Moshurian: Difference between revisions
Jukethatbox (talk | contribs) m →Tenses |
Jukethatbox (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
It is one of the only surviving languages indigenous to the Munsanukh Valley, which is generally considered, alongside Tuloor Lake, to be the birthplace of the Moshurian race, culture and language. | It is one of the only surviving languages indigenous to the Munsanukh Valley, which is generally considered, alongside Tuloor Lake, to be the birthplace of the Moshurian race, culture and language. | ||
==Origin== | ==Origin== | ||
Moshurian originates in Kóftąbriác Yeldha, the language spoken by the Paleoyeldhic people who first settled the Munsanukh<ref>''Munsanukh'' is a loanword from the indigenous Sudún language, ''*mzṹ'waẜn'', meaning "river through mountains".</ref> Valley following the eastern exodus of indigenous peoples. Eventually, a landslide blocked off any sort of entry or exit of the Munsanukh Valley save for the surrounding mountains and Tuloor Lake, forcing the Paleoyeldhic settlers to begin to congregate in larger "cities<ref>Translated from Zeror of Ilda's '' | Moshurian originates in Kóftąbriác Yeldha, the language spoken by the Paleoyeldhic people who first settled the Munsanukh<ref>''Munsanukh'' is a loanword from the indigenous Sudún language, ''*mzṹ'waẜn'', meaning "river through mountains".</ref> Valley following the eastern exodus of indigenous peoples. Eventually, a landslide blocked off any sort of entry or exit of the Munsanukh Valley save for the surrounding mountains and Tuloor Lake, forcing the Paleoyeldhic settlers to begin to congregate in larger "cities<ref>Translated from Zeror of Ilda's ''Ildaska Mondenikās'', where the word ''ogetöhmnudu''(''lit'' many houses built of wood) is used to probably refer to the congregated settlements of the Paleoyeldhic settlers.</ref>". These consecutive events over centuries eventually led to the establishment of Ťhàfhü, which further began to centralise the now incredibly diverse populations of the valley. | ||
The first mention of the Moshurians in literature was in Zeror of Ilda's<ref>in 406 BH, during the golden age of Moshuria, Zeror of Ilda wrote the '' | The first mention of the Moshurians in literature was in Zeror of Ilda's<ref>in 406 BH, during the golden age of Moshuria, Zeror of Ilda wrote the ''Ildaska Mondenikās''(''History of Ilda'', ''Ilda'' being a synonym for the wider eastern Talkoch coast.), which documented the history of eastern Talkoch as he knew it.</ref> ''Ildaska Mondenikās''. in the literary work, the Moshurians are called by various names: Zeror states that in his home region of Ilda, they are called the ''Tulōrii''(people of Tuloor (Lake)), while in neighbouring Maranösia they are known by their most common exonym, the ''Muẕorii''([[Ilda]]nified version of [[Ancient Yeldha]] ''möşhüř''). in the Mezcof Basin, they were apparently known by two names; ''Oētuɫii''<ref>From the Moshurian endonym, ''uthilikh''</ref> and ''Meizirii''<ref>How the exonym arrived in the Mezcof is unclear, although Zeror theorises that it may have been from the Piryētk word ''mud̪ēbe''.</ref>. | ||
==Phonology== | ==Phonology== | ||
Revision as of 21:59, 15 October 2023
| Moshurian | |
|---|---|
| uthilikh | |
 The Moshurian endonym(uthilikh) written in Moshurian script. | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈuðˌilix] |
| Created by | Jukethatbox |
| Setting | Radael |
| Native to | Moshurian Empire |
| Ethnicity | Moshurians, Kă people |
| Native speakers | ~450,000,000 (400 UH) |
Yeldhic
| |
Early forms | Kóftąbriác Yeldha
|
Standard form | Taráhus Moshurian
|
Dialects |
|
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Moshurian Empire Iśatúr Confederacy |
Recognised minority language in | Eastern Gegfen Alliance |
| Regulated by | Ministry of Linguistic Regulation |
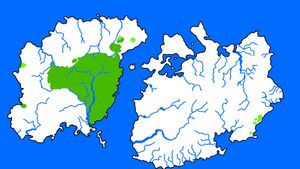 Map of Moshurian speakers. Dark green represents a Moshurian-speaking majority and light green represents a significant minority. | |
Moshurian(uthilikh) is a Týbric language spoken in mostly Talkoch. It is the most spoken language in Talkoch, and also has significant minority communities on Etzeán Island and the Eastern Gegfen Alliance, also called the Dmuriékh(lit. "far away east"). It is the sole official language of the Moshurian Empire, and is thoroughly used administratively and academically in the Moshurian Empire, no matter what one's mother tongue is.
