are several issues in the pronunciation of individual sounds. The rhotic of Weddish is either alveolar or uvular<ref>As in Hebrew, uvular may be seen as the most prestigious form: http://wals.info/chapter/6</ref> and may be anything from a fricative, to a flap, to a trill, to an approximant. No R-colors vowels are permitted. Words that begin with a vowel are separated from a prior open syllable by a glottal stop. The velar nasal only occurs when an "n" is assimilated in place of articular before or after an "x", "k", or "g", in a syllable coda<ref>http://wals.info/chapter/9</ref>. '''ng''' is pronounced <tt>/ŋg/</tt>, not just <tt>/ŋ/</tt>. '''L''' is typically dark (aka "velarized") except before '''i'''. '''Ayen''' is always romanized '''e''', but signifies the schwa in unaccented syllables. | ||
In the dialect of the Americas, central vowels retain a color of their original/short form. Elsewhere, they are all central, except <tt>/a/</tt> before glottals and <tt>/ɪ/</tt> before labials. Another dialect difference is that '''c''' and '''dž''' are sometimes pronounced <tt>/θ/</tt> and <tt>/ð/</tt><ref>http://wals.info/chapter/19</ref>. However, the rhotic is still not retroflex! | In the dialect of the Americas, central vowels retain a color of their original/short form. Elsewhere, they are all central, except <tt>/a/</tt> before glottals and <tt>/ɪ/</tt> before labials. Another dialect difference is that '''c''' and '''dž''' are sometimes pronounced <tt>/θ/</tt> and <tt>/ð/</tt><ref>http://wals.info/chapter/19</ref>. However, the rhotic is still not retroflex! Americans also pronounce '''aw''' and '''ow''' as diphthongs, which is completely understandable. | ||
=== Orthography === | === Orthography === | ||
Weddish written in the Hebrew alphabet, following the standard of YIVO Yiddish. There is a one-to-one correspondence between grapheme and phoneme, except for three digraphs and one trigraph. Weddish also has its own Romanization scheme, largely Slavic in appearance. In it, <tt>/ʃ/</tt> is written '''š''', <tt>/ʒ/</tt> is written '''ž''', <tt>/j/</tt> is written '''y''', <tt>/ts/</tt> is written '''c''', <tt>/tʃ/</tt> is written '''č''', <tt>/dʒ/</tt> is written '''dž''', and <tt>/ʁ/</tt> is written '''r'''. | Weddish written in the Hebrew alphabet, mostly following the standard of YIVO Yiddish. '''A''' and '''O''' are handled differently, as is the šva. There is a one-to-one correspondence between grapheme and phoneme, except for three digraphs and one trigraph. Weddish also has its own Romanization scheme, largely Slavic in appearance. In it, <tt>/ʃ/</tt> is written '''š''', <tt>/ʒ/</tt> is written '''ž''', <tt>/j/</tt> is written '''y''', <tt>/ts/</tt> is written '''c''', <tt>/tʃ/</tt> is written '''č''', <tt>/dʒ/</tt> is written '''dž''', and <tt>/ʁ/</tt> is written '''r'''. | ||
If the syllable after a diphthong begins with a vowel, the off-glide of the diphthong is doubled as the onset of that next syllable, '''''without being written again'''''. Thus '''zeyer''' is pronounced <tt>/zey.yer/</tt>. | If the syllable after a diphthong begins with a vowel, the off-glide of the diphthong is doubled as the onset of that next syllable, '''''without being written again'''''. Thus '''zeyer''' is pronounced <tt>/zey.yer/</tt>. | ||
As in Hebrew, five letters have "final" forms, when they occur at the end of a word. These forms do not affect pronunciation at all. | As in Hebrew, five letters have "final" forms, when they occur at the end of a word. These forms do not affect pronunciation at all. | ||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} | {| {{Table/bluetable}} style="font-size:large;" | ||
! Initial/Medial | ! Initial/Medial | ||
| '''מ''' | | '''מ''' | ||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Alphabetical order is ''' | Alphabetical order is ('''gereš''',) '''alef''', '''alefol''', '''beys''', ('''veys''',) '''giml''', '''dalet''', '''dalet''', '''hey''', '''vov''', '''gvováyin''', '''šurek''', '''zayen''', ('''xes''',) '''tes''', '''yud''', '''yud xirik''', '''gyudayin''', '''gyudayin pasex''', '''vov yud''', '''xof''', ('''xof dageš''',) '''lamed''', '''mem''', '''nun''', '''samex''', '''ayen''', '''pey''', '''fey''', '''cadek''', '''kuf''', '''reyš''', ('''sin''',) '''šin''' (, '''tav''', '''sav'''). | ||
When necessary to avoid confusion, <tt>/u/</tt> can be precisely specified with a '''וּ''', called a '''šurek'''. <tt>/i/</tt> can be invoked as '''יִ''', that is a '''yud xirek'''. | When necessary to avoid confusion, <tt>/u/</tt> can be precisely specified with a '''וּ''', called a '''šurek'''. <tt>/i/</tt> can be invoked as '''יִ''', that is a '''yud xirek'''. | ||
==== Others ==== | ==== Others ==== | ||
Yiddish has many loanwords from Hebrew and Aramaic which are written using the Hebrew abjad in the Semitic way. Weddish, however, writes these words out according to its own orthographic conventions. There are times when it is necessary to use the ancient letters, especially in religious settings. | Yiddish has many loanwords from Hebrew and Aramaic which are written using the Hebrew abjad in the Semitic way. Weddish, however, writes these words out according to its own orthographic conventions. There are times when it is necessary to use the ancient letters, especially in religious settings. | ||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} | {| {{Table/bluetable}} style="font-size:large;" | ||
! Lošn Koydeš Letter | ! Lošn Koydeš Letter | ||
| '''בֿ''' | | '''בֿ''' | ||
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
