Template:Front/featured: Difference between revisions
Chrysophylax (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Chrysophylax (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
# Fusional verb inflection for person, number, mood, and tense. | # Fusional verb inflection for person, number, mood, and tense. | ||
However, noun and adjective declension endings, along with the ablaut in strong verbs are elements derived from Germanic. | However, noun and adjective declension endings, along with the ablaut in strong verbs are elements derived from Germanic. | ||
There are six major dialects of Avendonian. Central Avendonian (or '''midio''') is considered the standard language, and it is the language most of the author's work is based upon. The main features of the other five dialects will be discussed in the following sections. | There are six major dialects of Avendonian. Central Avendonian (or '''midio''') is considered the standard language, and it is the language most of the author's work is based upon. The main features of the other five dialects will be discussed in the following sections. | ||
<noinclude>[[Category:Templates]][[Category:Main page]][[Category:Meta]]</noinclude> | <noinclude>[[Category:Templates]][[Category:Main page]][[Category:Meta]]</noinclude> | ||
Revision as of 09:23, 19 July 2021
| Avendonian | |
|---|---|
| avendoniano | |
 | |
| Pronunciation | [avendoˈni̯ano] |
| Created by | S.C. |
| Date | 2009 |
| Setting | Alt-history Europe, Northern Italic Peninsula |
| Native to | Avendonia |
Indo-European
| |
Early form | Pre-Avendonian
|
Standard form | Central Avendonian dialect
|
Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Official language in | Avendonia |
| Regulated by | Grunditio Cuningica per la Spraca Avendoniana |
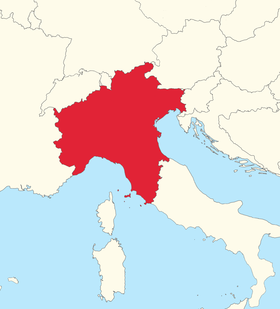 Approximate borders of Avendonia | |
Avendonian (autoglossonym: avendoniano; Avendonian: [avendoˈni̯ano]) is a West Germanic language, with strong influence of Vulgar Latin. It is the result of a prolonged contact among members of both regions, after West Germanic merchants began travelling to and from the Western Roman Empire. These connections—and the conquest by the Germanic tribes of the northern skirts of the Roman Empire—slowly formed a creole for mutual communication. Eventually, permanent settlements were established in what would become modern-day Avendonia, where Avendonian is primarily spoken, with official status.
While its vocabulary derives for the most part from Proto-Germanic, Latin influence is most notable in its phonology and its grammar.
Avendonian grammar is relatively straightforward and akin to the grammar of other Romance languages, due to the influence of Latin.
- Two sets of articles, indefinite and definite, preceding the noun.
- Gender and number inflection in nouns, adjectives, and pronouns. Articles and adjectives must agree inflection-wise with the noun or pronoun they modify.
- Twofold gender system, masculine and feminine. Loss of Latin neuter gender.
- Fusional verb inflection for person, number, mood, and tense.
However, noun and adjective declension endings, along with the ablaut in strong verbs are elements derived from Germanic.
There are six major dialects of Avendonian. Central Avendonian (or midio) is considered the standard language, and it is the language most of the author's work is based upon. The main features of the other five dialects will be discussed in the following sections.