Avendonian: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
: etc. | : etc. | ||
The definite article '''el''' forms a contraction with prepositions '''{{term|a}}''' and '''{{term|de}}''', using an apostrophe: '''a'l''', '''d'el'''. These are the only standard contractions; other contractions like '''[[Contionary:ca ga't|Ca ga't?]]''' from '''{{term|ga}}''' + '''{{term|et}}''' (“How goes it?”, greeting) are not disallowed but are discouraged in formal writing. | The definite article '''el''' forms a contraction with prepositions '''{{term|a}}''' and '''{{term|de}}''', using an apostrophe: '''a'l''', '''d'el'''. These are the only standard contractions; other contractions like '''[[Contionary:ca ga't|Ca ga't?]]''' from '''{{term|ga}}''' + '''{{term|et}}''' (“How goes it?”, greeting) are not disallowed but are discouraged in formal writing. | ||
===Demonstratives=== | |||
In Avendonian there are two sets of demonstratives, which can be used either as determiners or pronouns: [[w:Demonstrative#Distal and proximal demonstratives|proximal and distal]]. As adjectives, the stem may be suffixed with '''-ie''' to form adverbs, '''{{term|ecie}}''' ''here'' and '''{{term|elie}}''' ''there'' respectively. | |||
{| class="multicol" role="presentation" style="border-collapse: collapse; padding: 0; border: 0; background:transparent; width:auto; text-align: center;" | |||
| rowspan="2" style="text-align: center; vertical-align: top;" | | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Proximal demonstratives | |||
|- | |||
! !! masculine !! feminine | |||
|- | |||
! singular | |||
| {{term|eco}} || {{term|eca}} | |||
|- | |||
! plural | |||
| {{term|eci}} || {{term|ece}} | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
  | |||
| style="text-align: center; vertical-align: top;" | | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Distal demonstratives | |||
|- | |||
! !! masculine !! feminine | |||
|- | |||
! singular | |||
| {{term|elo}} || {{term|ela}} | |||
|- | |||
! plural | |||
| {{term|eli}} || {{term|ele}} | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
===Nouns=== | ===Nouns=== | ||
| Line 267: | Line 299: | ||
===Adjectives=== | ===Adjectives=== | ||
As said above, adjectives agree in gender and number with the noun, and are placed after them. They exist in three [[w:Comparison (grammar)|degrees]]: positive, comparative, and superlative. All three | As said above, adjectives agree in gender and number with the noun, and are placed after them. They exist in three [[w:Comparison (grammar)|degrees]]: positive, comparative, and superlative. All three degrees have an adverbial form, using the suffix '''-ie'''. In other words, every adjective can be morphed into an adverb. | ||
====Positive degree==== | ====Positive degree==== | ||
The positive degree is the default form of Avendonian adjectives, which simply describes the noun. It is also the only degree subject to declensional variation. The declension patterns are exactly as those of nouns, although '''{{term|porpora}}''' is considered irregular, not a-stem. | The positive degree is the default form of Avendonian adjectives, which simply describes the noun. It is also the only degree subject to declensional variation. The declension patterns are exactly as those of nouns, although '''{{term|porpora}}''' is considered irregular, not a-stem. | ||
| Line 847: | Line 879: | ||
:::: {{legend|#b8b8ff|From [[w:Latin language|Latin]] ''[[wikt:sum#Latin|sum]]''.}} | :::: {{legend|#b8b8ff|From [[w:Latin language|Latin]] ''[[wikt:sum#Latin|sum]]''.}} | ||
:::: {{legend|#ffca95|From Proto-Germanic ''[[wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/beuną|*beuną]]''.}} | :::: {{legend|#ffca95|From Proto-Germanic ''[[wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/beuną|*beuną]]''.}} | ||
===Dialects=== | |||
{{Ambox | |||
| name = Planned revamp | |||
| small = left | |||
| subst = <includeonly>{{subst:substcheck}}</includeonly> | |||
| issue = The creator of the language has expressed their intent of overhauling the dialect system. Thus, the information hereon provided is the latest available.<br>This section will be updated with the newest information once it is released. | |||