There is also a highly ornate style of writing Weddish, called '''xtiv qoydeš''' ("holy writing", abbr. x"q) where letters are used not as an alphabet, but as an abjad. Vowels may or may not be written in this style. When written, they are written as diacritical marks ("points") around the consonants. In this style, '''v''' is written as '''ו''' and '''y''' as '''י'''. Vowels are as follows, with the '''א''' written in syllables with no onset: | There is also a highly ornate style of writing Weddish, called '''xtiv qoydeš''' ("holy writing", abbr. x"q) where letters are used not as an alphabet, but as an abjad. Vowels may or may not be written in this style. When written, they are written as diacritical marks ("points") around the consonants. In this style, '''v''' is written as '''ו''' and '''y''' as '''י'''. Vowels are as follows, with the '''א''' written in syllables with no onset: | ||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} | {| {{Table/bluetable}} style="font-size:large;" | ||
! Standard | ! Standard | ||
! X"Q | ! X"Q | ||
| Line 206: | Line 206: | ||
| '''a''' | | '''a''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ''' | | '''ﭏ''' | ||
| '''אָ''' | | '''אָ''' | ||
| '''o''' | | '''o''' | ||
| Line 227: | Line 227: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''ײַ''' | | '''ײַ''' | ||
| ''' | | '''אַי''' | ||
| '''ay''' | | '''ay''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 235: | Line 235: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''אָו''' | | '''אָו''' | ||
| ''' | | '''אָי''' | ||
| '''ow''' | | '''ow''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''אַו''' | | '''אַו''' | ||
| ''' | | '''אַו''' | ||
| '''aw''' | | '''aw''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 474: | Line 474: | ||
|order = SVO | |order = SVO | ||
}} | }} | ||
Weddish aims to appeal to English speakers. While the verbal-system is somewhat new, the noun-system should be easy. Nouns are not inflected, but pronouns have unique forms that show part of speech. Like German, articles inflect. | Weddish aims to appeal to English speakers. While the verbal-system is somewhat new, the noun-system should be easy. Nouns are not inflected, but pronouns have unique forms that show part of speech. Like German, articles inflect, not the noun. Weddish (like English) only has gender on the independent third person personal pronouns. Otherwise there are just noun classes, a system taken from Basque. People, animals, and things that can move on their own are "animate", while plants and other objects are "inanimate". Adjectives do not inflect unless substantive, and there are not many adjectives. Most descriptors are intransitive verbs. | ||
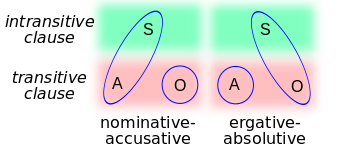
[[File:MorphSyntAlign2.png|left]]Weddish has an ergative-absolutive morphosyntactic alignment. This was purposefully chosen to stimulate thinking, and done in imitation of Basque. Most languages in the world treat the actor of transitive verb and the subject of an intransitive verb in the same way. The object of a transitive verb is special in these systems. It can be promoted to the subject via the passive voice. Normally, it must come after the verb. Weddish treats the ''object'' of a transitive verb and the subject of a transitive verb the same, called the "absolutive case". Actors of transitive verbs are specially, called the "ergative case". This is the special case in Weddish. It must come before the verb and can be demoted by the anti-passive voice. | [[File:MorphSyntAlign2.png|left]]Weddish has an ergative-absolutive morphosyntactic alignment. This was purposefully chosen to stimulate thinking, and done in imitation of Basque. Most languages in the world treat the actor of transitive verb and the subject of an intransitive verb in the same way. The object of a transitive verb is special in these systems. It can be promoted to the subject via the passive voice. Normally, it must come after the verb. Weddish treats the ''object'' of a transitive verb and the subject of a transitive verb the same, called the "absolutive case". Actors of transitive verbs are specially, called the "ergative case". This is the special case in Weddish. It must come before the verb and can be demoted by the anti-passive voice. | ||
| Line 480: | Line 480: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
It would be tempting to classify Weddish as VSO (subject-veb-object) like Hebrew, but that's not quite right. It is, in fact, a V2 language, which means the verb always wants to come second. (Discourse particles and few other things do not count towards calculating where "second" is, and entire phrases are taken as a whole when counting this place.) Because core cases are marked almost solely by word order, the actor of a transitive verb (the ergative case) must come before the verb, i.e. first in the sentence. | It would be tempting to classify Weddish as VSO (subject-veb-object) like Hebrew, but that's not quite right. It is, in fact, a V2 language, which means the verb always wants to come second. (Discourse particles and few other things do not count towards calculating where "second" is, and entire phrases are taken as a whole when counting this place.) Because core cases are marked almost solely by word order, the actor of a transitive verb (the ergative case) must come before the verb, i.e. first in the sentence. It could also be said that intransitive sentences are VSO and transitive ones are SVO. | ||
