Soc'ul': Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
*Glottalized consonants are realized with simultaneous creaky voicing for most speakers, but some speakers realize glottalized stops as implosive either in free variation or word-initially. | *Glottalized consonants are realized with simultaneous creaky voicing for most speakers, but some speakers realize glottalized stops as implosive either in free variation or word-initially. | ||
*Aspirated consonants have light to moderate aspiration. | *Aspirated consonants have light to moderate aspiration. | ||
*Pre-stopped nasals may be initially either voiced or voiceless, but are more often voiceless. | |||
*In far western dialects, palatalized and plain velar consonants may be realized as prevelar and postvelar respectively. | *In far western dialects, palatalized and plain velar consonants may be realized as prevelar and postvelar respectively. | ||
**/ɰ(ˀ)/ and [ɣ(ˀ)] may be realized as either prevelar or postvelar, or merge into [j(ˀ) ʝ(ˀ)]. | **/ɰ(ˀ)/ and [ɣ(ˀ)] may be realized as either prevelar or postvelar, or merge into [j(ˀ) ʝ(ˀ)]. | ||
Revision as of 22:58, 22 November 2024
| Soc'ul' | |
|---|---|
| soc'ul' | |
 Jul soc'ul', "Soc'ul' language" in the Wacag script | |
| Pronunciation | [so̞˧kʷʰu˩lˀ] |
| Created by | Dillon Hartwig |
| Date | 2020 |
| Setting | Pollasena |
| Native to | Knrawi Isles |
| Ethnicity | Cuoñ'o |
| Era | -1700 to -700 MT |
Wasc
| |
Early form | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Knrawi Empire |
| Language codes | |
| CLCR | qsc |
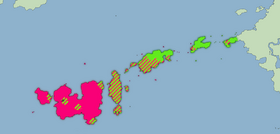 Range map of Soc'ul' (green) and Knrawi (pink), c. -1200 MT | |
Soc'ul' /ˈsoʊkʊl/ (Soc'ul': [so̞˧kʷʰu˩lˀ]) is a Wasc language spoken primarily by the Cuoñ'o people, with strong influence from Knrawi and other languages of the Knrawi Isles.
Etymology
Soc'ul', the language's autonym, is inherited from the Sekhulla autonym səkʰulːa, from Wascotl *(cek)-cek-sole-la "our tongue".
Orthography
Soc'ul' is written with the Wacag logography. Its romanization is as follows.
| A a | Á á | Ā ā | B b | B' b' | C c | C' c' | Cñ cñ | Cñ' cñ' | D d | D' d' |
| E e | É é | Ē ē | H h | I i | Í í | Ī ī | Ï ï | J j | L l | L' l' |
| M m | M' m' | N n | N' n' | Ñ ñ | Ñ' ñ' | O o | Ó ó | Ō ō | P p | Pf pf |
| Pm pm | Pm' pm' | R r | R' r' | S s | T t | Tn tn | Tn' tn' | Ts ts | Tx tx | T' t' |
| U u | Ú ú | Ū ū | Ü ü | V v | V' v' | X x | Y y | Ý ý | Z z | Z' z' |
This romanization matches IPA except
- ⟨c⟩, ⟨e⟩, ⟨h⟩, ⟨j⟩, ⟨ñ⟩, ⟨x⟩, and ⟨y⟩ represent /k/, /ə/, /ʔ/, /x/, /ŋ/, /ʃ/, and /ɰ/
- ⟨pm⟩, ⟨tn⟩, ⟨cñ⟩, ⟨pf⟩, ⟨ts⟩, and ⟨tx⟩ represent /ᵖm/, /ᵗn/, /ᵏŋ/, /p͡f/, /t͡s/, and /t͡ʃ/
- ⟨ü⟩ and ⟨ï⟩ represent /u/ and /i/ when ⟨u⟩ and ⟨i⟩ would cause ambiguity
- ⟨o⟩ represents /ə/ when realized as [o̞] except between a labialized consonant (except allophones of /u(ː)/) and a plain velar consonant (except /ɰˀ/)
- Apostrophes mark glottalization and aspiration.
- Acutes and macrons mark long and overlong vowels respectively, except in ⟨ý⟩ in which it marks glottalization.
- Labialization and palatalization are marked by surrounding vowel letters.
