We're back! Sorry, bad combo of sickness, funeral and a month-long trip abroad. The site is back now. |
Lahob languages: Difference between revisions
m (→Name) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
==Common characteristics== | ==Common characteristics== | ||
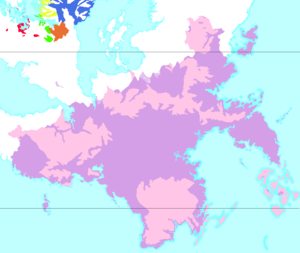
[[File:Lahob languages.png|thumb|Distribution of the Lahob branches in their home continent of Márusúturon.]] | |||
It is difficult to point out general characteristics common to all Lahob languages because of the high divergence between the Core Lahob ones and the Chlouvānem branch. General traits are: | It is difficult to point out general characteristics common to all Lahob languages because of the high divergence between the Core Lahob ones and the Chlouvānem branch. General traits are: | ||
* A complex morphosyntactic alignment based on triggers, present with seven triggers in Proto-Lahob and retained with no change in classical Chlouvānem, and varyingly modified in other languages, typically with a few less voices (among modern languages, the only ones that retain the full set of triggers are some Southern Chlouvānem languages, notably including the Hālyanēṃṣi vernacular). The most typical trigger system surviving among Core Lahob languages is patient-agent-locative(-instrumental). | * A complex morphosyntactic alignment based on triggers, present with seven triggers in Proto-Lahob and retained with no change in classical Chlouvānem, and varyingly modified in other languages, typically with a few less voices (among modern languages, the only ones that retain the full set of triggers are some Southern Chlouvānem languages, notably including the Hālyanēṃṣi vernacular). The most typical trigger system surviving among Core Lahob languages is patient-agent-locative(-instrumental). | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 31 July 2019
- Not to be confused with the Lakovic languages.
| Lahob | |
|---|---|
| Lahob-Imuniguronian; Lahobic | |
| Created by | – |
| Geographic distribution | most of Márusúturon |
| Linguistic classification | One of Calémere's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Lahob |
| Subdivisions |
|
The Lahob languages (also known as Lahou, Lahobic, Neshlenkentian, or Lahob-Imuniguronian; Yeł. Lawo: tławiyuk notłe; Łaȟoḇaror: łaȟoḇu sorä; Chl.: hūlisakhāni dhāḍai (rarely lahāvumi dhāḍai; Nor.: þêukor Lahou, Cer.: šérošu Raó) are a large Calémerian language family, most widely spoken on the continent of Márusúturon[1].
There are six currently recognized living Lahob branches, often grouped in two macro-branches:
- Northern Lahob, Core Lahob, or Lahob proper - an occasionally used, at least geographically relevant, category for the five non-Chlouvānem branches spoken in Northern Márusúturon:
- Kenaywanic languages, spoken mainly in western Sprêny, including Łōplan and others, but also Kȯtıme Qoşazırme, spoken at Taiga Crane Lake (Kȯt Qoşazırme) in central Kerbellion, the westernmost Core Lahob language and one of the most divergent.
- Central Lahobic languages, spoken across the country of Peħlleit and a few communities in the far southwest (Konyzałay peninsula) of Koitrûx; including Łohofál, Sulutamilian Minwan, Łokudár, Dal Ming Wang, and Tłowpedar.
- Łogawenek languages, spoken in the countries of Ferbêny, most of Alêig, and moribund in far northern Soenjŏ-tave; including ...
- Nayzehenyn languages, spoken mainly across most of central, northern, and eastern Koitrûx, including Yełeshian Lawo, Shershan Lawo, Nahawi, and others;
- Tłašnelek languages, spoken in northwestern Koitrûx as well as some isolated coastal communities further north and west, both on Gurdugal and on the Márusúturonian mainland.
- Chlouvānem languages (or Imuniguronian languages), including Chlouvānem and all of its descendants, which is the most spoken and widespread branch, counting for nearly the entirety of all Lahob speakers.
The Lahob family is one of many language families - including the unrelated Kenengyry and Samaidulic families, as well as various not better classified isolates - that most likely originated in the area of Márusúturon between the Carpan and the Skyrdegan seas, roughly between 30° and 40°N. The Urheimat of Proto-Lahob speakers is thought to be either the western shore of the High Ivulit (i.e. modern day Leñ-ṱef or Ebed-dowa) or the area around the Little Ivulit (today southern Leñ-ṱef, Līnajoṭa, or southern Qualdomailor). From there, the Lahob peoples mainly expanded northwards, up to the taiga of northern Márusúturon, except for a few tribes (notably the Ur-Chlouvānem) who migrated southeastwards, into the Nīmbaṇḍhāra-Lāmberah plain. In most of this area, however, Lahob languages were replaced by the later spread first of Samaidulic and then of Kenengyry languages, so that practically all non-Chlouvānem Lahob languages are spoken in the Northern Márusúturonian taiga, along the Orcish Straits.
The Ur-Chlouvānem eventually settled in the far southern part of the Plains, where they intermixed with the local populations, forming a distinct ethnicity whose main connection with the other Lahob peoples is linguistic rather than genetic. Eventually the Chlouvānem language, the only attested ancient Lahob language, became the liturgical language of the Yunyalīlta, which led it to be spread across all of Márusúturon and become, as of today, the most spoken language of the planet.
By number of native speakers, they are the second-largest on the planet (just slightly behind the mostly Védrenian Yombu-Raina languages), however the vast majority of Lahob speakers speak a language belonging to the Chlouvānem branch.
Excluding Chlouvānem (and its daughter languages) with more than 1,9 billion speakers, the other Lahob languages are fairly small by number of speakers, with less than 100,000 speakers collectively: Nordûlaki is the only official language, and the main lingua franca, across the area (except for the areas in Soenjŏ-tave), and in the most densely populated areas the vast majority of people are Nordûlaki-speaking descendants of Evandorian colonists. Lahob speakers are mostly clustered in a few villages, rarely exceeding a thousand inhabitants. Central Lahobic and Nayzehenyn are the most spoken among these branches, with the three most spoken languages being, in order, Yełeshian Lawo, Łohof-aðá, and Nahawi.
