Moshurian: Difference between revisions
Jukethatbox (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Jukethatbox (talk | contribs) (add tenses) |
||
| Line 235: | Line 235: | ||
===Morphophonology=== | ===Morphophonology=== | ||
==Morphology== | ==Morphology== | ||
===Tenses=== | |||
In Moshurian, there are four main tenses- the present, the future, the far future and the simple past. To indicate that a phrase is in a certain tense, an ''indicator'' is used just before the object, e.g. '''''öş''' gersetigéd kestolék''(I built a house). | |||
{|class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | |||
|+ Tense indicators | |||
|- | |||
! Present !! Future !! Far Future !! Simple Past | |||
|- | |||
| (uź) || ïş || ïşé || öş | |||
|} | |||
The present tense indicator, ''uź'', is used like a [[w:Accidental (music)|natural]] in music. By default, no indicator is used to indicate the present in a non-contextual sentence, but as indicators are continuous, meaning that if an indicator is placed then all succeeding sentences will be in the indicator's tense until a new indicator appears, ''uź'' may be needed to clarify that a sentence does not follow the tense of the previous sentence.<br> | |||
'''Example:''' ''öş abáragéd udubék. budur ibiş.'' - ''I went to the park. It '''was'''<ref>Note the continuous past tense.</ref> great.''<br> | |||
''ös abáragéd udubék. uź budur ibiş.'' - ''I went to the park. (The park) '''is''' great.'' | |||
===Verbs=== | ===Verbs=== | ||
Verbs in Moshurian are inflected by default with the infinitve suffix ''-omh'', and then the root of the verb (e.g. ''dáfhér'' in ''dáfhéromh'', to eat) is inflected with a different suffix depending on the pronoun. | Verbs in Moshurian are inflected by default with the infinitve suffix ''-omh'', and then the root of the verb (e.g. ''dáfhér'' in ''dáfhéromh'', to eat) is inflected with a different suffix depending on the pronoun. | ||
| Line 242: | Line 254: | ||
! !! '''Singular''' !! '''Plural''' | ! !! '''Singular''' !! '''Plural''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Infinitive''' || ''-omh'' | | '''Infinitive''' ||colspan="2"| ''-omh'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''First person''' || ''-ék(-ïk)'' || ''-ékeŋ(-ïkeŋ)'' | | '''First person''' || ''-ék(-ïk)'' || ''-ékeŋ(-ïkeŋ)'' | ||
Revision as of 00:45, 7 October 2023
This article is a construction site. This project is currently undergoing significant construction and/or revamp. By all means, take a look around, thank you. |
| Moshurian | |
|---|---|
| uthilikh | |
 The Moshurian endonym(uthilikh) written in Moshurian script. | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈuð.ilix] |
| Created by | Jukethatbox |
| Setting | Radael |
| Native to | Moshurian Empire |
| Native speakers | ~450,000,000 (400 UH) |
Yeldhic
| |
Early forms | Kóftąbriác Yeldha
|
Standard form | Taráhus Moshurian
|
Dialects |
|
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Moshurian Empire Iśatúr Confederacy |
Recognised minority language in | Eastern Gegfen Alliance |
| Regulated by | Ministry of Linguistic Regulation |
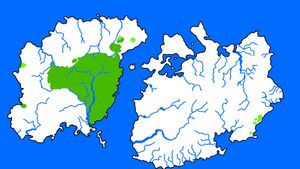 Map of Moshurian speakers. Dark green represents a Moshurian-speaking majority and light green represents a significant minority. | |
Moshurian(uthilikh) is a Týbric language spoken in mostly Talkoch. It is the most spoken language in Talkoch, and also has significant minority communities on Etzeán Island and the Eastern Gegfen Alliance, also called the Dmuriékh(lit. "far away east"). It is the sole official language of the Moshurian Empire, and is thoroughly used administratively and academically in the Moshurian Empire, no matter what one's mother tongue is.