Their exonym of Moshurian comes from a nomadic legend of the god of travel and nomads, Dündŵęk, who traveled to Tuloor Lake(the homeland of the Moshurians) in search of an inn to rest. The Moshurians had plenty of inns(möşhüř as they are called in Ancient Yeldha), and Dündŵęk was finally able to rest. After departing, he thanked the Moshurians, and later mentioned them to the other gods as simply möşhüřiànöřmà, or "inn people". This exonym stuck within nomadic circles, who then passed the exonym to the more settled peoples of Talkoch.
It is one of the only surviving languages indigenous to the Munsanukh Valley, which is generally considered, alongside Tuloor Lake, to be the birthplace of the Moshurian race, culture and language.
Origin
Moshurian originates in Kóftąbriác Yeldha, the language spoken by the Paleoyeldhic people who first settled the Munsanukh[1] Valley following the eastern exodus of indigenous peoples. Eventually, a landslide blocked off any sort of entry or exit of the Munsanukh Valley save for the surrounding mountains and Tuloor Lake, forcing the Paleoyeldhic settlers to begin to congregate in larger "cities[2]". These consecutive events over centuries eventually led to the establishment of Ťhàfhü, which further began to centralise the now incredibly diverse populations of the valley.
The first mention of the Moshurians in literature was in Zeror of Ilda's[3] Ildaska Mondenikās. in the literary work, the Moshurians are called by various names: Zeror states that in his home region of Ilda, they are called the Tulōrii(people of Tuloor (Lake)), while in neighbouring Maranösia they are known by their most common exonym, the Muẕorii(Ildanified version of Ancient Yeldha möşhüř). in the Mezcof Basin, they were apparently known by two names; Oētuɫii[4] and Meizirii[5].
Phonology
Orthography
Moshurian has its own script that is read right-to-left, top-to-bottom. Each symbol can be easily deciphered by simply looking at how high or low the symbol is. If the symbol goes down below the line on the paper, it is a consonant.
The origin of the Moshurian alphabet is heavily debated. According to the Gécheb Bizörith, the Moshurian alphabet was designed by a secret society called Akhakuöm, who took inspiration from the Tiragii military cuneiform. Eventually after the bust of Akhakuöm by the Moshurian state, the script was changed to fit the standard Moshurian dialect and re-issued as the government Moshurian alphabet.
in the Sóvók religion, one of the books in the Idērigidwi claims that a man named Udeldoi presented a script to the king of Moshuria so as to record military victories for propaganda.
Both of these interpretations are considered simply as urban legend, as orthographic analysis of the Izkanà(one of the earliest Moshurian documents) by calligraphers showed that the early Moshurian alphabet had many similarities with the logographic Oalanii[6] script, which may have influenced Munsanukh orthographies as a whole.
in fact, the glyph for /b/ may be descended from the Oalanii glyph for the word *ʔbVn, meaning "tree", which influenced its shape.
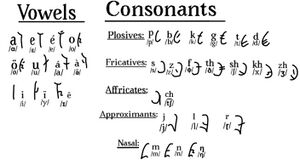
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Post- alveolar/ palatal |
Retroflex | Velar | Glottal | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||||||||
| Stop | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | ||||||||
| Affricate | t͡ʃ | |||||||||||||
| Fricative | ɸ | (θ)[7] | ð | s | z | ʃ | ʒ | x | h | |||||
| Approximant | j | |||||||||||||
| Lateral | l | |||||||||||||
| Flap | ɽ | |||||||||||||
Vowels
| Front | Near-front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | y | u | ||
| Near-close | ɪ | ||||
| Close-mid | e | ø | o | ||
| Mid | ə̃ | ||||
| Open-mid | ε | ||||
| Open | a | ɑ | |||
Prosody
Stress
Stress in Moshurian is paroxytonic, meaning stress is placed on the penultimate syllable of a word, e.g. zazuŋ, pronounced [ˈzaˌzuŋ], or uthilikh, pronounced [ˈuð.ilix].
