Verse:Hmøøh/Talma
- The similarity of the name to the Terran composer Louise Talma is coincidental.
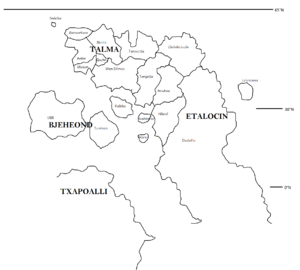
Talma (Skellan: Talma /tʰãmə/, from Windermere Tălma /təlˈma/, from tăle ăma 'mother land') is a (culturally-defined) continent of the conplanet Tricin. It is actually the northwestern portion of a landmass called Eta-Talma (Windermere: Eta-Tălma), the southern part of which is Etalocin. Bjeheond is located to the south of Talma.
Todo
History
Pre-Calamities
"Warring States" period
Windermere Empire
Grouidite Revolution and aftermath
A major war broke out about 80 years after the publication of Grouid's manifesto.
Post-Revolution
Geography and climate
Talma is located 30°N - 65°N and has a temperate climate. A natural barrier separates it from Etalocin.
Isolated areas:
- Bhadhagha Island
- Nūrē
- The Tumacas
- Qaaroshter
- Skella (to an extent)
Economy
Languages
Modern Talman languages
These are some modern Talman languages:
- Talmic
- Skellan
- Snachian
- Anbirese
- [ejectiveWelsh thing]
- Qenian
- Qazhrian
- Roshterian
- Lakovic
- Windermere
- Tseezh
- Häskä
- Tsrovesh
- Tsimulh
- Mategian
Of these, Anbirese and Windermere are the most spoken languages. Many modern Talmans, especially Talmic speakers, speak Skellan as a second language. Swuntsim is spoken by some people in the minority Swuntsim ethnicity.
Society
Talma boasts a robust tradition of intellectual activity in the sciences, philosophy, and music. However, Talman society historically was a highly stratified meritocracy, which historically caused considerable friction between social classes.
Historically the social cost of nonconformity was quite severe. Crimes were punished harshly. Legally, the most common punishments were exile, imprisonment and forced labor but often the criminals were tortured, castrated, or executed, in addition to public shaming.
Impact of birth control
Hmlai (Skellan) is a contraceptive plant native to Talma that's easy to farm, thus providing premodern Talmans with cheap birth control. (We'll call it silphium in English.)
Some possible consequences of Talman silphium:
- Polygamy was legally recognized in Talman cultures, though many people are monogamous.
- Premodern Talman culture doesn't have a traditionalist sexual morality (neither does modern Talman culture).
- Equal rights for women has always been an ideal, if not reality, in Talman culture in recorded history. (This is not because of some innate moral superiority of Talmans but largely due to external factors.)
- Women are less likely to die young in childbirth and thus more likely to participate in public society.
Pre-modern vulgar culture
The plebs were largely semi-literate but otherwise uneducated and were forced to do menial labor and/or live in unsanitary places. Non-elite military-age men were often drafted into wars.
The common people had plays, and later novels, as forms of entertainment.
Modern
The rise of the merchant class and the free-market economy marks the beginning of Etalocian modernity.
Contemporary social issues include:
- how much welfare?
- size of standing army?
- death penalty
- national parks etc.
- basic income and its effects
- automation
- effective altruism
- gender stuff
- etc.
The election system used is usually approval voting. Some countries use ranked-choice voting.
Agile legislation is considered a design ideal to strive for in Etalocian democracies.
There is no legal concept of marriage in modern Etalocian societies; marriage is essentially a "religious" concept to be negotiated by individuals.
Education
Traditional education
Elite education
Elite boys were first educated in either a "boarding school" which taught a curriculum of rhetoric, poetry, classical language, math, fine arts, and science, or a military academy. By age 15 they were expected to enter into university study (or military service) in order to specialize into one or more roles in elite society. To enter specialization one was required to pass the entrance exam administered by a university. If one could not enter specialist training he was effectively banished from elite society. Those who passed the "boarding school" curriculum but failed to specialize usually worked as "managers", low-level officials or schoolteachers. One or more requirements could be waived for a child of exceptional ability in one area.
Elite girls also had access to a full boarding school education (though not to a military education), enough for them to be independent. Unlike males, however, they were not expected to undergo male specialization. Women who wished to become schoolteachers or musicians received appropriate additional training. Some women, mostly courtesans-in-training or those who aspired to marry the most powerful aristocrats, underwent education meant for male specialists.