The situation in the Chlouvānem-speaking areas is almost the reverse, as it is the Dachsprache everywhere across the Chlouvānem Inquisition, in a state of diglossia with thousands of local vernaculars which are either descendants of Chlouvānem itself, Chlouvānem-based creoles, or totally unrelated languages.
Name
The Lahob languages have a few competing names, all ultimately derived from Lahob proper:
- Lahob, Lahou, or Lahobic all derive from the ethnonym Łaȟoḇ [ɬaˈχɔβ] in Łaȟobarir, through Nordulaki Lahou [laˈhɔʊ̯]; the ultimate origin is Proto-Lahob *ɬakʰober, which is the common self-designation for many Lahob peoples (e.g. Łohof, Łogawe, Łokow, Łoku, Tɬow).
- Neshlenkentian derives from Łogawe nɛ łenkɛnt, meaning either "our family" or "we are a family"; łenkɛnt is ultimately connected to Proto-Lahob *liŋkajnet, the root for "family" in many non-Chlouvānem Lahob languages.
- Lahob-Imuniguronian is an outdated term which was common when the relationship between the Core Lahob languages and Chlouvānem hadn't been proved yet; as acceptance of the theory grew, the term Lahob-Imuniguronian was replaced by the simpler Lahob, that had been used for the Core Lahob languages until then. "Imuniguronian" is the English adaptation of imúnigúronen, the Cerian term (common to most Western languages) for "Chlouvānem".
Chlouvānem linguists have largely adopted the Nordûlaki term Lahou as the ethnonym for all Lahob peoples in the form lahāvai; however, the whole of the language family is most often referred to as hūlisakhāni dhāḍai, after the mythological ancestral land of Hūlisakhāna mentioned in early Chlouvānem literature. Curiously, the legend of Hūlisakhāna was probably non-Lahob in origin and the term is most likely not of Lahob origin too.
The form lahāvumi dhāḍai (or the rarer lahau ga dhāḍai) usually refers to what is known as Northern Lahob, Core Lahob, or Lahob proper in Western linguistics, however recently (and especially in Chlouvānem-language papers written by linguists from Qualdomailor, Brono, or the Kenengyry area) some linguists have begun using it for the whole family. Somewhat confusingly, kēhamyuñci lahāvumi dhāḍai, an exact translation of "Northern Lahob languages", is typically used for the Nayzehenyn languages only.
Ethnonyms
It is notable how the vast majority of Lahob peoples have ethnonyms based on two single Proto-Lahob roots, which however are still present in some way in nearly all languages of the family, *ɬakʰober (people) and *wānəme (horde, tribe, group):
- *ɬakʰober as ethnonym for e.g. the Łaȟob, Łohof, Łokow, Łogawe, Tɬow, Nahawi; also reflexed as e.g. tɬawpe in Bɔni, tłɔwr in Waam (both "family"), şakȯf (house, home) in Kȯtıme Qoşazırme, or chlågbhah (tribe) in Chlouvānem;
- *wānəme as ethnonym for e.g. the Aem, Bɔni, Wonum, Waam, Bāmn, the -vānem part in Chlouvānem (chlǣvānem originally meant "Golden Horde"), and the -wan in Minwan (min wan meaning "our folk"); also reflected as e.g. wang (group) in Łohof-aðá and womme (village) in Tɬow.
Common characteristics
It is difficult to point out general characteristics common to all Lahob languages because of the high divergence between the Core Lahob ones and the Chlouvānem branch. General traits are:
- A complex morphosyntactic alignment based on triggers, present with seven triggers in Proto-Lahob and retained with no change in classical Chlouvānem, and varyingly modified in other languages, typically with a few less voices (among modern languages, the only ones that retain the full set of triggers are some Southern Chlouvānem languages, notably including the Hālyanēṃṣi vernacular). The most typical trigger system surviving among Core Lahob languages is patient-agent-locative(-instrumental).
- Unmarked SOV word order (with S being the direct-case argument selected by the trigger) and consistently head-final. A change to SVO has however taken place in the central Core Lahob area (i.e. all Łogawenek languages, most Central Lahobic ones, and a few Nayzehenyn ones) and, independently, in the Near Eastern Chlouvānem languages.
- All Lahob languages express location by means of numerous verbs with changing prefixes in order to convey the sense of different English prepositions; motion verbs have two series of these prefixes, one lative and one ablative.
- Verbs are typically a closed class: most Lahob languages have a very small set of verbs in common use, and use many of those as light verbs with other roots in order to form newer meanings; verbs can typically only be formed by other verbs, and only with causative, applicative, or frequentative meanings. Chlouvānem is a partial exception, because while sharing the same restrictions to forming new verbs it has some hundreds of verb roots in common use. Some vernaculars, particularly the Jade Coastal ones, however, have developed on their own traits closer to other Lahob languages, particularly the heavy use of light verbs.
The following traits are widely found across most Core Lahob languages (which share many grammatical features), but not in Chlouvānem ones:
- A relatively small phonemic inventory, averaging around 15 consonants (all pulmonic) and 5 vowels (all oral). Tone is not phonemic.
- Small case systems (if they have case at all), with rarely more than three cases.
- In all Lahob languages that have it (incl. Chlouvānem ones), the dative doubles as a lative case.