The V2 Principle is carried throughout Weddish, to the point where it might be labeled a "head second" language. This is not a recognized typology, since languages are either head-initial, head-final, or mixed. In compound nouns, the head is second. For auxiliary verbs, the head verb is second. For nouns with attributive modifiers, the article comes first, but adjectives come after the noun, making it head-second as well. | The V2 Principle is carried throughout Weddish, to the point where it might be labeled a "head second" language. This is not a recognized typology, since languages are either head-initial, head-final, or mixed. In compound nouns, the head is second. For auxiliary verbs, the head verb is second. For nouns with attributive modifiers, the article comes first, but adjectives come after the noun, making it head-second as well. | ||
| Line 507: | Line 507: | ||
|} | |} | ||
By default, all nouns are in the ''absolutive'' case. But, if they are placed '''''before''''' the verb, then they are said to be in the ergative case, though their morphology is unchanged. Linguists call these two case the "core cases" of a language, since they are fundamental. There are five additional cases --- called "non-core" cases --- | By default, all nouns are in the ''absolutive'' case. But, if they are placed '''''before''''' the verb, then they are said to be in the ergative case, though their morphology is unchanged. Linguists call these two case the "core cases" of a language, since they are fundamental. There are five additional cases --- called "non-core" cases --- that are also very important. Unlike many languages that have ''suffixing'' case marking, Weddish has ''prefixing''. This is because they are derived from Hebrew Inseparable Prepositions. Phrases in the non-core cases either relate to the verb (and are hence, adverbial), or are in a noun phrase. In relation to nouns, the core cases are all seen as greater specificity ''within'' the genitive case. | ||
Non-core cases all fall under the umbrella term "genitive". The generic genitive is not a case ''per se'', but a preposition (meaning, a separable preposition). An expression like ''' | Non-core cases all fall under the umbrella term "genitive". The generic genitive is not a case ''per se'', but a preposition (meaning, a separable preposition). An expression like '''די לינע פֿונ געלט/di line fun gelt'''/''the love of money'' is even more ambiguous in Weddish than in English. It may mean ''the love [belonging] to money'', ''the love in/by money'', ''the love from/composed of money'', or ''the love as/according to money''. After a genitive phrase has been established or is implicitly understood, the phrase may incorporated be into a compound noun using the "head-second" structure. | ||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} | {| {{Table/bluetable}} | ||
|+ '''Case, Articles, and IP's''' | |+ '''Case, Articles, and IP's''' | ||
| Line 591: | Line 591: | ||
| '''געפֿרײַנדינז''' <br /> '''gefrayndinz''' <br /> ''a group of friends and associates'' | | '''געפֿרײַנדינז''' <br /> '''gefrayndinz''' <br /> ''a group of friends and associates'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
There are a plethora of paradigms for the distributive plural formations, 99% of which time come straight from the Yiddish plural. | |||
The dual ending is unique, in that is shifts the accent pattern of the root to itself. It may be written '''-áyim''' to indicate that shift. This shift triggers vowel reduction of of the previous syllable, if it is a diphthong (cutting it down to its first vowel). | The dual ending is unique, in that is shifts the accent pattern of the root to itself. It may be written '''-áyim''' to indicate that shift. This shift triggers vowel reduction of of the previous syllable, if it is a diphthong (cutting it down to its first vowel). | ||
| Line 768: | Line 770: | ||
=== Verbs === | === Verbs === | ||
Weddish verbs | Weddish verbs conjugate first for aspect, then use auxiliaries for tense and mood. | ||
==== Aspect Ablaut ==== | ==== Aspect Ablaut ==== | ||
Aspect is specified by changing the theme vowel of the verb. The right vowel may not be part of a compound, prefix, or suffix. As with nounal plurals, these changes fall into patterns, but are somewhat unpredictable. | |||
{| {{Table/bluetable}} | {| {{Table/bluetable}} | ||
! | ! Imperfective || Perfective | ||
|- | |- | ||
| -ei- || - | | -ei- || -a- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | -o- || -ow- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | -oy- || -a- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| -e- || - | | -e- || -u- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | -i- || -a-/-e-/-u- | ||
|} | |} | ||
==== Voices ==== | ==== Voices ==== | ||
Revision as of 00:38, 22 April 2014
| Weddish | |
|---|---|
| Vediš | |
 | |
| Pronunciation | [/ˈve(ː).dɪʃ/] |
| Created by | Robert Murphy |
| Date | 2013 |
| Setting | Jewish intermarriage / Systematic Theology |
| Native speakers | 0.01 (2014) |
| Sources | Yiddish |
Weddish (Weddish: װעדיש, X"Q: וֶדִש, Romanization: Vediš) is a constructed, a posteriori, naturalistic auxlang, made from Yiddish with heavy influences from Hebrew, English, German, and Basque ideas. It has ergative-absolutive morphosyntactic alignment and a pervasive yet symbolic use of the dual. It is meant to promote the institution of marriage, foster better communication between persons, and improve the constructs of Systematic Theological discussions. It is well-suited as an auxlang for Jewish intermarriage.
