Knrawi: Difference between revisions
(→Vowels) |
|||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
*[ɛ] and [ɔ] are unstressed allophones of /ɪ/ or /a/ and /ʊ/ or /a/ respectively | *[ɛ] and [ɔ] are unstressed allophones of /ɪ/ or /a/ and /ʊ/ or /a/ respectively | ||
*/ɪ/, /ʊ/, and /a/ are realized as [j], [w], and [ʔ̞] postvocalically | |||
*Epenthetic [ə] is placed between | *Epenthetic [ə] is placed between | ||
**voiceless consonants and /h/ or /x̠/ | **voiceless consonants and /h/ or /x̠/ | ||
Revision as of 10:38, 14 July 2023
| Knrawi | |
|---|---|
| knrawi | |
 knrawìguaa, "Knrawi language" in the Wacag script | |
| Pronunciation | [k̠n̩˥ɹɔʍɛ] |
| Created by | Dillon Hartwig |
| Date | 2020 |
| Setting | Pollasena |
| Native to | Knrawi Isles |
Wasc
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Knrawi Empire |
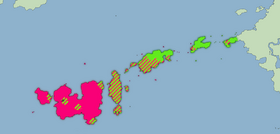
Range map of Knrawi (pink) and Soc'ul' (green) | |
Knrawi /kənˈrɑwi/ (standard Knrawi: [k̠n̩˥ɹɔʍɛ]) is an isolate spoken across the Knrawi Empire, with moderate influence from Soc'ul' and other languages of the Knrawi Isles.
Etymology
Knrawi is autonym of both the language and the Knrawi ethnic group. Its further etymology is not known.
Orthography
Knrawi is written with the Wacag logography. Its romanization is as follows.
| a | c | ch | cj | e | f | fh | fj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /a/ | /k̟/ | /k̟ʰ/ | /k̟ˣ/ | [ə] | [ɸ] | [ɸʰ] | [ɸˣ] |
| g | h | i | j | k | kh | kj | m |
| /ŋ/ | /h/ | /ɪ/ | /x̠/ | /k̠/ | /k̠ʰ/ | /k̠ˣ/ | /m/ |
| n | p | ph | pj | q | qh | qj | r |
| /n/ | [p] | [pʰ] | [pˣ] | /kʷ/ | /kʷʰ/ | /kʷˣ/ | /ɹ/ |
| s | sh | sj | t | th | tj | u | v |
| /x̟/ | /x̟ʰ/ | /x̟ˣ/ | /t/ | /tʰ/ | /tˣ/ | /ʊ/ | [β̞] |
| w | y | z | zh | zj | á | à | â |
| /ʍ/ | /ɉ/ | /θ/ | /θʰ/ | /θˣ/ | /a˥/ | /a˩/ | /a˥˩/ |
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Prevelar | Postvelar | Labialized velar | Glottal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | (mʷ) | n | (ŋ̟) | ŋ | (ŋ̠) | (ŋʷ) | |||||
| Stop | Plain | (p) | t | k̟ | k̠ | kʷ | ||||||
| Aspirated | (pʰ) | (pˣ) | tʰ | tˣ | k̟ʰ | t͡ʃˣ | k̠ʰ | k̠ˣ | kʷʰ | kʷˣ | ||
| Fricative | Plain | (ɸ) | (β) | θ | (ð) | x̟ | (ʒ) | x̠ | ʍ | |||
| Aspirated | (ɸʰ) | (ɸˣ) | θʰ | θˣ | x̟ʰ | ʃˣ | h | |||||
| Approximant | (β̞) | ɹ | (j) | ɉ | (w) | (ʔ̞) | ||||||
- Alveolar consonants become bilabial adjacent to /m/, /ʊ/, and labialized consonants.
- /n/ becomes what is notated here as [mʷ], but is merged into /m/ in most regions and in standard Knrawi.
- /ŋ/ assimilates to following velars in articulation.
- /ɪ/, /ʊ/, and /a/ are realized as [j], [w], and [ʔ̞] postvocalically
- The conditions for approximants being realized as fricatives varies by region
- In standard Knrawi they are realized as fricatives on word boundaries and after non-syllabic vowels
- In some regions alveolar consonants are realized as dental (except when realized as bilabial) or vice versa
- In some regions [j] and [ɉ] are merged
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | ɪ | ʊ | |
| Mid | (ə) | ||
| Low mid | (ɛ) | (ɔ) | |
| Low | a |
- [ɛ] and [ɔ] are unstressed allophones of /ɪ/ or /a/ and /ʊ/ or /a/ respectively
- /ɪ/, /ʊ/, and /a/ are realized as [j], [w], and [ʔ̞] postvocalically
- Epenthetic [ə] is placed between
- voiceless consonants and /h/ or /x̠/
- In standard Knrawi an exception is /hC/ and /x̠h/ clusters
- aspirated consonants and non-nasal consonants
- C₁CC₁, #CC₁, and C₁C# clusters with the C₁ being less sonorous than C (not including syllabic consonants)
- voiceless consonants and /h/ or /x̠/
The conditions in which unstressed /a/ becomes [ɛ] or [ɔ] varies by region; in standard Knrawi [ɛ] is the realization adjacent to coronal and glottal consonants or when the previous vowel is [ɔ], and [ɔ] is the realization otherwise.
Pitch accent
Prosody
Stress
Intonation
Rhythm
Phonotactics
Syllables are at most (C(C₁))V((C₁)C), with C₁ being more sonorous than the adjacent consonant and syllabic consonants functioning as V.
Morphology
Alignment
Knrawi has nominative-accusative morphosyntactic alignment.
Nouns and pronouns
Possession
Noun negation
Verbs
Copula
The copula su inflects as follows.
Serial verbs
Adjectives and adverbs
Adpositions
Numerals
Knrawi uses base-24 numerals.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tì | qûat | càvu | shuga | kaau | fùch |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| m̀vis | khain | kàtiu | huc | chaua | ycham |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| tìm | quâpm | cavùm | shugám | kaáum | fuchm̀ |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| mvìsm | khaímm | katìum | hucḿ | chaúam | ychámm |
| 25 | 48 | 576 | 13,824 | 331,776 | |
| ychámm hn tì | qûat ychámm | sûign | suîgmm | ychámm suîgmm | |
Nouns are not marked for number when using numerals.
Derivational morphology
Part-of-speech modifiers
Reduplication
Syntax
Constituent order
Word order is flexible with sufficient marking or context, but SOV order is most common in the western Knrawi Isles and VSO order is most common in the eastern Knrawi Isles.
Noun and verb phrases
Dependent clauses
Dependent clauses follow the head they modify after all other dependents, and their head noun is often backed to the end of its clause.
Example texts
Universal Declaration of Human Rights Article 1
Thaágg jua r yamúszaq ih r azjnázaq wuicsjḿjr ih r zauákejr. Gufḿqhvi ih guwúiri r̀ iaràm, quatîtg hu qakhúy sugkúkujr.
Thaag-g
person-NOM
jua
all
r
PASS
yamús-zaq
free-bear
ih
and
r
PASS
azjna-zaq
equal-bear
wuícsjm-jr
dignified-ADVZ
ih
and
r
PASS
zauak-jr.
own-ADVZ
Gu-fmqh-ri
NZ-think-NOM.PTV
ih
and
gu-wui-ri
NZ-good-NOM.PTV
r̀
PASS
iaràm,
give
quatît-g
RECP-NZ
hu
JUS.3>3
qa-khuy
do-toward
sug-kuku-jr.
brother-way-ADVZ