Phonotactics
Syllables in Moshurian typically follow the pattern of (C)V(C), or (consonant)-vowel-(consonant).
Morphology
See also: Moshurian/Swadesh list.
Tenses
In Moshurian, there are four main tenses- the present, the future, the far future and the simple past. To indicate that a phrase is in a certain tense, an indicator is used just before the object, e.g. öş gersetigéd kestolék(I built a house).
| Present | Future | Far Future | Simple Past |
|---|---|---|---|
| (uź) | ïş | ïşé | öş |
The present tense indicator, uź, is used like a natural in music. By default, no indicator is used to indicate the present in a non-contextual sentence, but as indicators are continuous, meaning that if an indicator is placed then all succeeding sentences will be in the indicator's tense until a new indicator appears, uź may be needed to clarify that a sentence does not follow the tense of the previous sentence.
Example: öş abáragéd udubék. budur ibiş. - I went to the park. It was[8] great.
ös abáragéd udubék. uź budur ibiş. - I went to the park. (The park) is great.
Nouns
Nouns in Moshurian have two forms: the infinitive and the accusative. The infinitive, like with verbs, is essentially the raw form of the noun, with no suffixes. The accusative is the infinitive + the suffix -géd, and is used when a verb is acting upon an object in a sentence. There are some exceptions, such as nouns who's infinitive end with /ŋ/, such as zazuŋ, and in this case the suffix changes from -géd to -éd.
Verbs
Verbs in Moshurian are inflected by default with the infinitve suffix -omh, and then the root of the verb (e.g. dáfhér in dáfhéromh, to eat) is inflected with a different suffix depending on the pronoun.
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| infinitive | -omh | |
| First person | -ék(-ïk) | -ékeŋ(-ïkeŋ) |
| Second person | -ot | -(o)tuŋ |
| He | -eź | -iŋź |
| She | -aş | -aŋéş |
| They | -iş | -éiméş |
Example: ché dáfhérék, er dáfhérot.(lit. no eat-1.SG, but eat-2.SG.)
Syntax
Constituent order
Moshurian uses an OSV(object-subject-verb) sentence structure.
Noun phrase
- Sögéd kél mosok dáfhéréiméş.
- grass-ACC PL cow(PL) eat-3PL.
- Cows eat grass.
- grass-ACC PL cow(PL) eat-3PL.
in this sentence, sögéd is the object, mosok is the subject, and dáfhéréiméş is the verb with inflection. in noun phrases, Moshurian still uses the object-subject-verb structure.
Verb phrase
See also:Verbs.
Imperative
- sögéd duà ché dáfhér!
- grass-ACC IMP no eat.ROOT!
- Do not eat the grass!
- grass-ACC IMP no eat.ROOT!
In imperative verb phrases, the imperative indicator, duà, is put before the verb, as ché is still considered, at least grammatically, part of the verb when present. Additionally, verbs take on their root form, as opposed to their infinitive form in said sentence type.
In this sentence, sögéd is the object, and the verb is dáfhér. The subject does not appear and is instead implied to be the recipient of the imperative phrase.
Sentence phrase
Dialects
Standard dialect
The standard dialect of Moshurian is, according to the Ministry of Linguistic Regulation(MLR), officially the Taráhus dialect spoken in the capital, although Tárahus is so large that several districts have developed their own dialects, many of which who are vastly different from each other, so it is still unclear on which is considered the standard within the family of Taráhus dialects.
Inner Taráhus dialect
The Inner Taráhus dialect is generally considered by Moshurian linguistics to be what the MLR constitution means in the line:
"[...] The dialect spoken around the capitol and the [MLR] shall be considered the dialect to be used for the transmission of necessary information to Moshurian citizens. For non-Moshurian areas of the Empire, the standard [dialect][9] of the most prominent non-Moshurian language shall be used to convey said information."