The language was created in 2013 by Robert Murphy as part of an assignment at Covenant Theological Seminary for Professor Jerram Barrs.
Philosophy
First and foremost, there is the Creator-Creature distinction. That means, God is wholly other than the Universe. Second, human beings are made in the image of God. This means that we are persons -- like God is -- and our agency is our single-most important feature. Third, we reflect the image of God as females or males. The marriage bond is God-created and a fundamental part of our identity in this life. Hence it is, that we may divide the world into: actors, non-actors, and actions. Stated grammatically, this list becomes: ergative nouns, absolutive nouns, and verbs. Furthermore, ergative nouns may be divided up into married and non-married actors, which we will mark with the dual or not.
We have said that ontologically speaking, there are ultimately only Two (God and not-God). However, the 800lb. gorilla in the room -- philosophically speaking -- is abstraction. Since before Pythagoras, abstract nouns (such as numbers, "goodness", etc.) had been held by the Greeks to be ontic. Westerners betray their affinity to Greek ideals, classifying humanity as homo sapiens - "thinking man". We seek to disenthrall ourselves from this metaphysic and therefore banish abstract nouns from our language. Numerals are adjectives. Infinity is that which we cannot see the end of. Universals are the same as aggregates ("all" is the same as "sum" ... but not "some"!).
The Language Creation Society (an excellent institution) waves the flag of the Tower of Babel. Unlike the hubristic men of the initial chapters In the Land of Invented Languages (Arika Okrent's chronicle), we do not believe we can undo what God has done to human speech by intellectual rigor. Our aim is for Jews and Christians to discuss the truth in better terms. The status of English as a lingua franca, German as a language of science, and Hebrew as a holy language suggests that an Indo-European language is still the best option for an a posteriori auxlang, but with Semitic components. Rather than compete with those vital languages, however, it seems most prudent to build upon a base of all at once, utilizing a language that is already as eclectic as English, similar to German, and informed by Hebrew. That language is Yiddish. Basque serves as an inspiration for new categories and "outside the box" thinking.
Phonology
Weddish has 25 consonantal sounds, which is typologically average [1], and common in Europe as well as the Middle East. English speakers will find it to be common, apart from the lack of /w/ and the abundance of /x/ (like the ch in Bach or loch). Weddish has 6 vowels, which is also average[2], as is the resulting consonant-to-vowel ration[3]. This is typologically equivalent to Yiddish and Hebrew, but far less than German or English.
| Consonant phonemes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labial | Alveolar | Post-Alveolar | Dorsal | Glottal | ||||
| Nasals | מ /m/ | נ /n/ | * /ŋ/ | |||||
| Stops | voiceless | פ /p/ | ט /t/ | ק /k/ | א /ʔ/ | |||
| voiced | ב /b/ | ד /d/ | ג /g/ | |||||
| Fricatives | voiceless | פֿ /f/ | ס /s/ | ש /ʃ/ | כ /x/ | ה /h/ | ||
| voiced | װ /v/ | ז /z/ | זש /ʒ/ | ר /ʁ/ | ||||
| Affricates | voiceless | צ /ts/ | טש /tʃ/ | |||||
| voiced | דז /dz/ | דזש /dʒ/ | ||||||
| Approximants | ל /l/ | י /j/ | ||||||
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | י /i/~/ɪ/ | ו /u/~/ʊ/ | |
| Mid | ע /e/~/ɛ/ | ׳ /ə/ | ﭏ /o/~/ɔ/ |
| Low | א /ɐ/~/ä/ |
| +y | +w | |
|---|---|---|
| a | ײַ = ay | אַו = aw * |
| e | ײ = ey | |
| o | ױ = oy | אָו = ow * |
Voicing is contrastive in both plosives and fricatives, like Yiddish and English[4]. Vowel nasalization and rounding are not phonemic[5].
There are several issues in the pronunciation of individual sounds. The rhotic of Weddish is either alveolar or uvular[6] and may be anything from a fricative, to a flap, to a trill, to an approximant. No R-colors vowels are permitted. Words that begin with a vowel are separated from a prior open syllable by a glottal stop. The velar nasal only occurs when an "n" is assimilated in place of articular before or after an "x", "k", or "g", in a syllable coda[7]. ng is pronounced /ŋg/, not just /ŋ/. L is typically dark (aka "velarized") except before i. Ayen is always romanized e, but signifies the schwa in unaccented syllables.