| talk = Dialects | |||
| style = width: auto; margin-right: 0px; | |||
| textstyle = width: auto; | |||
| date = {{CURRENTMONTHNAME}} {{CURRENTYEAR}} | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:Avendonian]][[Category:Germanic languages]][[Category:West Germanic languages]][[Category:Languages]][[Category:Conlangs]] | [[Category:Avendonian]][[Category:Germanic languages]][[Category:West Germanic languages]][[Category:Languages]][[Category:Conlangs]] | ||
Revision as of 17:24, 17 September 2020
This article is a construction site. This project is currently undergoing significant construction and/or revamp. By all means, take a look around, thank you. (15:14, 9 September 2020 (UTC)) |
| Avendonian | |
|---|---|
| avendoniano | |
| Pronunciation | [[Help:IPA|[[[IPA for Avendonian|[avendoˈni̯ano]]]]]] |
| Created by | S.C. |
| Setting | Alt-history Europe |
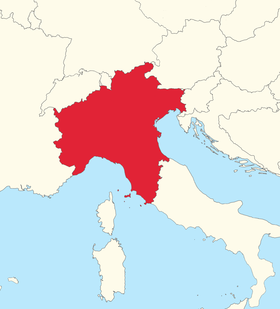
| Native to | Avendonia |
Indo-European
| |
Early form | Old Avendonian
|
Standard form | Central Avendonian dialect
|
Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Official language in | Avendonia |
Approximate borders of Avendonia | |
Avendonian (autoglossonym: avendoniano; Avendonian: [avendoˈni̯ano]) is a West Germanic language, with strong influence of Vulgar Latin. It is the result of a prolonged contact among members of both regions, after West Germanic merchants began travelling to and from the Western Roman Empire. These connections—and the conquest by the Germanic tribes of the northern skirts of the Roman Empire—slowly formed a creole for mutual communication. Eventually, permanent settlements were established in what would become modern-day Avendonia, where Avendonian is primarily spoken, with official status.
While its vocabulary derives for the most part from Proto-Germanic, Latin influence is most notable in its phonology and its grammar.
Etymology
The language name derives directly from the country it is spoken in, Avendonia. It makes reference to the Roman description of the Avendonian peoples, which were settled west of Rome; in the direction of the setting sun. Ultimately from Proto-Germanic *ēbanþs (“evening”), it came to mean “sunset people” or “people of the setting sun”.
Orthography
The Avendonian alphabet consists of 18 letters, five of which are vowels and 13 consonants. There are no diacritics, and contractions make use of the apostrophe to mark vowel omission.
| Letters of the Avendonian alphabet | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aa | Bb | Cc | Dd | Ee | Ff | Gg | Ii | Ll | Mm | Nn | Oo | Pp | Rr | Ss | Tt | Uu | Vv |
Non-native letters such as J, K, Q, Z, etc. may occur in some foreign words or proper nouns, chiefly in toponyms and given names. Yy is part of the alphabet of the Burgundian dialects of Avendonian, like in dydere.
The letters correspond almost one to one to their pronunciation. The Avendonian orthography is considered shallow or phonetic, as opposed to deep orthographies like French's. The orthography features that do not follow the correspondance are:
- The letters ⟨c⟩ and ⟨g⟩ make the sound /t͡ʃ/ and /d͡ʒ/, respectively, if followed by ⟨e⟩ or ⟨i⟩. Examples: cicare /t͡͡ʃiˈkare/, geldo /ˈd͡ʒeldo/.
- ⟨t⟩ in the combination ⟨ti⟩ makes the sound /t͡s/. Example: tite /ˈt͡site/.
- The combination ⟨gn⟩ makes the sound /ɲ/, as in Italian or Spanish ñ. Example: gnagare /ɲaˈgare/.
- ⟨i⟩ in intervocalic position or word-initially turns into the semivowel /j/. Examples: iaro /ˈjaro/, bluiare /bluˈjare/.
- The digraph ⟨sc⟩ before front vowels (i.e. ⟨i⟩ and ⟨e⟩) makes the sound /ʃ/. Example: sciio /ˈʃijo/.
- The digraph ⟨ch⟩ makes the sound /k/, and it is only found in loanwords.
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Dental/ alveolar |
Post- alveolar/ palatal |
Velar | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | (ŋ) | ||||
| Stop | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | ||
| Affricate | t͡s | t͡ʃ | d͡ʒ | |||||
| Fricative | f | v | s | ʃ | ||||
| Approximant | j | |||||||
| Lateral | l | |||||||
| Trill | r | |||||||
| Flap | (ɾ) | |||||||
Notes:
- As stated in §Orthography, /k, g, sk/ palatalize to /t͡ʃ, d͡ʒ, ʃ/ before front vowels /i, e/.