Proto-Lahob
Phonology
Consonants
Proto-Lahob's reconstructed phonemic inventory is almost universally agreed on by Calemerian linguists (apart from the phonemicity of *ŋʷ), with only some doubts about the realizations of certain phonemes. Its consonant inventory was the following:
| → PoA ↓ Manner |
Labials | Dentals | Palatals | Velars | Labiovelars | Laryngeals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasals | m | n | ŋ | (ŋʷ) | |||
| Stops | Unvoiced | p pʰ | t̪ t̪ʰ | c cʰ | k kʰ | kʷ kʷʰ | |
| Voiced | b bʱ | d̪ d̪ʱ | ɟ ɟʱ | g gʱ | gʷ gʷʱ | ||
| Fricatives | f v | s ɬ | š | x ɣ | h ʕ | ||
| Approximants | r l | j | w | ||||
The exact quality of the reconstructed phonemes *š and *ʕ is unclear. For *š, the various theories are about substantially close phones such as [ʃ ʂ ɕ] or even [ç]. *ʕ is much more problematic. In most Lahob languages, this phoneme is only shown by its effect on neighboring vowels, which is different depending on the language but it always backs the vowel, lowers it, or does both. Chlouvānem is the exception as it directly reflects it, without any change in vowel quality, as its infamous /ɴ̆/ phoneme, whose extremely high occurrence is due to Proto-Lahob *ʕ, *l, (often) *ɬ, and *ŋ having all merged into it. As, however, other Lahob languages have a backed or lowered vowel, but never a nasalized one in the contexts where *ʕ is reconstructed, Calemerian linguists think that the Chlouvānem phoneme being nasal is a post-Proto-Lahob development.
Vowels
Proto-Lahob's vowel inventory, on the other hand, is fairly simple, with five pairs of long and short vowels - /a aː e eː o oː i iː u uː/ - plus the two vowels /ɨ ə/. The non-high vowels could also form diphthongs with /ɨ̯ ɪ̯ ʊ̯/, while /i iː/ only could with /ʊ̯/ and /u uː/ only with /ɪ̯/. Diphthongs centered on schwa, once controversial among Lahob linguists, have now become accepted by most linguists because of *əj being so far the only reasonable explanation for palatalized consonants in Chlouvānem - as with e.g. *nodəjn-ə- "to hit, strike" > nadьn- "to trip into, to hit" - much like the *əjV sequence explains the distinction between CʲV and CjV (as with *ʕiŋjō > liliā "my, mine" (*CjV > CʲV) and *ērəjo > yarya "beer" (*CəjV > CjV)).
Sound correspondences in daughter languages
The following table lists the general reflexes of Proto-Lahob phonemes in the major attested Lahob languages. For sake of brevity, different outcomes caused by splits in earlier times of the language are not noted (e.g. *d having different outcomes in Yełeshian Lawo due to original intervocalic *d being n and secondary intervocalic *d (post-Proto-Nayzehenyn) being r):
| Proto-Lahob | Chlouvānem | Nayzehenyn | Central Lahobic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yełeshian Lawo | Shershan Lawo | Łohofál | Sulutamilian Minwan | ||
| *p | p | p | p | f | f |
| *pʰ | ħ | h, kp1 | h, kp1 | f, kp1 | f, kp1 |
| *b | b | b, w | b, w | p, f | p |
| *bʱ | bh | w, gb1 | w, gb1 | p, f, gb1 | p, gb1 |
| *t | t, ṭ2 | t | t | t | t, s |
| *tʰ | th, ṭh2 | n | y | s | s, t |
| *d | d, ḍ2 | d, r, n | d, y | d, ð | d, n, r |
| *dʱ | dh, ḍh2 | n | y | ||
| *c | c | č, š | č, š | s | s, t |
| *cʰ | ch | š | š | ||
| *ɟ | j | ž | dž, ž | d, ð | d, n, r |
| *ɟʱ | jh | ž | |||
| *k | k, c3 | k, q2 | k | k, r, ȟ | k, l, s |
| *kʰ | kh, ch3 | ħ, ∅ | ħ, h | ||
| *ɡ | g, j3 | g, ∅ | g, h | k, ð, ȟ, ∅ | k, n, s, ∅ |
| *ɡʱ | gh, jh3 | ħ, ∅ | ħ, h | ||
| *kʷ | ɂ | kp | kp | kp | kp |
| *kʷʰ | ph | ||||
| *ɡʷ | ɂ | gb | gb | gb | gb |
| *ɡʷʱ | bh | ||||
| *x | h, V̤4, V̤k5 | k1, ∅, š | k1, ∅, š | ∅, l1 | ∅ |
| *ɣ | h, V̤4, V̤g5 | k1, ∅, ž | k1, ∅, ž, h | ||
| *h | h, V̤4 | h, ħ | ħ, h | ∅ | |
| *f | p | h | h | f | f |
| *w | v | w, ∅ | w, ∅ | w | w |
| *s | s, š3 | s, ∅6 | s, ∅6 | ∅ | ∅ |
| *š | ṣ, ∅7 | ||||
| *[z] | Vː8, ∅9 | z | z | ||
| *r | r, h6, l | r, ∅ | y, ∅ | l, ∅1, 10 | l, ∅1, 10 |
| *l | l | ł | ł | ł | ł |
| *ɬ | l, chl1 | tł | tł | tł | |
Table notes:
- Word-initially.
- Usually through assimilation of a following *r.
- When followed by *j.
- In coda.
- Intervocalic.
- Word-finally.
- Word-initially when followed by *j.
- Before voiced consonants.
- Adjacent to *d or *dʱ (resulting in ḍ, ḍh respectively).
- Before stops.
Morphology
First declension
First declension nouns are those also known as *-s nouns, and distinguished four types of stems: o-stems, u-stems, i-stems, and *n-stems (cf. Chlouvānem s-nouns in -as, -us, -is, -oe). Here follows the declension of first declension nouns with a comparison in Chlouvānem and Yełeshian Lawo (a Nayzehenyn language), which only keeps this declension as a relic in a few nouns - not the root *frātos "wind" but, as in the table, *gistoros "young" (> Proto-Nayzehenyn *yestor > ehtu, cf. Chl. giṣṭaras).