In the dialect of the Americas, central vowels retain a color of their original/short form. Elsewhere, they are all central, except /a/ before glottals and /ɪ/ before labials. Another dialect difference is that c and dž are sometimes pronounced /θ/ and /ð/[8]. However, the rhotic is still not retroflex! Americans also pronounce aw and ow as diphthongs, which is completely understandable.
Orthography
Weddish written in the Hebrew alphabet, mostly following the standard of YIVO Yiddish. A and O are handled differently, as is the šva. There is a one-to-one correspondence between grapheme and phoneme, except for three digraphs and one trigraph. Weddish also has its own Romanization scheme, largely Slavic in appearance. In it, /ʃ/ is written š, /ʒ/ is written ž, /j/ is written y, /ts/ is written c, /tʃ/ is written č, /dʒ/ is written dž, and /ʁ/ is written r.
If the syllable after a diphthong begins with a vowel, the off-glide of the diphthong is doubled as the onset of that next syllable, without being written again. Thus zeyer is pronounced /zey.yer/.
As in Hebrew, five letters have "final" forms, when they occur at the end of a word. These forms do not affect pronunciation at all.
| Initial/Medial | מ | נ | פֿ | צ | כ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final | ם | ן | ף | ץ | ך |
Alphabetical order is (gereš,) alef, alefol, beys, (veys,) giml, dalet, dalet, hey, vov, gvováyin, šurek, zayen, (xes,) tes, yud, yud xirik, gyudayin, gyudayin pasex, vov yud, xof, (xof dageš,) lamed, mem, nun, samex, ayen, pey, fey, cadek, kuf, reyš, (sin,) šin (, tav, sav).
When necessary to avoid confusion, /u/ can be precisely specified with a וּ, called a šurek. /i/ can be invoked as יִ, that is a yud xirek.
Others
Yiddish has many loanwords from Hebrew and Aramaic which are written using the Hebrew abjad in the Semitic way. Weddish, however, writes these words out according to its own orthographic conventions. There are times when it is necessary to use the ancient letters, especially in religious settings.
| Lošn Koydeš Letter | בֿ | ח | כּ | שׂ | ת | תֿ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equivalent | װ | כ | ק | ס | ט | ס |
There is also a highly ornate style of writing Weddish, called xtiv qoydeš ("holy writing", abbr. x"q) where letters are used not as an alphabet, but as an abjad. Vowels may or may not be written in this style. When written, they are written as diacritical marks ("points") around the consonants. In this style, v is written as ו and y as י. Vowels are as follows, with the א written in syllables with no onset:
| Standard | X"Q | Roman. |
|---|---|---|
| אַ | אַ | a |
| ﭏ | אָ | o |
| ע | אֶ | e |
| י | אִ | i |
| ו | אֻ | u |
| ײ | אֵ | ey |
| ײַ | אַי | ay |
| ױ | אֹ | oy |
| אָו | אָי | ow |
| אַו | אַו | aw |
| ø | אְ | /ə/ or syllabic |
Handwriting, or cursive, as the same as Hebrew and Yiddish.

Phonotactics
Weddish phonotactics are inherited from Yiddish, which are quite permissive on the world scale[9]. While they do not rise to the level of Georgian or Salish, they are nevertheless sometimes difficult for English speakers. Gemination only becomes phonemic across word boundaries. Consonant clusters are spontaneously broken up across syllables in order to make codas less complicated and, if necessary, onsets more so.
Syllabic Consonants
Liquids and fricatives may be said syllabically. Syllabic consonants often occur at the end of a word. In an unstressed syllable, syllabic sonorants and syllables with a reduced vowel are indistinguishable. In stressed syllables, no vowel is written, the onset and coda are optional or may consist of a single stop.
Onsets
| Onset Consonant Clusters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | g | d | dz | dž | h | v | z | ž | t | č | y | x | l | m | n | s | p | f | c | k | r | š | ||
| b | bg | bd | by | bl | br | |||||||||||||||||||
| g | gv | gz | gy | gl | gn | gr | ||||||||||||||||||
| d | dv | dz | dy | dl | dn | dr | ||||||||||||||||||
| dz | dzv | dzy | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| dž | džy | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| h | hy | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| v | vy | vl | vr | |||||||||||||||||||||
| z | zb | zg | zv | zy | zl | zm | zn | zr | ||||||||||||||||
| ž | žb | žg | žv | žy | žl | žm | ||||||||||||||||||
| t | tv | ty | tx | tl | tm | tn | c | tf | tk | tr | č | |||||||||||||
| č | čv | čy | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| y | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| x | xv | xy | xl | xm | xn | xs | xc | xk | xr | xš | ||||||||||||||
| l | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| m | my | ml | mr | |||||||||||||||||||||
| n | ny | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| s | sd | sv | st | sč | sy | sx | sl | sm | sn | sp | sf | sk | sr | |||||||||||
| p | pv | pt | py | px | pl | pn | ps | pf | pk | pr | pš | |||||||||||||
| f | fy | fl | fr | |||||||||||||||||||||
| c | cd | cv | cy | cl | cn | cr | ||||||||||||||||||
| k | kd | kv | kt | ky | kx | kl | kn | ks | kr | |||||||||||||||
| r | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| š | šv | št | šč | šy | šx | šl | šm | šn | šp | šf | šk | šr | ||||||||||||
There are three-consonant clusters allowed that begin with s or š plus a voiceless stop plus a liquid: spl, spr, str, skr, skl, špl, špr, štr, škl, and škr but not stl or štl.