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial/ labiodental |
Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatalized velar/ palatal |
Velar | Labialized velar | Glottal | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | ᵖm | m | ᵖmˀ | mˀ | ᵗn | n | nˀ | ᵗnˀ | ᵏŋʲ | ŋʲ | ᵏŋʲˀ | ŋʲˀ | ᵏŋ | ŋ | ᵏŋˀ | ŋˀ | ᵏŋʷ | ŋʷ | ᵏŋʷˀ | ŋʷˀ | ||
| Stop | b | bˀ | t | d | tʰ | dˀ | kʲ | kʲʰ | k | kʰ | kʷ | kʷʰ | ʔ | |||||||||
| Affricate | p͡f | t͡s | t͡ʃ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fricative | v | vˀ | s | z | zˀ | ʃ | xʲ | (ʝ) | (ʝˀ) | x | (ɣ) | (ɣˀ) | xʷ | (ɣʷ) | (ɣʷˀ) | |||||||
| Approximant | l | lˀ | (j) | (jˀ) | ɰ | ɰˀ | (w) | (wˀ) | ||||||||||||||
| Trill | r | rˀ | ||||||||||||||||||||
- Glottalized consonants are realized with simultaneous creaky voicing for most speakers, but some speakers realize glottalized stops as implosive either in free variation or word-initially.
- Aspirated consonants have light to moderate aspiration.
- Pre-stopped nasals may be initially either voiced or voiceless, but are more often voiceless.
- In far western dialects, palatalized and plain velar consonants may be realized as prevelar and postvelar respectively.
- /ɰ(ˀ)/ and [ɣ(ˀ)] may be realized as either prevelar or postvelar, or merge into [j(ˀ) ʝ(ˀ)].
- [j(ˀ)] and [w(ˀ)] are allophones of /i(ː)/ and /u(ː)/ adjacent to vowels.
- [j(ˀ)], /ɰ(ˀ)/, and [w(ˀ)] are realized as [ʝ(ˀ)], [ɣ(ˀ)], and [ɣʷ(ˀ)] adjacent to high vowels.
- Some speakers devoice voiced obstruents adjacent to voiceless consonants.
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | i | (y) | u | |
| Mid | ə | (o̞) | ||
| Low | a | (ɒ) | ||
- All vowels can be long or overlong
- [y], [o̞], and [ɒ] are allophones of /i/, /ə/, and /a/ adjacent to labialized consonants except allophones of /u(ː)/ (though some dialects don't make this exception)
Prosody
Stress and pitch
There is no set stress position, but allophonic pitch based on vowels' surrounding consonants. For most speakers these pitches are not contrastive but are seen as proper and are required in recitations; marginal exceptions occur for speakers occur that assimilate voicing in clusters and for speakers that retain tone to some degree in loaned Knrawi or tonal substrate words. Ideophones also form an exception, often ignoring/violating pitch allophony.
| Voiceless /pre-stopped consonant |
Aspirated /voiced consonant |
Word boundary /vowel |
Glottalized consonant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voiceless /pre-stopped consonant |
high | mid | high | low |
| Aspirated /voiced consonant |
mid | |||
| Word boundary /vowel | ||||
| Glottalized consonant | mid | low | ||
| Voiceless /pre-stopped consonant |
Aspirated /voiced consonant |
Word boundary /vowel |
Glottalized consonant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voiceless /pre-stopped consonant |
high | high falling | sharp falling | |
| Aspirated /voiced consonant |
high rising | mid | low falling | |
| Word boundary /vowel | ||||
| Glottalized consonant | sharp rising | low rising | low | |
Whether glottalized pre-stopped nasals pattern as pre-stopped or glottalized varies by speaker and region.
Intonation
Declarative sentences generally have a falling pitch throughout, but volume and pitch range can be used for emphasis.
In questions the particle xen and/or the proform xad may also be emphasized with a sharp falling pitch followed by higher pitch in the following word.
Rhythm
Syllables are generally mora-timed, with syllables containing long and overlong vowels having two and three morae; in recitations, continuant coda consonants or coda clusters with them may have their own mora, and overlong syllables may instead have four morae.
Phonotactics
Syllables are at most (C(C₁))V((C₂)C), with C₁ being a non-lateral approximant and C₂ being C₁ or /ʔ/, but these maximal syllables are very rare. There are no restrictions on what clusters can occur.