Note that Yełeshian Lawo, and all Nayzehenyn languages anyway, keeps the original instrumental plural suffix as an adverb-forming suffix, e.g. ehtuwenik "in the way of a young person". This use of the instrumental plural is considered a Proto-Lahob feature, as it is still found in most other branches, and is also common in Archaic and Early Classical Chlouvānem texts.
| Proto-Lahob | Chlouvānem | Yełeshian Lawo | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| o-stems | |||||||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Direct[2] | *frāt-os | *frāt-ant | *frāt-aj | prātas | prātāt | prāte | ehtu | ehtuwe | |
| Vocative | *frāt-āw | prātau | |||||||
| Accusative | *frāt-u | *frāt-asuj | *frāt-ajir | prātu | prātāṣa | prātaih | |||
| Ergative | *frāt-ej | *frāt-ōjo | *frāt-ōn | prātei | prātāya | prātān | |||
| Genitive | *frāt-i | *frāt-ajwo | *frāt-umi | prāti | prāteva | prātumi | ehtuy | ehtum | |
| Instrumental | *frāt-op | *frāt-ōbʱan | *frāt-ajnīko | prātap | prātābhan | prātenīka | ehtuwenik | ||
| Exessive | *frāt-ot | *frāt-ōmōn | prātat | prātāmān | |||||
| Ablative | *frāt-ux | *frāt-ajnits | prātų | prātenīs | |||||
| Translative | *frāt-on | *frāt-oguš | *frāt-ijawr | prātan | prātaus | prātyoh | |||
| Dative | *frāt-awm | *frāt-osām | prātom | prātasām | ehtowe | ehtuswe | |||
| Essive | *frāt-ox | *frāt-iŋgin | *frāt-egem | prātą | prātigin | prātēm | |||
| Locative | *frāt-e | *frāt-iʕīm | prāte | prātilīm | |||||
| u-stems | |||||||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Direct | *kewʕəd-u-s | *kewʕəd-u-nt | *kewʕəd-āw-s | kældus | kældūt | kældaus | koru | korwe | |
| Vocative | *kewʕəd-u | kældu | |||||||
| Accusative | *kewʕəd-aw-u | *kewʕəd-u-suj | *kewʕəd-aw-ir | kældavu | kældūṣa | kældavih | |||
| Ergative | *kewʕəd-aw-e(j) | *kewʕəd-ū-jo | *kewʕəd-ū-n | kældave | kældūya | kældūn | |||
| Genitive | *kewʕəd-aw-i | *kewʕəd-owwo | *kewʕəd-owmi | kældavi | kældagva | kældǣmi | korwe | korum | |
| Instrumental | *kewʕəd-u-p | *kewʕəd-aw-bʱan | *kewʕəd-u-nīko | kældup | kældobhan | kældunīka | korunik | ||
| Exessive | *kewʕəd-u-t | *kewʕəd-aw-mōn | kældut | kældomān | |||||
| Ablative | *kewʕəd-u-ux | *kewʕəd-u-nits | kældų | kældunīs | |||||
| Translative | *kewʕəd-u-n | *kewʕəd-u-guš | *kewʕəd-u-jawr | kældun | kældugus | kælduyoh | |||
| Dative | *kewʕəd-aw-awm | *kewʕəd-u-sām | kældavom | kældusām | korwe | koruswe | |||
| Essive | *kewʕəd-aw-x | *kewʕəd-u-ŋgin | *kewʕəd-aw-egem | kældą | kældugin | kældavēm | |||
| Locative | *kewʕəd-aw-e | *kewʕəd-u-ʕīm | kældave | kældulīm | |||||
| i-stems | |||||||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Direct | *əskutr-i-s | *əskutr-i-nt | *əskutr-āj-s | skuṭis | skuṭīt | skuṭais | kutłi | kutłe | |
| Vocative | *əskutr-i | skuṭi | |||||||
| Accusative | *əskutr-aj-u | *əskutr-i-suj | *əskutr-aj-ir | skuṭayu | skuṭīṣa | skuṭaih | |||
| Ergative | *əskutr-aj-e(j) | *əskutr-ī-jo | *əskutr-ī-n | skuṭaye | skuṭīya | skuṭīn | |||
| Genitive | *əskutr-aj-i | *əskutr-ojjo | *əskutr-j-umi | skuṭayi | skuṭajña | skuṭyumi | kutłey | kutłim | |
| Instrumental | *əskutr-i-p | *əskutr-aj-bʱan | *əskutr-i-nīko | skuṭip | skuṭebhan | skuṭinīka | kutłinik | ||
| Exessive | *əskutr-i-t | *əskutr-aj-mōn | skuṭit | skuṭemān | |||||
| Ablative | *əskutr-j-ux | *əskutr-i-nits | skuṭyų | skuṭinīs | |||||
| Translative | *əskutr-i-n | *əskutr-i-guš | *əskutr-i-jawr | skuṭin | skuṭigus | skuṭyoh | |||
| Dative | *əskutr-aj-awm | *əskutr-i-sām | skuṭayom | skuṭisām | kutłewe | kutłiswe | |||
| Essive | *əskutr-aj-x | *əskutr-i-ŋgin | *əskutr-aj-egem | skuṭę | skuṭigin | skuṭayēm | |||
| Locative | *əskutr-aj-e | *əskutr-i-ʕīm | skuṭaye | skuṭilīm | |||||
| n-stems | |||||||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Direct | *hoʕ-õ | *hoʕ-en-ant | *hoʕ-en-ī | haloe | halenāt | halenī | |||
| Vocative | |||||||||
| Accusative | *hoʕ-en-u | *hoʕ-en-asuj | *hoʕ-en-ajir | halenu | halenāṣa | halenaih | |||
| Ergative | *hoʕ-en-ej | *hoʕ-en-ōjo | *hoʕ-en-ōn | halenei | halenāya | halenān | |||
| Genitive | *hoʕ-en-jes | *hoʕ-en-wo | *hoʕ-õ-mi | halenies | halemva | haloemi | |||
| Instrumental | *hoʕ-en-op | *hoʕ-õ-bʱan | *hoʕ-õ-nīko | halenap | haloebhan | haloenīka | |||
| Exessive | *hoʕ-en-ot | *hoʕ-õ-mōn | halenat | haloemān | |||||
| Ablative | *hoʕ-en-ux | *hoʕ-õ-nits | halenų | haloenīs | |||||
| Translative | *hoʕ-en-on | *hoʕ-en-oguš | *hoʕ-en-ijawr | halenan | halenaus | halenyoh | |||
| Dative | *hoʕ-en-awm | *hoʕ-õ-sām | halenom | haloesām | |||||
| Essive | *hoʕ-en-î(x) | *hoʕ-õ-gin | *hoʕ-õ-gem | halen | haloegin | haloem | |||
| Locative | *hoʕ-en-je | *hoʕ-en-iʕīm | halenie | halenilīm | |||||
Second declension
Second declension nouns are those that end in -m (except for -āj nouns), and also have three different possible stems: o-stems, u-stems, and i-stems. Here follows the declension of first declension nouns with a comparison in Chlouvānem, Yełeshian Lawo, and Tundra Pwaɬasd.