- When followed or preceded by a vowel but not word-initially, /i/ shortens and forms a diphthong with the adjacent vowel. Examples: sigie /ˈsid͡ʒi̯e/, perstelitio /persteˈlit͡si̯o/.
- [ɾ] is a permissible allophone of /r/ in fast speech.
- [ŋ] is an allophone of /n/ before velar stops /k, g/, both intra- and intersyllabically, although the former can only happen in the Low Burgundian dialect.
Examples: drincare /driŋˈkare/, anguste /aŋˈguste/, Low Burgundian clang /klaŋg/ (standard clango).
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | (y) | u | |
| Close-mid | e | o | ||
| Open | a | |||
Notes:
- /y/ is native to the Burgundian dialects, evolved from Proto-Germanic *iu which merged with /i/ in the rest of dialects.
- /e, o/ may be realized as [e̞, o̞].
Prosody
Avendonian is strictly paroxytonic, meaning words always receive stress on their second-to-last syllable.
Monosyllabic words like blio have the stress in their only syllable, but it is weaker than those in polysyllabic words, unless emphasized. Enclitic and other unstressed personal pronouns do not affect stress patterns:
Longer words (four or more syllables) may receive a secondary stress in the fourth-to-last syllable (i.e. two syllables before the main or primary stress):
- sobgrundsporvego /sob.ˌgrund.spor.ˈve.go/, surstopitio /ˌsur.sto.ˈpi.t͡si̯o/
Grammar
Avendonian grammar is relatively straightforward and akin to the grammar of other Romance languages, due to the influence of Latin.
- Two sets of articles, indefinite and definite, preceding the noun.
- Gender and number inflection in nouns, adjectives, and pronouns. Articles and adjectives must agree inflection-wise with the noun or pronoun they modify.
- Twofold gender system, masculine and feminine. Loss of Latin neuter gender.
- Fusional verb inflection for person, number, mood, and tense.
However, noun and adjective declension endings, along with the ablaut in strong verbs are elements derived from Germanic.
Articles
Both definite and indefinite articles have four distinct forms, for number and gender:
|
|
Avendonian articles function similarly as English a and the, but gender and number of the following noun determine the form that must be used. For example:
- buce m sg → el buce (“the book”), uno buce (“a book”).
- frage f pl → le frage (“the questions”), une frage (“some questions”).
- etc.
The definite article el forms a contraction with prepositions a and de, using an apostrophe: a'l, d'el. These are the only standard contractions; other contractions like Ca ga't? from ga + et (“How goes it?”, greeting) are not disallowed but are discouraged in formal writing.
Demonstratives
In Avendonian there are two sets of demonstratives, which can be used either as determiners or pronouns: proximal and distal. As adjectives, the stem may be suffixed with -ie to form adverbs, ecie here and elie there respectively.
|
|
Nouns
| A-stem | O-stem | E-stem | U-stem | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| singular | -a | -o | -e | -o |
| plural | -e | -i | -u |
Nouns in Avendonian fall in one of the following almost fully regular declensions:
- A-stem: mostly feminine nouns. From Latin first declension and Germanic ō- and ōn-stems. E.g. erda.
- O-stem: chiefly masculine nouns. From Latin second declension and Germanic a-stems. E.g. vundro.
- E-stem: both genders. From the third and fifth declensions of Latin and various Germanic stems (like an-stems). E.g. snege.
- U-stem: both genders but mainly masculine. From Latin fourth declension and u-stem from Germanic. E.g. vintro.
Notable exceptions are the productive suffix -tio, which forms feminine o-stem nouns from verbs, and the -ista suffix forms epicene a-stem nouns. Other words have no distinctive feature in the modern language, i.e. differences are etymological.
Personal pronouns
| personal pronouns | possessive pronoun | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| subjective | objective | ||||
| first person |
singular | eo | me | mede | |
| plural | vi | nos | nosde | ||
| second person |
singular | standard | tu | te | tede |
| formal | Si | Side | |||
| plural | i | vos | vosde | ||
| third person |
singular | masculine | e | si | side |
| feminine | si | ||||
| neuter | et | ||||
| plural | si | ||||
Personal pronouns in Avendonian have the following forms:
- Avendonian is not a pro-drop language, as other Romance languages. In other words, the subject, which may or may not be a personal pronoun must appear in every sentence, except in relative clauses where the subject of both statements is the same.
- Eo spreco avendoniano. I speak Avendonian
- El hundo ce (et) va mudio asatui. The dog which was tired sat down.