Morphology
Alignment
Soc'ul' has split-S morphosyntactic alignment.
Nouns and pronouns
Nouns fall into five classes which are unmarked directly on the noun but trigger agreement in verbs and some particles. In informal speech class-2 marking is often used for class-1 nouns.
Nouns are marked for number, case, and possession by particles before the noun as follows.
| acc/erg | poss/dat | indef/pl | inal/loc/adjz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | en | ez' | he |
| 2 | nej | hej | ||
| cl1/cl2 | nu | hé | ||
| cl3 | al | nil | ez'e | hel |
| cl4 | ax | nux | hex | |
| cl5 | ád | nid' | hed' |
- Case and number/definiteness marking are optional in non-formal speech, and on nouns with suppletive plural/indefinite forms or nouns modified by numerators plural/indefinite particles are only used as a plural indefinite marker.
- Other particle groups above are optional in non-formal speech when verb agreement marking gives sufficient context.
As in Knrawi, plurality and indefiniteness are treated as one category, and many nouns mark plurality or indefiniteness with suppletion. This suppletion is most often from fossilized final-syllable reduplication in Wascotl.
Pronouns
Pronouns do not exist independently (except see Possession); the person and class of dropped nouns are instead only shown through verb agreement.
The demonstrative jál can also be used as a pronoun.
Possession
Possessive particles (alienable or inalienable) can also serve as possessive pronouns when verb agreement marking does not give sufficient context.
Inalienable possession is generally restricted to family members, body parts, inherent or permanent qualities (for example tumiad "sanctity"), and internal processes (for example c'uád "thought"). Words in the latter two categories are more flexible in which type of possession they take, varying by speaker and region.
Noun negation
Noun phrases are negated with xen', which can also function as a negative pronoun "nothing."
See also Aspect, mood, and negation
Verbs
Alignment
All verbs trigger either nominative-accusative or ergative-absolutive marking on nouns.
Aspect, mood, and negation
Verbs are marked for aspect and mood by particles preceding the verb.
| pfv | prog | cont | subj | abil | res | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| en | miu | ji, laz | uc' | c'e | c'ez | |
| inch | r'uz | miur' | jir', lar' | r'uc' | c'er' | r'ez |
| term | coi | miuc | jiuc, lauc | cuc' | c'oc | coz |
| neg/q | xen | miun | jin, lan | nuc' | c'en | nez |
- The perfective particle en is optional except in formal speech, and in non-formal speech can used to reset aspect-mood in embedded or sequential clauses or to contrast with other nearby markers.
- The progressive and continuative particles are often used contrastively as imperfective nonpresent and imperfective present markers respectively.
- Subjunctive mood is often also used for future marking.
- The negation/question particle xen can be reduplicated after the verb to disambiguate it as a question particle.
These particles can cooccur, and are often combined for more specific or otherwise combined meanings, but in serial verbs are only used before the first verb. All but en can also be used as standalone verbs (see Copula), but do not need to take any agreement.
xen and xen' can be used together with the same meaning as the latter on its own, and in formal speech prohibitive sentences use jaj in place of xen.
Agreement
Verbs agree with the person and class of their agent and patient as follows.
| >1 | >2 | >cl1 | >cl2 | >cl3/cl4 | >cl5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sec- | soc- | seic- | seh- | setn- | cu- |
| 2 | cor- | coz- | cor- | coh- | cox- | |
| cl1 | íús- | íúy- | aí- | íúh- | íún- | íū- |
| cl2 | har- | hau- | z'ai- | ∅- | han- | hu- |
| cl3 | in- | nau- | ixú- | nal'- | iy- | nu- |
| cl4 | an'- | ñ'o- | ñ'ai- | ñ'ih- | añ'- | u- |
| cl5 | us- | úu- | úi- | ba- | úx- |
- Intransitive verbs are marked with patient agreement of the agent's class, and impersonal verbs are unmarked.
- Possessed nouns trigger agreement as their possessor unless a possessive particle is used.