| Proto-Lahob | Chlouvānem | Yełeshian Lawo | Łahoḇarir | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| o-stems | |||||||||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Direct | *juɟ-om | *juɟ-iwā | *juɟ-oms | yujam | yujivā | yujās | yiž | yižus | sur | susur | |
| Vocative | *juɟ-e | yuje | |||||||||
| Accusative | *juɟ-om-u | *juɟ-m-es | *juɟ-m-ajir | yujamu | yujmes | yujmaih | |||||
| Ergative | *juɟ-m-ego | *juɟ-m-ēn | *juɟ-ōm-ūn | yujmæ | yujmian | yujāmūn | |||||
| Genitive | *juɟ-om-i | *juɟ-m-ajwo | *juɟ-om-nān | yujami | yujmeva | yujaṃrān | yižom | yižonwe | susome | susunä | |
| Instrumental | *juɟ-om-op | *juɟ-o-bʱan | *juɟ-om-nīko | yujamap | yujabhan | yujaṃrīka | yižonik | ||||
| Exessive | *juɟ-om-ot | *juɟ-o-mōn | yujamat | yujamān | |||||||
| Ablative | *juɟ-om-ux | *juɟ-m-ajnits | yujamų | yujmenīs | |||||||
| Translative | *juɟ-om-on | *juɟ-m-ix | *juɟ-m-ent | yujaman | yujmį | yujmēt | |||||
| Dative | *juɟ-om-awm | *juɟ-om-sām | yujamom | yujaṃsām | yižom̃e | yižuže | susumaw | sususä | |||
| Essive | *juɟ-om-x | *juɟ-m-enne | *juɟ-m-egem | yujmą | yujmenne | yujmēm | |||||
| Locative | *juɟ-om-n(j)aj | *juɟ-m-iʕīm | yujaṃrye | yujmilīm | |||||||
| u-stems | |||||||||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Direct | *tūl-u-m | *tūl-w-iwā | *tūl-u-ms | tūlum | tūlvivā | tūlūs | |||||
| Vocative | *tūl-w-e | tūlve | |||||||||
| Accusative | *tūl-u-m-u | *tūl-w-es | *tūl-u-jir | tūlumu | tūlves | tūluyih | |||||
| Ergative | *tūl-u-go | *tūl-w-ēn | *tūl-u-m-ūn | tūluga | tūlvyan | tūlumūn | |||||
| Genitive | *tūl-u-m-i | *tūl-w-ajwo | *tūl-u-m-nān | tūlumi | tūlveva | tūluṃrān | |||||
| Instrumental | *tūl-u-m-op | *tūl-u-bʱan | *tūl-um-nīko | tūlumap | tūlubhan | tūluṃrīka | |||||
| Exessive | *tūl-u-m-ot | *tūl-u-mōn | tūlumat | tūlumān | |||||||
| Ablative | *tūl-u-m-ux | *tūl-w-ajnits | tūlumų | tūlvenīs | |||||||
| Translative | *tūl-u-m-on | *tūl-w-ix | *tūl-u-nt | tūluman | tūlvį | tūlūt | |||||
| Dative | *tūl-u-m-awm | *tūl-u-m-sām | tūlumom | tūluṃsām | |||||||
| Essive | *tūl-u-m-x | *tūl-u-nne | *tūl-u-gem | tūlų | tūlunne | tūlugem | |||||
| Locative | *tūl-u-m-n(j)aj | *tūl-u-ʕīm | tūluṃrye | tūlulīm | |||||||
| i-stems | |||||||||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Direct | *sgāt-i-m | *sgāt-i-iwā | *sgāt-i-ms | ṛgātim | ṛgātīvā | ṛgātīs | |||||
| Vocative | *sgāt-j-e | ṛgātie | |||||||||
| Accusative | *sgāt-i-m-u | *sgāt-j-es | *sgāt-i-jir | ṛgātimu | ṛgāties | ṛgātīh | |||||
| Ergative | *sgāt-i-go | *sgāt-j-ēn | *sgāt-i-m-ūn | ṛgātya | ṛgātiyan | ṛgātimūn | |||||
| Genitive | *sgāt-i-m-i | *sgāt-j-ajwo | *sgāt-i-m-nān | ṛgātimi | ṛgātieva | ṛgātiṃrān | |||||
| Instrumental | *sgāt-i-m-op | *sgāt-i-bʱan | *sgāt-im-nīko | ṛgātimap | ṛgātibhan | ṛgātiṃrīka | |||||
| Exessive | *sgāt-i-m-ot | *sgāt-i-mōn | ṛgātimat | ṛgātimān | |||||||
| Ablative | *sgāt-i-m-ux | *sgāt-j-ajnits | ṛgātimų | ṛgātienīs | |||||||
| Translative | *sgāt-i-m-on | *sgāt-j-ix | *sgāt-i-nt | ṛgātiman | ṛgātį | ṛgātīt | |||||
| Dative | *sgāt-i-m-awm | *sgāt-i-m-sām | ṛgātimom | ṛgātiṃsām | |||||||
| Essive | *sgāt-i-m-x | *sgāt-i-nne | *sgāt-i-gem | ṛgātį | ṛgātinne | ṛgātiem | |||||
| Locative | *sgāt-i-m-n(j)aj | *sgāt-i-ʕīm | ṛgātiṃrye | ṛgātilīm | |||||||
*-ōj declension
A class of nouns which ended in *-ōj in their direct case forms had a particular declension, with forms mostly taken from the first and the second declension but varying between the two. The essive and the locative singular are from the third.