- Objective pronouns act as the direct object of a sentence. If the verb is an infinitive or an imperative, the pronoun is attached to it with a hyphen; otherwise, it precedes the verb.
- E me gavo uno scenco en el burddago mede. He gave me a present for my birthday.
- Bido, sende-me uno posrito cando si encumen. Please, send me a message when they arrive.
- Possessive pronouns can function as determiners and pronouns, i.e. my and mine. Possessives
must be written in the form of article + noun + possessive. The article still agrees in gender and number with the noun.
- El vagno mede. My car. Le sceiate side. His/Her/Their stories.
- Perlosasti tu el buce tede? Eo cuno liare el mede. You lost your book? I can lend you mine.
- Avendonian has, as in the Romance languages, T–V distinction. This distinction is lost in the plural. Formal second person pronouns are always capitalized, in all forms, no matter the environment.
- Bido ero, ce bi el name Side? Excuse me sir, what is your name? (formal)
- Si Si bi perlisato, vi cunamos ledere-Si. If you are lost, we can guide you. (formal)
Adjectives
As said above, adjectives agree in gender and number with the noun, and are placed after them. They exist in three degrees: positive, comparative, and superlative. All three degrees have an adverbial form, using the suffix -ie. In other words, every adjective can be morphed into an adverb.
Positive degree
The positive degree is the default form of Avendonian adjectives, which simply describes the noun. It is also the only degree subject to declensional variation. The declension patterns are exactly as those of nouns, although porpora is considered irregular, not a-stem.
|
|
|
The same forms can also be used predicatively. Thus: La dotre mede bi sciia. My daughter is shy., Li landi bin fere. The countries are far (away)., etc. Passive participles can function as regular adjectives, and active participles (or gerunds) result in undeclinable adjectives. An example of an adjective of each declension is given:
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comparative degree
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Avendonian comparative adjectives can establish three sorts of comparison: equative (X is as Y as Z), superior (X is more Y than Z), and inferior (X is less Y than Z). Fusional endings are only used in
equative comparatives. Consider the following example:
- Iane is shorter than Vilelmo. Iane bi curtior ce Vilelmo.
- Iane is as short as Vilelmo. Iane bi ta curto ca Vilelmo.
- Iane is “less short” than Vilelmo. Iane bi minire curto ca Vilelmo.
Notice the use of different prepositions in each comparison. Both X and Z can be personal pronouns, only in the subject form.
- You are shorter than me. Tu bis curtior ce eo.
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Superlative degree
Superlatives are always preceded by a definite article, and both must agree with the noun they are modifying. Thus:
- Iane bi el curtesmo. Iane is the shortest.
- Iane e Vilelmo bin li curtesmi. Iane and Vilelmo are the shortest.
Indeclinable adjectives
Some adjectives have a single form for all degrees, but the same effect is achieved placing before them the adverbs mere and mesto. Some of this adjectives are indeclinable for etymological reasons (e.g. na) or because of their nature as active participles (e.g. denemanti). Mesto however does inflect for gender and number, like a regular adjective.
|
|
|
Verbs
Verbs are the part of speech that exhibits the most morphology in Avendonian. There are ten main tenses, three moods, six persons and two numbers—passive participles inflect for gender too. Verbs in Avendonian are, in general, very regular except a small set of verbs, which includes the copula sire.
Avendonian classifies both weak and strong verbs in two conjugations, -are (first conjugation) and -ere (second conjugation). The former are the most prone to have ablaut, which changes the vowel of the stem in the perfect tenses.