Copula
The copula hazen inflects as follows.
| >1 | >2 | >cl1 | >cl2 | >cl3/cl4 | >cl5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | syen | suén | syíún' | sehan' | setnayn | sun' |
| 2 | coren | cozen | coríún' | coban' | coriyn | cun' |
| cl1 | íúsyen | íúzen | aíún' | íúban' | íúnen | íún' |
| cl2 | haryen | huén | hazíún' | hazen | harin' | hun' |
| cl3 | nasen | nuén | naíún' | nahlan' | nayn | nun' |
| cl4 | an'yen | ñ'ón | ñ'aíún' | ñ'iban' | ñ'in' | un' |
| cl5 | sén | uén | uaíún' | ban' | uinayn |
If aspect-mood marking is used, the copula is optionally dropped.
Serial verbs
Verbs are often serialized in non-formal speech, in which the verbs' agreement marking may or may not match.
Aspect-mood marking and preceding particles are applied to the first verb in the serialization. Following particles are applied after either the first or last verb.
Serialization is especially common when the first verb is an intransitive or sensory verb.
Adjectives and adverbs
Adjectives are not their own class of words, but are derived from nouns or verbs. Most often they are derived by zero-marking before other nouns or verbs, or with suffixes or particles (see Part-of-speech modifiers).
Some of these derived adjectives and adverbs have meanings that don't directly correspond to the word they are derived from; in most cases this is due to homophony in ancestral Wascotl words after dropping of the adjective suffix *-(c)osc or regular merging with forms ending in *-(o)tl (*-osc and *-otl both becoming -ux), for example toc "knife" or "sharp" from Wascotl *tequ- and *tequ-osc respectively.
Comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs are formed by placing the second compared word after with the postposition je, but see also (see Reduplication).
Postpositions
Soc'ul' has a limited set of general postpositions: locative eý, lative je, proximal/comitative ne, ablative xenuz, and distal/ablative/abessive xen'e.
More specific adpositions, when needed, are formed with {location} ... {postposition} constructions (for example m'e ... eý "on" from m'e "top").
Numerals
Soc'ul' uses base-12 numerals except in formal writing and very formal speech, which uses base-24 numerals with 13-24 derived from Knrawi.
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nouns are not marked for number when using numerals.
Derivational morphology
Part-of-speech modifiers
The plural/indefinite particle ez'e is also used to nominalize words from other parts of speech. Agentive nouns can be derived either from ez' (the class-2 inflection of ez'e) or from dedicated agentive suffixes -uóc and -ih.
The suffix -z'i is
Inalienable pronouns can also be used as particles following adjectives to disambiguate them from possessor nouns; this disambiguation can also be done with the suffix -jí (which is also used to disambiguate adjectives from verbs, and to derive verbs adjectives).
The preceding particle hez'i disambiguates and derives adverbs from other parts of speech.
-ax
The causative suffix -ax can be used productively on any verb, as well as being used nonproductively on some verbs deriving verbs of new meanings.
Reduplication
Most words (other than nouns and conjunctions, but including some particles) can be fully reduplicated after the word for augmented or intensified meaning. In verbs this can also mark an iterative or contrastive meaning, and in adjectives and adverbs it can also mark a comparative or superlative meaning when the thing being compared to is absent in the sentence.
The reduplicated word comes after any particles that would otherwise be directly after the word. Reduplicated verbs only mark agreement on the first verb.
Triplication is also used by some speakers for further augmentation/intensification, but this is not considered standard.
Syntax
Constituent order
All clauses are strictly VO, and subject and object order are flexible with sufficient marking or context, but VSO order is most common.
Noun and verb phrases
All modifiers follow their head noun or verb, except aspect-mood particles precede verbs and the demonstrative jál precedes nouns. Generally numerators follow adjectives and possessors follow all other modifiers, but otherwise modifier order is flexible.
Dependent clauses
Dependent clauses follow the head they modify after all other dependents, and are usually marked with a relativizer āh-.
Example texts
Universal Declaration of Human Rights Article 1
Habaiý co jutxux hez'i yanux jem'uj ne hez'i diuzi ez'e muzm'e. Sauciý xeu txisye uc' āhjí xec hez'i r'úiad ez'e céuxz'i.
Habai-(i)ý
bear-PASS
co
person
jutxux
all
hez'i
advz
yanux
freedom
jem'uj
equality
ne
with
hez'i
advz
diuzi
dignity
ez'e
NZ
muzm'e.
own
Sauc-iý
grant-PASS
xeu
reason
txisye
conscience
uc'
SUBJ
āh-jí
REL-do
xec
RECP
hez'i
advz
r'úiad
way
ez'e
NZ
céux-z'i.
brother-VBZ