Chlouvānem, Yełeshian and Shershan Lawo, and Šlokhowdeš all have many remnants from this class (and in Chl. and Šlk. it is still productive), while other languages may keep the odd irregular noun (as the root used in the example, *gjun-ōj, meaning "foot").
| Proto-Lahob | Chlouvānem | Yeł. Lawo | Šlokhowdeš | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Direct and Vocative | *gjun-ōj | *gjun-ōj-wā | *gjun-ōj-aj | junai | junaivā | junāye | ||||
| Accusative | *gjun-ōj-u | *gjun-ōj-es | *gjun-ōj-ajir | junāyu | junāyes | junāyaih | ||||
| Ergative | *gjun-ōj-ej | *gjun-ōj-ēn | *gjun-ōj-ūn | junǣ | junāyēn | junāyūn | ||||
| Genitive | *gjun-ōj-i | *gjun-ōj-wo | *gjun-ōj-ān | junāyi | junaiva | junāyān | ||||
| Instrumental | *gjun-ōj-p | *gjun-ōj-bʱan | *gjun-ōj-nīko | junaip | junaibhan | junainīka | ||||
| Exessive | *gjun-ōj-t | *gjun-ōj-mōn | junait | junaimān | ||||||
| Ablative | *gjun-ōj-ux | *gjun-ōj-ajnits | junāyų | junǣnīs | ||||||
| Translative | *gjun-ōj-n | *gjun-ōj-ix | *gjun-ōj-ent | junain | junāyį | junāyēt | ||||
| Dative | *gjun-ōj-awm | *gjun-ōj-sām | junāyom | junaisām | ||||||
| Essive | *gjun-ōj-xəs | *gjun-ōj-nne | *gjun-ōj-gem | junąis | junainne | junaigem | ||||
| Locative | *gjun-ōj-aj | *gjun-ōj-ʕīm | junāye | junailīm | ||||||
Pronouns
Only the first- and second-person pronouns are reliably reconstructible in Proto-Lahob; it probably did not have common third person pronouns nor those differing in formality (which are found in Chlouvānem, most of its descendants, and, in a different way, in many Kenaywanic languages) - the pronoun declension was apparently marginally productive and terms which were used as pronouns were sometimes analogically added to it — first of all, the development of Chlouvānem's 2SG formal equal pronoun tami starting from the Lällshag borrowing tame can be seen in texts from the early centuries of the Second Era; also using nouns instead of pronouns is not uncommon among Lahob languages, as do, without a change in declension, contemporary Chlouvānem, most of its descendants, as well as some Tłašnelek languages.
Like most modern Lahob languages - Chlouvānem is, this time, the exception - the Proto-Lahob second person pronouns distinguished natural gender both in the singular and in the plural; while all plural pronouns have vanished from Chlouvānem (though the 2PL feminine one's direct and genitive cases only are attested in Archaic Chlouvānem), the feminine singular is reflected as the formal superior and the masculine singular as the formal inferior. Some Kenaywanic languages, as e.g. Łōpian, have also simplified the system by only retaining the originally masculine forms.
The dual forms may not be reliably reconstructed (as anywhere in Proto-Lahob morphology) because Chlouvānem is the only attested Lahob language with a dual form (excluding a few of its daughter languages).
| Proto-Lahob | Chlouvānem | Central Lahobic | Nayzehenyn | Łogawenek | Kenaywanic | Tłašnelek | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-CL | Łohofál | Sulutamilian Minwan |
Łokudár | Proto-N. | Yełeshian Lawo | Shershan Lawo | Nahawi | Proto-Ł. | Łaȟoḇaror | Łogawe | Aem | Proto-K. | Łōpian | Proto-T. | Kpunnuan Tłašnelek | ||
| *ʕiŋi, *ʕ- "I" | lili | *oŋi | ngi | oni | oni | *eŋ͡mi | em̃e | em̃ | im̃ | *eŋ | eng | en | eng | *emʲe | emь | *oŋ͡mi | oŋmi |
| *rowi, *r- "you (masculine sg)" | ravi | *rōy | loy | loa | roy | *roy | rwe | ya | rē | *ruy | yuy | ruy | ruy | *rᵞovʲi | rъey | *law | naw |
| *nomi, *nəj- "you (feminine sg)" | nami | *noy | no | noa | noy | *nay | ney | nē | nē | *nɔm | no | na | nwŏ | *nome | — | *nami | nai |
| *muxmō~mexjō, *mux-/*me- "we" | — | *muma | mun | mum | mun | *mɛy | me | mē | mē | *mɛn | nän | nɛ | mye | *mᵞen | mъen | *moȟō | mohu |
| *korin, *kro-/*koj- "you (masculine pl)" | — | *kōn | kon | kun | ku | *kran | qan | kan | qan | *kɔr | kon | kar | kwŏ | *korʲin | kerьn | *kōn | kuki |
| *nogin, *(ə)ŋg- "you (feminine pl)" | nagin | *olin | ðin | onen | thi | *nawn | non | nam̃ | nam̃ | *nɔk | — | nak | nwŏk | *nokin | — | *nokin | noki |
Basic cognates
Numbers 1-12
All Lahob languages have a duodecimal numeral system. Here are the numbers from 1 to 12 (1012) in some of them. Note that there is no common word for "zero" (most of them use the word for "nothing"; Chlouvānem has the Lällshag borrowing ajrā). The Proto-Lahob numerals for three and six are based on finger counting, being the word for "finger" and its dual form (some languages have innovated a newer word for finger with a later derivation, cf. Chl. pamuvis, Yeł. Lawo kpim̃í); Kenaywanic and Tłašnelek also have the root *den, "phalanx", for one – which is reflected in all languages' word for Ɛ, *wewʕe-den, or "one phalanx more [to twelve]". It is also notable that *tītijo, used for "eight" in all branches except for Nayzehenyn and Chlouvānem, also means "limbs", referring to legs, feet, arms, and hands.