However, this quote can be considered quite vague, as the MLR and the wider capitol has changed location many times in Taráhus. One year, the MLR headquarters was located in the district of Oźmaneli, where a borderline unintelligible dialect of Moshurian is spoken, and, for that year, the bizarre Oźmaneli dialect was considered the standard, causing great confusion to non-Oźmanelis.
Oźmaneli dialect
The Oźmaneli dialect is a dialect spoken in the inner city district of Oźmaneli. It has garnered much attention from linguists, as its pronunciation is widely different from typical pronunciation. Here are just a few differences between the Inner Taráhus and Oźmaneli dialects:
Phonetic differences
In general, the pattern seems to be that voiceless consonants tend to get voiced, but this is not always the case.
- /ŋ/ is pronounced [ɳ] or [ɟ][10]
- /x/ is pronounced [ɣ]
- /ð/ is pronounced [θ][11]
- /b/ is sometimes pronounced [ʙ] before a /ɽ/.
- Speaking of /ɽ/, it is pronounced [ɬ]
Morphological differences
- Standard mosok ⇒ Oźmaneli mudźuk.
- Standard pusadi ⇒ Oźmaneli bsédodifh.
- Standard uthilikh ⇒ Oźmaneli utuɟul.
- Standard surus/zazuŋ ⇒ Oźmaneli şild/soéş.
Oalan dialect
The Oalan dialect is the specific dialect of Moshurian spoken in the city of Oalan and its surrounding suburbs. The Oalan dialect is not as different from the Taráhus dialect, although /ð/ is pronounced [θ], which is a conventional pronunciation among most non-standard dialects.
Loïha dialect
The Loïha dialect is the dialect of Moshurian speakers who reside in the Golden Plain. Loïha is possibly the most distinct but still intelligible dialect of Moshurian. This is because there are very few morphological differences, but quite large sound changes.
Notably, the Loïha dialect can be split into two groups: the Western and Eastern dialects. Western Loïha tends to be a bit more distant from the standard, whereas Eastern is the opposite. However, what is universal across both dialects is that glottal stops are incorporated in everyday speech.
Sound changes
- From /ð/ → [ɖ](Western) or [θ](Eastern)
- From /x/ → [ʁ](Western) or [ʕ](Eastern)
- In diphthong 〈tu〉→ /ʈʊ/(Western) or /t̚y/(Eastern).
Odezyë dialect
Far East dialect
Sépenzg dialect
Example texts
Other resources
- ^ Munsanukh is a loanword from the indigenous Sudún language, *mzṹ'waẜn, meaning "river through mountains".
- ^ Translated from Zeror of Ilda's Ildaska Mondenikās, where the word ogetöhmnudu(lit many houses built of wood) is used to probably refer to the congregated settlements of the Paleoyeldhic settlers.
- ^ in 406 BH, during the golden age of Moshuria, Zeror of Ilda wrote the Ildaska Mondenikās(History of Ilda, Ilda being a synonym for the wider eastern Talkoch coast.), which documented the history of eastern Talkoch as he knew it.
- ^ From the Moshurian endonym, uthilikh
- ^ How the exonym arrived in the Mezcof is unclear, although Zeror theorises that it may have been from the Piryētk word mud̪ēbe.
- ^ Oalanii is an archeological term used to describe the Proto-Taskaric inhabitants of what is now the city of Oalan. Although the Oalanii had their own script, no surviving documentation mentions their actual endonym, so they are called the Oalanii after the city where the first archeological remains of ancient Oalan were found.
- ^ Only used in certain dialects. Still orthographically represented as 〈th〉.
- ^ Note the continuous past tense.
- ^ The original constitution uses the word "edition"(kuchbarà) to refer to standard dialects of minority languages, which is kind of confusing.
- ^ Why /ŋ/ is pronounced [ɟ] is one of the greatest mysteries of Moshurian.
- ^ The pronunciation of /ð/ as [θ] is a consistent pattern among most non-standard dialects of Moshurian, although some Oźmanelis pronounced /ð/ as [ɕ].