American's should take care with dr, tr, štr, and str not to "africatize" the cluster.
Codas
Final t's and c's devoice any other code consonants. In writing, it may look like there are therefore combinations not possible on the chart below, but they are pronounced devoiced.
| Coda Consonant Clusters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | g | d | dz | dž | h | v | z | ž | t | č | y | x | l | m | n | s | p | f | c | k | r | š | ||
| b | bd | bdz | bz | bž | ||||||||||||||||||||
| g | gd | gdz | gz | gž | ||||||||||||||||||||
| d | dz | dž | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| dz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| dž | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| h | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| v | vz | vž | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| z | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ž | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| t | tx | c | č | |||||||||||||||||||||
| č | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| y | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| x | xt | xs | xp | xk | xš | |||||||||||||||||||
| l | lb | lg | ld | ldz | ldž | lv | lz | lž | lt | lč | lx | lm | ln | ls | lp | lf | lc | lk | lš | |||||
| m | mb | md | mdz | mdž | =mdz | =mdž | =mps | mp | =mpf | =mpš | ||||||||||||||
| n | ng | nd | ndz | ndž | =ndz | =ndž | nt | nč | =nkx | =nc | nc | nk | =nč | |||||||||||
| s | st | sč | sp | sc | sk | |||||||||||||||||||
| p | pt | pč | ps | pf | pc | pk | pš | |||||||||||||||||
| f | ft | fč | fs | fp | fc | fk | fš | |||||||||||||||||
| c | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| k | kt | kč | kx | ks | kf | kc | kš | |||||||||||||||||
| r | rb | rg | rd | rdz | rdž | rv | rz | rž | rt | rč | rx | rm | rn | rs | rp | rf | rc | rk | rš | |||||
| š | št | šs | šp | šk | ||||||||||||||||||||
There are also liquids plus stop plus homorganic, alveolar fricative: lps, lbz, lks, lgz, rps, rbz, rks, rgz.
Suprasegmentals
Stress is predicable, if one knows the root of a word. The first syllable of the root receives primary stress, with secondary stresses proceed out onto alternating syllables, forwards and backwards. (The major exception is the dual, which moves the stress of a word with an odd number of syllables.) The default rhythm of Weddish is trochaic: stressed-unstressed. Neither vowel length nor stress is phonemic. Long vowels indicate stress. If the word is long, one of the first three syllables must have primary stress. Prefixes and suffixes all have an underlying vowel which is expressed or repressed in order to maintain the rhythm pattern. Two syllables with reduced vowels may not follow each other.
Polar and interrogative questions are both marked by a rising tone at the end of the utterance.
Syntax
| Weddish וועדיש | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progress: 43% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| fusional | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alignment | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ergative-Absolutive | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Head direction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Initial | Mixed | Final | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primary word order | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subject-verb-object | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tonal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Declensions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conjugations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Genders | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Verbs conjugate according to... | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voice | Mood | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Person | Number | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tense | Aspect | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Weddish aims to appeal to English speakers. While the verbal-system is somewhat new, the noun-system should be easy. Nouns are not inflected, but pronouns have unique forms that show part of speech. Like German, articles inflect, not the noun. Weddish (like English) only has gender on the independent third person personal pronouns. Otherwise there are just noun classes, a system taken from Basque. People, animals, and things that can move on their own are "animate", while plants and other objects are "inanimate". Adjectives do not inflect unless substantive, and there are not many adjectives. Most descriptors are intransitive verbs.
Weddish has an ergative-absolutive morphosyntactic alignment. This was purposefully chosen to stimulate thinking, and done in imitation of Basque. Most languages in the world treat the actor of transitive verb and the subject of an intransitive verb in the same way. The object of a transitive verb is special in these systems. It can be promoted to the subject via the passive voice. Normally, it must come after the verb. Weddish treats the object of a transitive verb and the subject of a transitive verb the same, called the "absolutive case". Actors of transitive verbs are specially, called the "ergative case". This is the special case in Weddish. It must come before the verb and can be demoted by the anti-passive voice.
It would be tempting to classify Weddish as VSO (subject-veb-object) like Hebrew, but that's not quite right. It is, in fact, a V2 language, which means the verb always wants to come second. (Discourse particles and few other things do not count towards calculating where "second" is, and entire phrases are taken as a whole when counting this place.) Because core cases are marked almost solely by word order, the actor of a transitive verb (the ergative case) must come before the verb, i.e. first in the sentence. It could also be said that intransitive sentences are VSO and transitive ones are SVO.
The V2 Principle is carried throughout Weddish, to the point where it might be labeled a "head second" language. This is not a recognized typology, since languages are either head-initial, head-final, or mixed. In compound nouns, the head is second. For auxiliary verbs, the head verb is second. For nouns with attributive modifiers, the article comes first, but adjectives come after the noun, making it head-second as well.