Their exonym of Moshurian comes from a nomadic legend of the god of travel and nomads, Dündŵęk, who traveled to Tuloor Lake(the homeland of the Moshurians) in search of an inn to rest. The Moshurians had plenty of inns(möşhüř as they are called in Ancient Yeldha), and Dündŵęk was finally able to rest. After departing, he thanked the Moshurians, and later mentioned them to the other gods as simply möşhüřiànöřmà, or "inn people". This exonym stuck within nomadic circles, who then passed the exonym to the more settled peoples of Talkoch.
Phonology
Orthography
Moshurian has its own script that is read right-to-left, top-to-bottom. It's origin is heavily debated. The general consensus is that it developed from Hátuli script which in itself probably developed from Kutic cuneiform, although some prominent alternate theories include a possible link to Proto-Yeldhic runes. Some have said the script originates in Proto-Taskaric record-taking which probably arrived during the Oalanii Period. Some have said that the shape of some plosive characters corresponds with the symbol for "blood" in the logographic orthography of Ancient Izhkut, which was pronounced gúp.
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Post- alveolar/ palatal |
Retroflex | Velar | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||||||
| Stop | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | ||||||
| Affricate | t͡ʃ | |||||||||||
| Fricative | f | ð | s | z | ʃ | x | ||||||
| Approximant | j | |||||||||||
| Lateral | l | |||||||||||
| Flap | ɽ | |||||||||||
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Post- alveolar/ palatal |
Retroflex | Velar | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||||||
| Stop | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | ||||||
| Affricate | ch | |||||||||||
| Fricative | f | th | s | z | ş | kh | ||||||
| Approximant | y | |||||||||||
| Lateral | l | |||||||||||
| Flap | r | |||||||||||
Vowels
| Front | Near-front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | y | u | ||
| Near-close | ɪ | ||||
| Close-mid | e | ø | o | ||
| Mid | ə(ə̃) | ||||
| Open-mid | ε | ||||
| Open | a | ɑ | |||
| Front | Near-front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | ï | u | ||
| Near-close | ë | ||||
| Close-mid | é | ö | o | ||
| Mid | (ə)à | ||||
| Open-mid | e | ||||
| Open | á | a | |||
Prosody
Stress
Stress in Moshurian is paroxytonic, meaning stress is placed on the penultimate syllable of a word, e.g. zazuŋ, pronounced [ˈzaˌzuŋ], or uthilikh, pronounced [ˈuð.ilix].
Phonotactics
Morphophonology
Morphology
Tenses
In Moshurian, there are four main tenses- the present, the future, the far future and the simple past. To indicate that a phrase is in a certain tense, an indicator is used just before the object, e.g. öş gersetigéd kestolék(I built a house).
| Present | Future | Far Future | Simple Past |
|---|---|---|---|
| (uź) | ïş | ïşé | öş |
The present tense indicator, uź, is used like a natural in music. By default, no indicator is used to indicate the present in a non-contextual sentence, but as indicators are continuous, meaning that if an indicator is placed then all succeeding sentences will be in the indicator's tense until a new indicator appears, uź may be needed to clarify that a sentence does not follow the tense of the previous sentence.
Example: öş abáragéd udubék. budur ibiş. - I went to the park. It was[1] great.
ös abáragéd udubék. uź budur ibiş. - I went to the park. (The park) is great.
Verbs
Verbs in Moshurian are inflected by default with the infinitve suffix -omh, and then the root of the verb (e.g. dáfhér in dáfhéromh, to eat) is inflected with a different suffix depending on the pronoun.
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Infinitive | -omh | |
| First person | -ék(-ïk) | -ékeŋ(-ïkeŋ) |
| Second person | -ot | -(o)tuŋ |
| He | -eź | -iŋź |
| She | -aş | -aŋéş |
| They | -iş | -éiméş |
Example: ché dáfhérék, er dáfhérot.(lit. no eat-1.SG, but eat-2.SG.)
Syntax
Constituent order
Moshurian uses an OSV(object-subject-verb) sentence structure, such as in the sentence sö kél mosok dáfhéréiméş(grass PL cow eat-3PL), or "cows eat grass".
Noun phrase
Verb phrase
Sentence phrase
Dependent clauses
Example texts
Other resources
- ^ Note the continuous past tense.