Weak verbs
| active participle | ladanti | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| passive participle |
| |||||||||||||||
person tense
|
first singular eo |
second singular tu |
third singular e, si, et |
first plural vi |
second plural i |
third plural si | ||||||||||
| indicative | present | lado | ladas | lada | ladamos | ladates | ladan | |||||||||
| perfect | lade | ladasti | lado | ladamos | ladastes | ladaron | ||||||||||
| imperfect | ladaba | ladabas | ladaba | ladabamos | ladabates | ladaban | ||||||||||
| future | ladarabo | ladarabes | ladarabe | ladarabemos | ladarabetes | ladaraben | ||||||||||
| conditional | ladaraba | ladarabas | ladaraba | ladarabamos | ladarabates | ladaraban | ||||||||||
| subjunctive | present | lade | lades | lade | lademos | ladetes | laden | |||||||||
| perfect | ladase | ladases | ladase | ladasemos | ladasetes | ladasen | ||||||||||
| imperative | lada | ladan | ||||||||||||||
| active participle | ladenti | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| passive participle |
| |||||||||||||||
person tense
|
first singular eo |
second singular tu |
third singular e, si, et |
first plural vi |
second plural i |
third plural si | ||||||||||
| indicative | present | lado | lades | lade | lademos | ladetes | laden | |||||||||
| perfect | ladui | laduis | ladui | laduimos | laduites | laduin | ||||||||||
| imperfect | ladia | ladias | ladia | ladiamos | ladiates | ladian | ||||||||||
| future | laderabo | laderabes | laderabe | laderabemos | laderabetes | laderaben | ||||||||||
| conditional | laderaba | laderabas | laderaba | laderabamos | laderabates | laderaban | ||||||||||
| subjunctive | present | lada | ladas | lada | ladamos | ladates | ladan | |||||||||
| perfect | laduise | laduises | laduise | laduisemos | laduisetes | laduisen | ||||||||||
| imperative | lade | laden | ||||||||||||||
Notice:
- The only difference between active and passive participles, present indicative, future, and conditional of each conjugation is the thematic vowel. E.g. 2sg prs ind ladas vs. lades.
- Perfect subjunctive forms are perfect indicative forms with a -se suffix.
- If the thematic vowel is ⟨a⟩, then the vowel in the present subjunctive endings is ⟨e⟩, and vice versa.
- The personal endings in their most basic form are -Ø, -s, -Ø, -mos, -tes, -n.
- Imperative forms are exactly as singular and plural third-person present indicative forms. Formal imperatives are formed similarly with present subjunctive forms.
Strong verbs
Strong verbs are conjugated as weak verbs, but the main stem vowel undergoes a phonological process known as ablaut. This is present in the indicative and subjunctive perfect tense. In the following example, the tenses that remain unchanged are omitted.
person tense
|
first singular eo |
second singular tu |
third singular e, si, et |
first plural vi |
second plural i |
third plural si | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| indicative | present | scedo | scedas | sceda | scedamos | scedates | scedan |
| perfect | scide | scidasti | scido | scidamos | scidastes | scidaron | |
| subjunctive | perfect | scidase | scidases | scidase | scidasemos | scidasetes | scidasen |
person tense
|
first singular eo |
second singular tu |
third singular e, si, et |
first plural vi |
second plural i |
third plural si | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| indicative | present | evo | eves | eve | evemos | evetes | even |
| perfect | uvui | uvuis | uvui | uvuimos | uvuites | uvuin | |
| subjunctive | perfect | uvuise | uvuises | uvuise | uvuisemos | uvuisetes | uvuisen |
Second-conjugation strong verbs are much less common than first-conjugation. They are derived from Proto-Germanic j-present strong verbs, and were already scarce.
Irregular vebrs
Besides the copula, there are only two irregular verbs: duere and friiere—and derivatives thereof. In the perfect tenses, duere uses ⟨v⟩ instead of the expected ⟨u⟩: eo davi, not *eo daui, tu davis, not *tu dauis, etc.; eo davise, tu davises, etc.
friiere, on the other hand, has an irregularity in the imperfect indicative tense. The expected *eo friiia, *tu friiias, etc. is rendered as eo frigia, tu frigias, etc.
sire, to be
Like many other languages, including Romance and Germanic, the verb “to be” is very irregular. The copula is suppletive, meaning the stem changes between stems. A full conjugation paradigm is given.
| infinitive | sire | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| active participle | vesanti | |||||||||||||||
| passive participle |
| |||||||||||||||
person tense
|
first singular eo |
second singular tu |
third singular e, si, et |
first plural vi |
second plural i |
third plural si | ||||||||||
| indicative | present | bi | bis | bin | bimos | bites | bin | |||||||||
| perfect | va | vas | va | vamos | vates | van | ||||||||||
| imperfect | era | eras | era | eramos | erates | eran | ||||||||||
| future | sirabo | sirabes | sirabe | sirabemos | sirabetes | siraben | ||||||||||
| conditional | siraba | sirabas | siraba | sirabamos | sirabates | siraban | ||||||||||
| subjunctive | present | si | sis | si | simos | sites | sin | |||||||||
| perfect | vari | varis | vari | varimos | varites | varin | ||||||||||
| imperative | si | sin | ||||||||||||||
- From Proto-Germanic *beuną.
Dialects
The creator of the language has expressed their intent of overhauling the dialect system. Thus, the information hereon provided is the latest available. This section will be updated with the newest information once it is released. (October 2024) |