Number
English, Hebrew, Yiddish and many other languages have two numbers: singular and plural. Weddish (like Arabic) has three: singular, dual, and plural. Obviously, the dual is for two of something, and the plural therefore means three or more. However, in regards to persons, the dual is used on married people, even if only one of them is being spoken about. Exceptions can be made in every case except the ergative, which is reserved for the spouses to use on each other. This distinction does not apply in the third person for people not present.
Weddish also distinguishes whether actions were done as individuals or all as a group. It also possible to add "associates" of a noun to it.
Copula
The verb "to be", "to become", and "to have" are all copulas in Weddish. That means they all use only the absolutive case, never the ergative. However, "to be" and "to have" are more like "to equal" and "to exist". "I have shoes" is literally "Shoes exist to me". This can be easier for Far East Asians to learn than Westerners.
Morphology
Case
| Genitive | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| פֿון/fun | |||
| Dative | Ablative | Partitive | Equative |
| ל־/l- | ב־/b- | מ־/m- | ק־/k- |
By default, all nouns are in the absolutive case. But, if they are placed before the verb, then they are said to be in the ergative case, though their morphology is unchanged. Linguists call these two case the "core cases" of a language, since they are fundamental. There are five additional cases --- called "non-core" cases --- that are also very important. Unlike many languages that have suffixing case marking, Weddish has prefixing. This is because they are derived from Hebrew Inseparable Prepositions. Phrases in the non-core cases either relate to the verb (and are hence, adverbial), or are in a noun phrase. In relation to nouns, the core cases are all seen as greater specificity within the genitive case.
Non-core cases all fall under the umbrella term "genitive". The generic genitive is not a case per se, but a preposition (meaning, a separable preposition). An expression like די לינע פֿונ געלט/di line fun gelt/the love of money is even more ambiguous in Weddish than in English. It may mean the love [belonging] to money, the love in/by money, the love from/composed of money, or the love as/according to money. After a genitive phrase has been established or is implicitly understood, the phrase may incorporated be into a compound noun using the "head-second" structure.
| Definite | Indefinite | Anarthrous | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anim.sg | dl | inan.sg/pl | sg/dl | ||
| Erg. | der | dos | di | a(n) | ø |
| Abs. | dem | ||||
| Dat. | lem | ler | li | lawn | l- |
| Abl. | bem | bos | bi | bawm | b- |
| Part. | mem | mos | mi | mawm | m-/min |
| Eq. | kem | kos | ki | kawm | k- |
The definite article is always determined. In the following hierarchy, if an article is any of these, it is also all those to the left:
- Identifying --> Anaphoric --> Well-Known --> Par Excellence --> Monadic
Number
Weddish verbs conjugate for three numbers (singular, dual, and plural), but nouns inflect eleven different ways! However, these myriad ways can be easily understood as the optional adding of "associates" to a noun, and distinguishing between masses of individuals and collectives (one forest vs. many trees). The following table is color-coded to show verb conjugation in the singular (light background), dual (purple), and plural (brown).
| Singular | Dual | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distributive | פֿרײַנד fraynd a friend |
פֿרינדײַים frindayim two friends each |
פֿרײַנדין frayndin friends each |
| Collective | געפֿרינדײַים gefrindayim a couple of friends |
געפֿרײַנדין gefrayndin a group of friends | |
| Distributive Associative |
פֿרײַנדז frayndz a friend and associates each |
פֿרינדײַיםז frindayimz two friends and associates each |
פֿרײַנדינז frayndinz friends and associates each |
| Collective Associative |
געפֿרײַנז gefrayndz a group of a friend and associates |
געפרינדײַימז gefrindayimz a group of two friends and associates |
געפֿרײַנדינז gefrayndinz a group of friends and associates |
There are a plethora of paradigms for the distributive plural formations, 99% of which time come straight from the Yiddish plural.
The dual ending is unique, in that is shifts the accent pattern of the root to itself. It may be written -áyim to indicate that shift. This shift triggers vowel reduction of of the previous syllable, if it is a diphthong (cutting it down to its first vowel).
The number affixes may be summarized as follows:
- g- is the collective prefix, which turns most groups into "one's"
- -áyim is the dual suffix, while -s/es and -n/en/in are the inanimate and animate distributive plurals respectively. Vowel reduction and/or umlaut may occur.
- -z/ez is the associative plural
Forms lacking the collective plural endings are automatically distributive unless singular.