Nayzehenyn languages have three as a sub-base and their word for twelve is "four fingers" or "four times three".
| Proto-Lahob | Chlouvānem | Central Lahobic | Nayzehenyn | Łogawenek | Kenaywanic | Tłašnelek | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-CL | Łohofál | Sulutamilian Minwan |
Łokudár | Proto-N. | Yełeshian Lawo | Shershan Lawo | Nahawi | Proto-Ł. | Łaȟoḇaror | Łogawe | Aem | Proto-K. | Łōplan | Proto-T. | Kpunnuan Tłašnelek | ||
| *jemibɨ ~ *denə "one" | emibe | *yempu | yew | empu | yiw | *imbo | im̃u | im̃o | im̃u | *zɛmeb | sämeḇ | zɛwm | šeme | *deno | de | *ten | ti |
| *doni "two" | dani | *doni | doy | dun | don | *done | dun | dōn | dōn | *dɔn | don | da | dwŏ | *doni | ni | *tani | tani |
| *pāmwəj "three" | pāmvi | *faŋi | feng | fen | han | *pɔŋ͡me | kpem̃ | kpam̃ | kpam̃ | *paŋ | päng | pan | fang | *pᵞamᵞi | pъem | *pāmwe | paw |
| *nexɬə(te) "four" | nęlte | *netłet | nełe | netłe | nełë | *neetɬo | nitłu | nētło | nīnu | *nɛɬ | näł | nɛł | nyeł | *nehɬo | nał | *neȟtɬo | nihtło |
| *sjuŋko "five" | šulka | *sunko | suk | sunku | šonë | *siŋka | sink | sink | šinka | *huŋk | hing | hun | huk | *simʲo | sumь | *šoŋka | soka |
| *pāmujwā "six" | (tulūɂa) | *famowá | fangwá | famwá | howá | *pɔmewɔ́ | kpengbé | kpegbá | kpikpá | *pamuwa | pämiw | pamua | fawa | *pᵞɑmᵞiwɑ | pâmâ | *pāmowā | pamoa |
| *cʰīko "seven" | chīka | *siko | sik | siku | šikë | *ʃika | šika | šik | šia | *sik | siȟ | si | sik | *siko | suk | *čīka | kica |
| *tītijo ~ *məbuŋo "eight" | mbula | *tiso | tis | sisun | tišë | *g͡buŋ͡ma | gbum̃o | gbum̃a | kpuža | *tis | tis | tis | tis | *tiyo | ti | *tīča | tica |
| *mawɟo "nine" | moja | *mōlo | moð | munu | muthë | *mɔdʒa | mož | m̃až | maža | *mawz | nos | nawz | ma | *mᵞɑzo | moz | *mōča | muca |
| *tofaʕdo "ten" | tålda | *tofad | tof | tofa | toha | *tafoda | tor | tahoy | tawra | *tɔfɑd | torf | taha | twŏϑ | *tofᵞɑdo | tofъ | *tafōta | tafuta |
| *wewʕe-den "eleven" | vælden | *wālen | waðen | wane | wothi | *yɔwdin | wedin | wahdin | warin | *wɑdɛn | warä | waɛ | ŏye | *vʲɑden | ved | *wawaten | wate |
| *māmōwə ~ *nexɬəpāmwəj "twelve" | māmei | *mamō | maw | mamu | mu | *neetɬɔŋ͡me | nitłem̃ | nēłam̃ | nīnwam̃ | *mamu | näm | namu | mamu | *mᵞɑmᵞo | momъ | *māmōwo | mamo |
Miscellaneous words
If the meaning in a daughter language is not specified, then it has not shifted since PLB; if ... appears in a daughter language column it means that the word did not shift meaning but acquired new ones in addition to those it already had.
| Proto-Lahob | Chlouvānem | Central Lahobic | Nayzehenyn | Łogawenek | Kenaywanic | Tłašnelek | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-CL | Łohofál | Sulutamilian Minwan |
Łokudár | Proto-N. | Yełeshian Lawo |
Shershan Lawo |
Nahawi | Proto-Ł. | Łaȟoḇaror | Łogawe | Aem | Proto-K. | Łōpian | Proto-T. | Kpunnuan Tłašnelek | ||
| *bujnā"father" | būnā | *pōna | pon | puna | punë | *benɔ | bem̃e | bim̃a | pim̃a | *buna | bin | bun | bua | *pᵞinɑ | pъen | *ponā | pona |
| *mejnā "mother" | meinā | *mēna | mene | mina | minë | *menɔ | mem̃e | mim̃a | mim̃a | *mina | nin | nin | mia | *mʲena | mьan | *mīnā | mena |
| *ŋōntrom "head" | lāṇṭam | *ŋanto | ngat | nantu | notë | *ŋ͡montra | m̃ontła | m̃ontła | m̃uła | *ŋonots | ngunec | nonoc | ngonoc | *mᵞuntorᵞu | mūtrъ | *ŋ͡mōnča | ŋmuca |
| *ʕiken "arm" | — | *oken | ohen | oken | oke | *ekin | ekin | ičin | īn | *ɛkɛn | äȟän | ɛɛ | yehye | *eken | ikn | *oken | oke |
| *√ʕiŋ- "to live" | √lil- | *oŋ- | ang- | on- | an- | *eŋ͡m- | em̃- | im̃- | im̃- | *ɛŋ- | eng- | ɛn- | yeng- | *emʲ/mᵞ- | emь- ~ emъ- | *oŋ͡m- | oŋm- |
| *√gʷʱi-, "to take care of" | √bhi- | *ɡ͡bi- | gbi- | gbi- | gbi- | *ɡ͡bi- | gbi- | gbi- | kpi- | *ɡ͡bi- | gbi- | gbi- | gbi- | *ki- | ki- | *k͡pi- | kpi- |
| *mwerkos "black" | murkas | *ŋero | ngel | nel | nerë | *ŋ͡mereko | m̃ereku | m̃eyeko | m̃iriu | *ŋɛrk | ngäk | nɛk | ngek | *mᵞerʲɑ | marь | *mwēka | mwéka |