Pronouns
Independent Personal
Absolutive independent personal pronouns are most commonly used with ø-copula clauses to show predication. Such sentences are distinguished from those with the "to be" verb, which show absolute identity, as opposed to mere attribution. Gu Yidiš/We are Jewish vs. Big Džonzez/We are (the) Jones's.
| Ergative | Absolutive | Dative | Ablative | Partitive | Equative | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sg | 'ix | mix | mir | bix | mix | kix |
| dl | gurekin | gu | gir | bug | ming | kowg | |
| pl | vir | mir | undz | bu | minu | ku | |
| 2 | sg | du | dix | dir | bed | mind | ked |
| dl | stu | stuk | stire | bist | minst | kist | |
| pl | 'ir | ayx | 'ux | bikm | mint | kat | |
| 3 | m.a.sg | er | 'im | 'inen | bo | mino | ko |
| inam.sg | zi | es | aya | ba | mina | ka | |
| dl | bera | hura | hav | bav | minav | kav | |
| pl | zey | cey | čire | bouč | minč | kač | |
| f.a.sg | ši | her | herz | bau | mim | kauk | |
Interrogative
| Erg. | Abs. | Gen. | Dat. | Abl. | Part. | Eq. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | mi | ver | vermenc | vermen | bimi | mimi | komi |
| Impers. | ma | vos | fun vos | vu | vi | vat | ven |
The interrogative pronouns do not inflect for person, number, or gender. Linguists would say they are animate and inanimate, though Weddish grammar calls them "personal" and "impersonal". They are identical to the relative pronoun (just as in English) and must match their antecedent in animacy, but not in case. Instead (just as in English) they indicate their new role in the relative clause.
Affixes
Like Hebrew, Weddish uses enclitic forms of pronouns to indicate several things. On verbs, pronominal suffixes mark the absolutive argument of the clause. On nouns, they mark a genitive relationship. Pronominal prefixes are used exclusively on transitive verbs to mark the ergative argument, and are obligatory. Weddish is not pro-drop, and an affix on both ends is required on transitive verbs. Remember, there are no ambi-transitive verbs in Weddish. Use of the independent personal pronouns when the person has been specified on either end of the verb is considered emphatic.
| Person | # | Suffix | Prefix |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sg | -(n)i | ni- |
| dl | -(u)g | gu- | |
| pl | -(n)u | na- | |
| 2 | sg | -(e)d | de- |
| dl | -(e)st | sti- | |
| pl | -ti | ta- | |
| 3 | anim. | -o | ro- |
| inan. | -a | ya- | |
| dl | -av* | ø | |
| n/pl | -(ay/i)č | čay- |
Verbs
Weddish verbs conjugate first for aspect, then use auxiliaries for tense and mood.
Aspect Ablaut
Aspect is specified by changing the theme vowel of the verb. The right vowel may not be part of a compound, prefix, or suffix. As with nounal plurals, these changes fall into patterns, but are somewhat unpredictable.
| Imperfective | Perfective |
|---|---|
| -ei- | -a- |
| -o- | -ow- |
| -oy- | -a- |
| -e- | -u- |
| -i- | -a-/-e-/-u- |
Voices
- Causative: š/že-
- Reflexive: hit/hid-
- Antipassive: V-u
- Mixed
Non-finite
- participle -ing
- infinitive absolute: u-V
- infinitive construct: ge-
Incorporation
On the Mithun scale[10], Weddish does type-I and type-II noun incorporation. This means 1) I picked berries -> I berry-picked, and 2) I washed his face -> I face-washed him.
Derivation
Compounding
When the relationships between nouns is genitive, and it has already been stated or can easily be implied, compound nouns may be formed. For example, a field for football/soccer may become fusbolfeld. (Note the loss of abstraction suffixes.) Suppose it was an Australian rules football field. Would could make fusbolfeldeoystralie. Lastly, If one wanted to add that it is mgroz/composed of grass, this could become פֿוסבאָלפֿעלדעאויסטראליעגראָז/fusbolfeldeoystraliegroz. Words with greater than four parts are deemed colloquial. Word order is "head second", with the first specifier coming at the very front.
Abstract Nouns
All nouns in Weddish are inherently concrete. Two levels of abstraction are possible through suffixation. The first signifies the practice of one or more persons. The second signifies the understanding of the practice. Both are available in both noun classes, with the animate form referring to a person (of either gender). The "practice"-form occurs much more often in the animate and the "understanding"-form occurs much more often in the inanimate. Remember, this are no truly abstract nouns in Weddish, for they do not exist.
| Suffix | "Tennis" | gloss | "Peace" | gloss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø | a tenis | a game of tennis | a šolem | a season of peace |
| -ay | dos tenisayo | his tennis game | šolemaya | her (practice of) peace |
| dem tenisayt | the tennis player | dem šolemayt | the peacemaker | |
| -šaft | dos tenisšafte | the game of tennis / "tennisology" | šolemšafte | peace know-how |
| a tenisšaft | a tennisologist | a šolemšaft | a student of peace |
Discourse
Formality
Particles
By far the most commonly occurring particle is v-, which is like a verbal comma. Yiddish - like English - has the word and/un. Weddish, however, only uses that word to connect clauses. v- is a return to Hebrew, though typically not at the start of sentences.
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/1
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/2
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/3
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/4
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/11
- ^ As in Hebrew, uvular may be seen as the most prestigious form: http://wals.info/chapter/6
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/9
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/19
- ^ http://wals.info/chapter/12
- ^ Mithun, Marianne. 1984. The Evolution of Noun Incorporation. Language, Vol. 60, No. 4. pp. 847-894.