| *ɣuŋjā "moon" | huliā | *ruyà | uyá | oá | uyá | *guyyɔ́ | ožwé | ožwá | wožá | *xoja | ȟuy | goy | ea | *wumʲɑ | mьâ | *xonyā | hoya |
| *gistoros "young" | giṣṭaras | *kitoro | kitol | sitol | kitorë | *yestor | ehtu | ihtu | ihtur | *ketɔr | kedoy | kedar | keϑwŏ | *kitorᵞa | kurâ | *yešala | cihna |
| *tāmiro "stone" | tāmira | *tamiro | tamil | tamil | tamurë | *tomur | tom̃ | tomu | tumur | *tamer | tämey | tamer | tame | *tamʲirᵞo | temьurъ | *tāmila | temna |
| *liŋkajnet "family" | — | *ɬikēnet | łihet | łisine | łikinë | *ɬeŋkɛyni | łenkey | łinkēn | ninkēni | *ɬeŋkɛnɛt | łengkäd | łenkɛnt | łekyet | *lʲinkene | līkne | *ɬiŋkēne | łikéne |
| *frātos "wind" | prātas | *fato | fat | fat | hatë | *fwɔt | fuwe | wat | wat | *frat | rät | hrat | fat | *fʲatɑ | fьât | *fwāta | fwota |
| *xadono "sun" | hånna | *rolon | oðon | onon | othu | *kalona | kano | kayon | kanun | *xɑnd | ȟan | gan | ŏϑ | *wadon | wodn | *xatana | hahna |
| *ʕanaj "island" | lanai | *anē | ane | ani | ani | *ɔney | wene | wanē | wanē | *ɑnɛ | anä | onɛ | ŏi | *ɑne | ân | *onē | oné |
| *siwás "animal" | švas | *hiwó | iwó | hiwú | iwó | *siwá | swa | siwá | šiwá | *hew | hew | ew | hyŏ | *šiwa | šew | *šiwa | sia |
| *jetiror "stranger, foreigner" | etirah "customer" | *yetiru | yetil | esil | yetir | *yetir | eti | itir | itiš | *zɛter | särt | zɛc | šeϑe | *itirᵞo | iturъ | *yetila | citina |
| *ēʕto "trace, footprint" | yalta "symbol, ..." |
*āto | ato | at | otë | *aata | āta | āt | ēta | *ɛt | ät | ɛt | yet | *eta | eta | *āta | ata |
| *lanisí "braid" | lañši "marriage, ..." |
*ɬonisí | łonisí "sausage" | łonití "chain" | łuší "sausage" | *ɬanisi | łanisi "chain" | łanis "rope" | naniš "rope" | *ɬɑnes "chain" | łaner | łoz | łŏr | *lᵞaniší | weši | *ɬaniši | łanisi |
| *hōwrar "summer" | heirah "year" |
— | *hor | ho "heat" | ħor | hur | *urɑ | iya | ura | urŏ | — | — | |||||
Comparison sentences
Comparison of sentences in different Lahob languages:
- English: I ate three fish.
- Proto-Lahob (reconstructed): *ʕiŋi pāmwəju dalətu juxlāw te.
Chlouvānem languages
- Chlouvānem: (lili) pāmvyu daltu yųlaute. [ɴ̆iɴ̆i päːmʋju däɴ̆tu jṳɴ̆äʊ̯te]
- Līlasuṃghāṇi vernacular: lil pæmy dœlt jylåt. [ɴ̆ĩˤ pɛɪ̯myː dœ̃ˤt ɟ͡ʑyːɴ̆ɑʊ̯t]
Central Lahobic languages
- Łohofál: ngi yułot feng dołit. [ŋi ˈjuɬɔt fɛŋ ˈdɔɬit]
- Dal Ming Wang: ngi yułut fang dołit. [ŋi ˈjuɬut faŋ ˈdɔɬit]
- Sulutamilian Minwan: oni ułut fen dołet. [ˈoni ˈuɬut fen ˈdoɬet]
- Łokudár: oni yułutë han dołitë. [ˈoni ˈjuɬutə han ˈdoɬitə]
- Tłowpedar: on yołt fan dołit. [ˈɔn ˈjɔɬt fan ˈdɔɬit]
Nayzehenyn languages
- Yełeshian Lawo: em̃e kpem̃ dałit yułwet. [ˈɛŋ͡mɛ k͡pɛŋ͡m ˈdaɬit ˈjuɬwɛt]
- Shershan Lawo: em̃ kpam̃ dałit yułwat. [ɛŋ͡m k͡paŋ͡m ˈdaɬit ˈjuɬwat]
- Nahawi: im̃ kpam̃ tanit yum̃at. [ɪŋ͡m k͡paŋ͡m ˈtanit ˈjuŋ͡mat]
Tłašnelek languages
- Kpunnuan Tłašnelek: oŋmit paw tałca cohlo. [ˈɔŋ͡mit paw ˈtaɬt͡sa ˈt͡sɔɦlɔ]
- Temyaonean Tłašnelek: oŋmit po tatła cotło. [ˈɔŋ͡mit pɔ ˈtat͡ɬa ˈt͡sɔt͡ɬɔ]
External history
The history behind how I created the Lahob languages is somewhat curious: when I created Chlouvānem in my newer version of Calémere, I could not keep the same family I had already vastly developed for Laceyiam. But I didn't really like leaving it as an isolate, so that when I was filling the language infobox on the page for Chlouvānem I wrote down a meaningless "Lahob" on the language family parameter. Eventually I decided I liked the name and built the family around it.
The aesthetic inspirations for the individual non-Chlouvānem language families are varied, but overall I was mostly inspired by the Austronesian and Algonquian families.
Notes
- ^ The only core Lahob-speaking territories in other continents, except for the coasts of Gurdugal, are the Kāyīchah islands (geographically in Védren) and a handful of small Tłašnelek-speaking villages in far eastern Gathuráni - an area whose actual classification as Evandor or Márusúturon is disputed.
- ^ Absolutive in Woŋom.